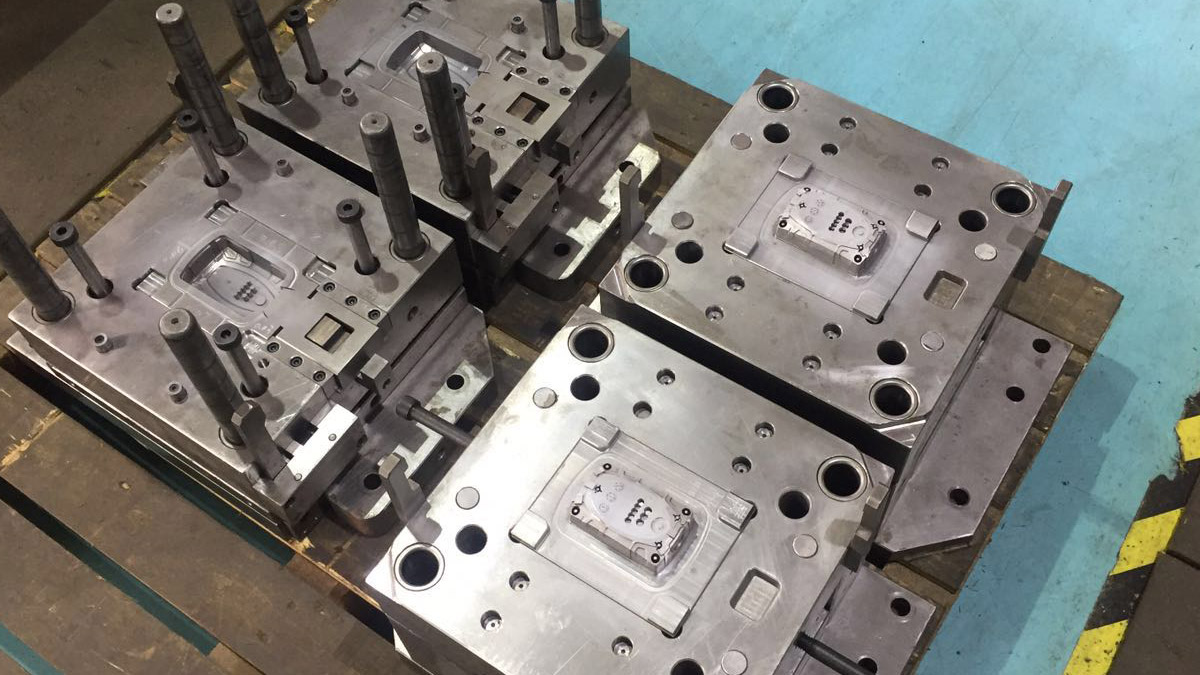
Most plastic products with colorful patterns are manufactured with two shot injection molding technique. Briefly, it’s about manufacturing one product with two types of plastic.
But choosing the perfect molding technique is crucial. It’s not just about dazzling colors and patterns; it’s about matching your product’s exact demands like strength and functionality, while navigating real-world production realities like cost budgets, efficiency targets, as well as the intense pressures & temperatures inside the mold. If you just happened to get confused by these options, this passage is what you need.
So in this article we will find out how to choose an appliable material for injection molds, as well as an introduction to different mold types. If you need any additional help on choosing molds, KingStar is willing to give practical advises based on our expertise in two shot injection molding, as well as providing further molding service for an efficient and reliable production.
1. Materials For Molds In Two Shot Injection Molding
Given its working condition inside the machine, it’s of paramount significance to pick the right material for the molds themselves. Here’s several crucial aspects to check out:
- Wearability. When the blank is being plasticized and reformed inside the mold’s cavity, it will flow and slide along the cavity’s surface, causing intense friction between the blank and the cavity’s surface, which could cause the mold to failure due to wearing. That’s why wearability stands out as one of the fundamental and principal performance indexes.
Hardness serves as a dominant factor in affecting wearability. Usually, higher the hardness for the mold’s parts, lower the wear rate, and better the wearability. Besides, factors of the carbide inside the mold’s material are also related to its wearability, including types, amount, status, size and distribution. - Toughness. Most two-shot injection molds have to endure harsh operating conditions, some of them are frequently exposed to substantial impact loads which could lead to a brittle fracture. The mold’s material must be tough enough to prevent their components from potential brittle fracture during operation. The toughness primarily depends on the material’s carbon content, grain size, and microstructure.
- Fatigue Fracture Resistance. During operation, two-shot injection molds are consistently subjected to cyclic stresses, which often lead to fatigue fractures over time. A range of failure modes may emerge, like low-energy multi-impact fatigue fracture, tensile fatigue fracture, contact fatigue fracture, and bending fatigue fracture, The fatigue fracture resistance of these molds primarily depends on their strength, toughness, hardness, and the content of inclusions within the material.
- High-Temperature Performance. When two-shot injection molds are operating at elevated temperatures, their hardness and strength decrease which could lead to premature wearing or even failure due to plastic deformation. To ensure the molds retain sufficient hardness and strength under working temperatures, their materials must exhibit high thermal stability to resist softening.
- Thermal Fatigue Resistance. During operation, some two-shot molds undergo repeated heating and cooling cycles which subject the cavity surface to tensile-compressive stresses, leading to surface checking and spalling. These defects increase friction, impede plastic deformation, and reduce dimensional precision—ultimately causing mold failure. As thermal fatigue is a primary failure mode for hot-work molds, such tooling requires high thermal fatigue resistance.
- Corrosion Resistance. During operation, some two-shot injection molds, such as those used in plastic molding might suffer from corrosion in its cavity’s surface. Because elements like chlorine and fluorine are present in the plastic, and these elements will decompose and release highly corrosive gases like HCl and HF upon heating, which will attack the surface of the mold cavity, increasing surface roughness and accelerating wear-induced failure. Therefore, it is essential to select materials with superior corrosion resistance for the fabrication of two-shot molds.
2. Types of Molds In Two Shot Injection Molding
To create the various and colorful plastic products we’re now seeing today, it’s not only molds’ material, but also their various structure that we should pay attention to. Each type of mold has their own operation mechanism, advantages and application. Here we will go over a few trending ones for introduction.
2.1. Two-Shot Injection Mold with a Rotating Core
Core Mechanism:
First, the initial part of the two-color component is formed through injection molding. Then, after mold opening and clamping, the first molded part is transferred to the large cavity to act as an insert. The injection unit then injects plastic of a different color into the large cavity, encapsulating the insert to form the complete two-color component. Simultaneously, the injection unit injects the first type of plastic into the small cavity, forming the next plastic insert. After the molded product solidifies and hardens, the mold is opened allowing the two-color plastic part to eject before the movable mold rotates. Finally, the whole injection mold is closed, indicating the completion of one full injection molding cycle.
This technology significantly boosts design freedom for products and is commonly used in manufacturing automotive adjustment wheels, toothbrushes, and disposable razors.
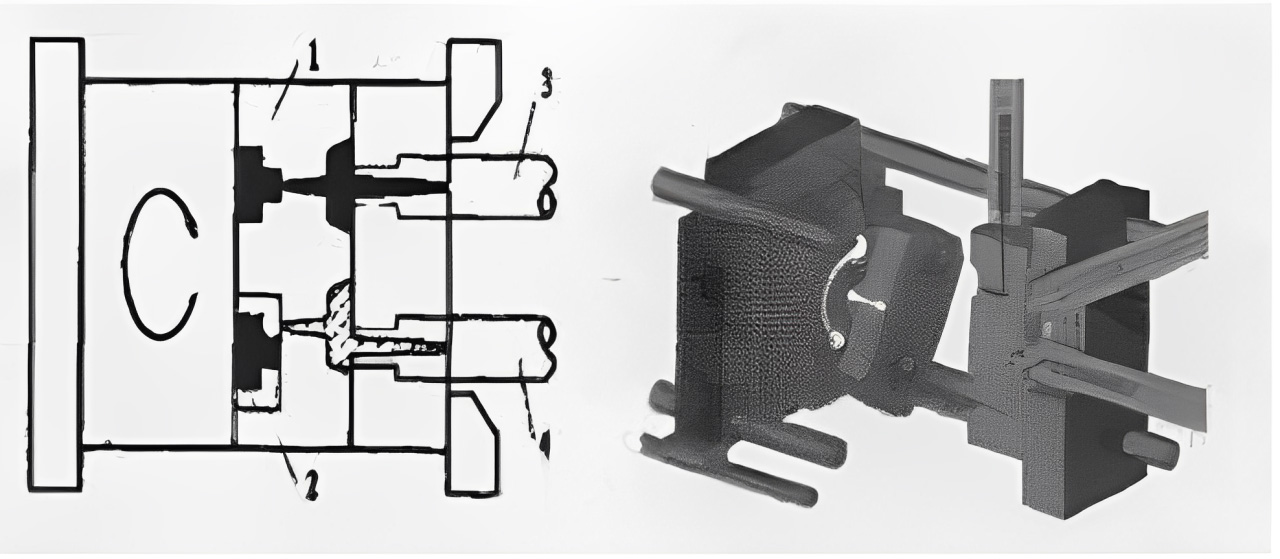
1-smaller cavity 2-larger cavity 3-injection device for smaller cavity
4-injection assembly for larger cavity
Technical Advantages:
-Products’ quality is improved, with a smooth surface without color glitches
-Can be easily handled with one single injection machine
-Multiple processing integrated in one procedure, granting more freedom for designing
Common Application:
-Multiple color required for the product
-Large production volume and short production cycle
2.2. Two-Shot Injection Mold with a Retractable Core
Core Mechanism:
This technique utilizes hydraulic mechanisms to compress the mold. First, a vertically movable core which acts like a piston is hydraulically raised to its top position, injecting plastic material into the cavity. After the first material solidifies, the core retracts downward and inject a second type of plastic material. Then the core rises again under hydraulic pressure to compact the mold, waiting for the components to solidify, forming the final product.
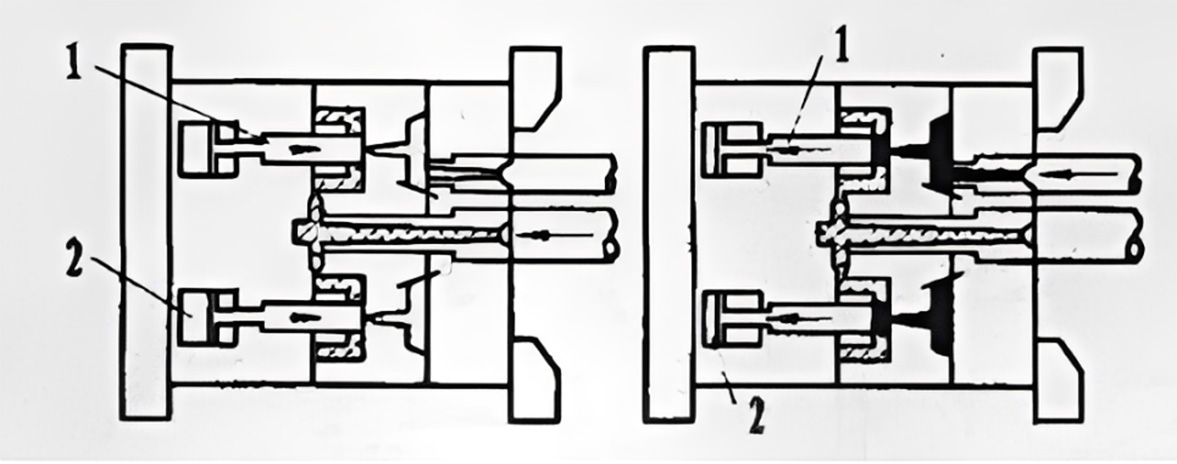
1-movable core 2-hydraulic device
Technical Advantages:
-Technical operation is simplified, but requires precise control over hydraulic actuation timing.
-Products exhibit smooth surfaces and dimensional accuracy, eliminating defects like warping, shrink voids, or sink marks.
-Significantly enhances production efficiency, reducing costs by minimizing post-processing steps.
Common Applications:
-Complex geometry components, like automotive trim parts, industrial machinery components, household appliance housings.
-High cosmetic-grade products, including smartphone casings, electronic enclosures, and other appearance-critical items.
2.3. Two-Shot Injection Mold with a Rotating Stripper Plate
Core Mechanism:
Plastic is first injected into Cavity #1 after mold clamping. Upon mold opening, the movable mold section retracts. Since the shear gate is positioned in the stationary mold half, the runner system separates from the core-component during mold parting, while the core-component remains on the stripper plate within the movable section. As the movable mold continues retracting, solidified material in the sprue is stripped from the cold slug well inside the rotating shaft via ejector pins and a sprue puller. Subsequently, the stripper plate is advanced by linkage mechanisms and the rotating shaft,
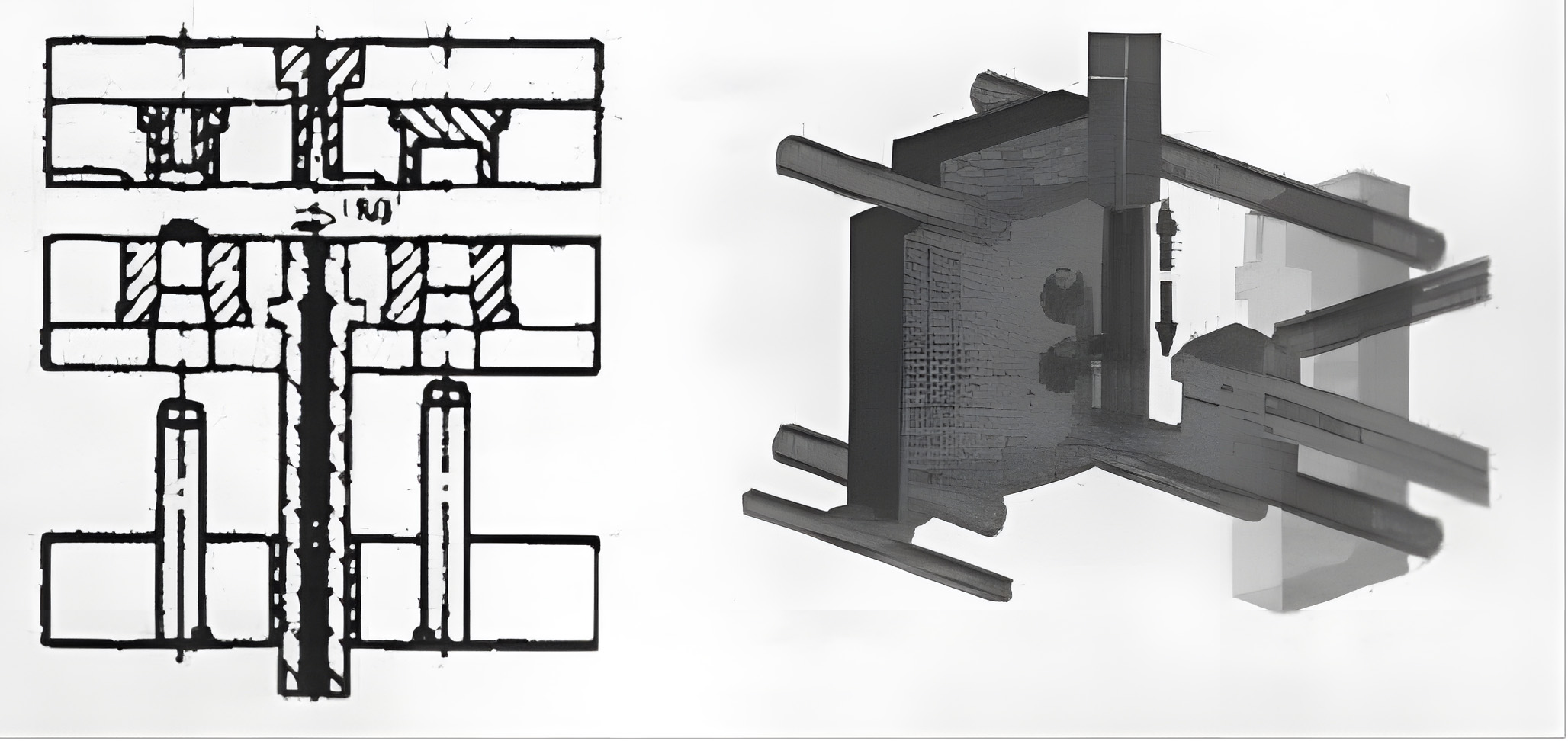
Technical Advantages
-While longer injection and operational times are required, this process is capable to produce vibrantly colored and geometrically unique products.
-Two distinct colors or materials are molded within one cycle, eliminating costly secondary assembly (e.g., bonding/insert placement)
-Complex geometries and advanced color effects are achievable thanks to this technique, boosting products’ quality and appearance.
Common Applications
-Suitable for production in middle or lower volume, as well as high-value components, due to an increased mold production cost
-Premium high-standard products with sharp color separation or improved texture resolution:
2.4. Two-Shot Injection Mold With a Sliding Core
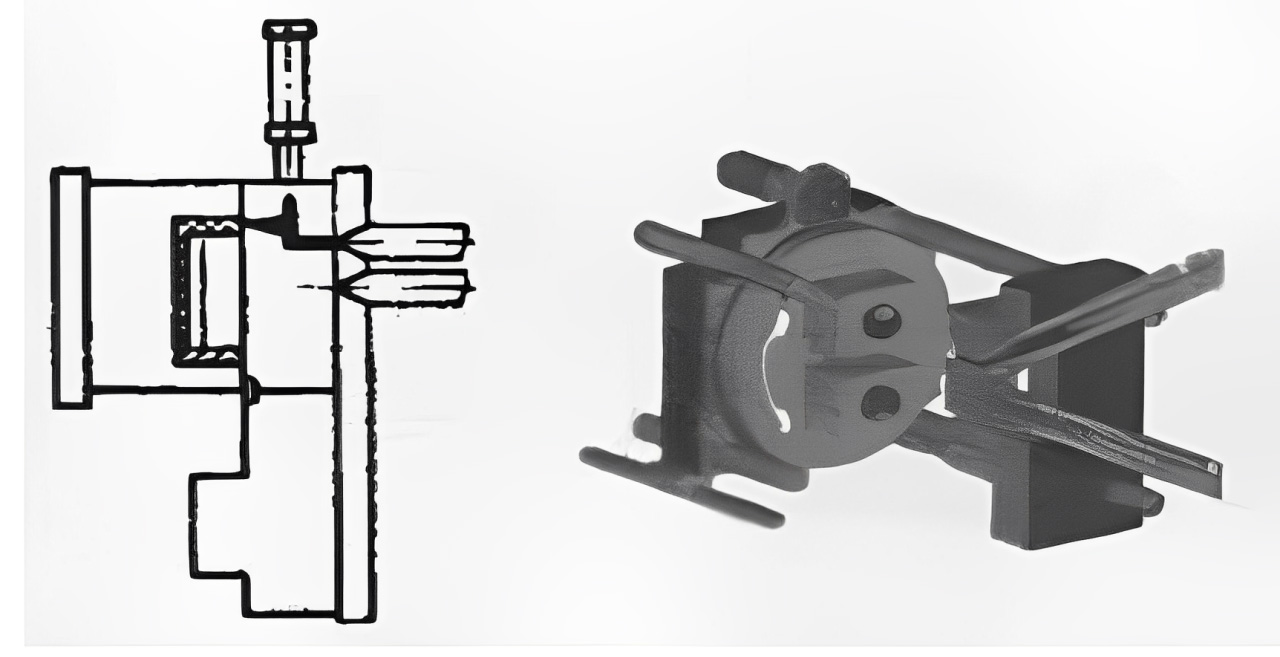
Core Mechanism:
The process begins by positioning the primary core within the mold cavity. First, the mold closes, and the first plastic is injected. After cooling and mold opening, a drive mechanism on the mold side slides both the primary and secondary cores, aligning the secondary core with the cavity. Then the mold closes again, injecting the second plastic. Following cooling, the mold opens again to eject the finished product, completing one molding cycle. This technique is primarily used for molding larger plastic components.
Technical Advantages:
-Products with multiple sizes and geometries, enabling the production for improved versatility and diversity
-Ensures high repeatable precision as well as consistence across mass production runs
-Step-Injection two shot technique is applied for optimizes cycle times, boosting overall production efficiency.
Common Applications:
-Ideal for large-scale components
-capable to handle parts with complex geometries, like integrated protrusions, recesses, or contoured surfaces
-Complex products with multiple raw materials like plastic gears or threaded caps requiring combined mechanical properties.
3. Conclusion
In summary, this article has delved into the key aspects of choosing two shot injection molds. We’ve explored the essential material properties such as wearability, toughness, fatigue fracture resistance, high-temperature performance, thermal fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance. Additionally, we’ve introduced four popular types of two shot injection molds, including those with a rotating core, retractable core, rotating stripper plate, and sliding core, each with its own core mechanism, advantages, and applications.
If you’re in the process of selecting injection molds and need professional guidance, KingStar is your ideal partner of custom manufacturing supplier. With our profound expertise in molding industry, we can offer you practical advice and efficient, reliable molding services. Contact us at sales@kingstarmold.com and experience the excellence of KingStar’s on demand manufacturing service.