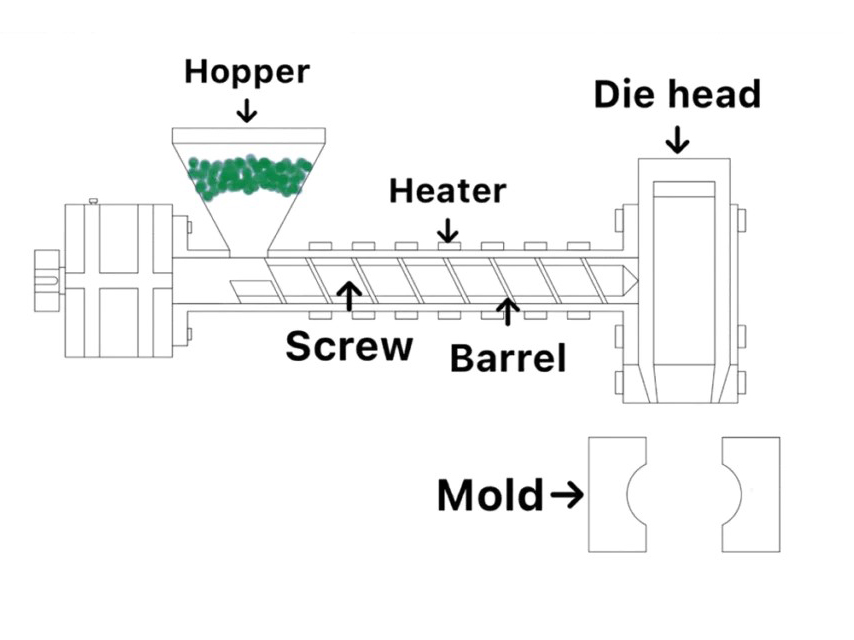
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is widely used in many industries due to its excellent elasticity, wear resistance, oil resistance, and other properties. Molding is the core method of TPU processing, covering various techniques such as blow molding, injection molding, extrusion molding, compression molding. Among them, injection molding technology has become the most commonly used processing method due to its strong applicability and high efficiency. The injection molding process is mainly divided into three discontinuous stages: plasticizing, injection, and ejection, which can accurately process TPU raw materials into various required parts.
KingStar has rich experience in TPU injection molding for many years and has accumulated rich technical experience. The following will provide a detailed breakdown of the key technical points of TPU injection molding and mold fabrication, providing professional reference for industry applications.

1. Selection and Design Requirements for Injection Machines
(1) Core Structural Design
The screw-type is preferred for injection machines, which can provide uniform plasticizing speed and melting effect, and is more suitable for TPU processing needs than the plunger-type machines. The liner of the barrel is made of copper aluminum alloy material, and the surface of the screw is chrome plated, which can effectively prevent wear and tear; The recommended length to diameter ratio (L/D) for the screw is 16-20, with a minimum of 15. The compression ratio should be controlled between 2.5/1 and 3.0/1, and the segmented design should be clear: the feeding section length accounts for 0.5L, the compression section accounts for 0.3L, and the metering section accounts for 0.2L. A check ring should be installed near the top of the screw to avoid molten material backflow and ensure stable molding pressure.
(2) Nozzle and Shot Volume Parameters
The nozzle adopts a self flowing type, with an inverted conical outlet design and a diameter of at least 4mm, which is 0.68mm smaller than the inlet of the sprue bushing. It is also equipped with a controllable heater band to prevent TPU material from solidifying at the nozzle. From the perspective of economy and molding effect, the shot volume should be controlled at 40%~80% of the equipment rated amount, and the screw speed should be set at 20~50r/min.
2. Key Points of TPU Injection Mold Design
(1) Consideration of Part Shrinkage Rate
The shrinkage rate of TPU parts is influenced by multiple factors such as raw material hardness, part thickness, shape, molding temperature, and mold temperature. The conventional shrinkage rate range is 0.005~0.020cm/cm. For example, a rectangular specimen with dimensions of 100*10*2mm has a shrinkage rate of 2-3 times that of 60D in the flow direction of the sprue along the length direction, with a hardness of 75A. The specific rule is that when the hardness is between Shore 78A and 90A, the shrinkage rate of the parts decrease with increasing thickness. When the hardness is between 95A and 74D, the shrinkage rate slightly increases with the increase of thickness.
(2) Runner and Cold Slug Well Design
As a sprue connecting the nozzle of the injection machine with the runners or cavity, the diameter of sprue needs to be enlarged inwardly at an angle of not less than 2° to facilitate the demolding of excess material in the runner. The runner is symmetrically and equally distributed in the multi-cavity mold, and the cross-section can be designed as circular, semi-circular, or rectangular. The diameter is suitable for 6-9mm, and polish the surface like the mold cavity so as to reduce flow resistance. The cold slug well is located at the end of the sprue to capture the cold material generated at the nozzle end between two injections, to avoid blocking runners or gates. Its diameter is 8-10mm and depth is about 6mm.
(3) Gate and Vent Design
The gate is the part with the smallest cross-sectional area in the runner system, and its length should be short. Its shape should be rectangular or circular, and its size should be adjusted according to the thickness of the workpiece: When the thickness is below 4mm, the diameter is 1mm; when it is 4-8mm, the diameter is 1.4mm; when it is above 8mm, the diameter is 2.0-2.7mm. Gate location should be selected first in the thickest area of the workpiece that does not affect its appearance and use, at a right angle to the mold wall, to reduce shrinkage and sink marks. The vent is located at the end of the molten material flow or on the parting line of the mold, designed as a slot with a depth of 0.15mm and a width of 6mm, used to exhaust the gas in the mold cavity and avoid defects such as pores, poor weld lines, burns, etc. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure uniform temperature of the mold to prevent warpage and distortion of the parts.
3. Key Molding Condition Control
(1) Temperature Parameter Adjustment
The temperature directly affects the plasticization, flow, and cooling effects of TPU, and it is necessary to focus on controlling the barrel temperature, nozzle temperature, and mold temperature.
- Barrel Temperature: Adjust according to the hardness of TPU, the higher the hardness, the higher the required melting temperature, with an overall range of 177-232℃. The temperature distribution gradually increases from the hopper end (rear end) to the nozzle end (front end), achieving smooth plasticization.
- Nozzle Temperature: Usually slightly lower than the maximum temperature of the barrel to avoid molten material salivation. If using a self-locking nozzle, it can be controlled within the highest temperature range of the material barrel.
- Mold Temperature: Controlled by a continuous temperature cooling medium (such as water), it is related to the crystallinity and part dimensions. The higher the hardness and crystallinity, the higher the mold temperature requirement, with a conventional range of 10-60 ℃. Low mold temperature can easily cause premature freezing of the melt, resulting in flow marks, reduced crystallinity of the product, and subsequent shrinkage and performance changes.
(2) Pressure Parameter Settings
The pressure during injection molding includes plasticizing pressure (back pressure) and injection pressure. The back pressure is adjusted by overflow valves, with a range of 0.3-4MPa. Increasing back pressure appropriately can improve the melt temperature, uniform temperature, and color mixing effect, while also releasing gas. However, it will prolong the molding cycle. The injection pressure range is 20~110MPa, used to overcome the flow resistance of the melt, control the filling rate, and compact the melt. The holding pressure is about half of the injection pressure. And the back pressure needs to be controlled below 1.4 MPa to ensure uniform plasticization of TPU.

(3) Time Parameter Optimization
The molding cycle including filling time, holding time, cooling time, and other times such as mold opening, part ejection, and mold closing, directly affects production efficiency. Cycle length depends on the hardness of TPU, part thickness and configuration of the parts. If the hardness is high, the cycle is short. If the thickness or configuration of the parts is complex, the cycle is long. At the same time, it is affected by the mold temperature, with a conventional range of 20~60 seconds.
(4) Other Key Parameters
The injection speed is adjusted according to the configuration of the component. Products with thick wall sections require lower injection speeds, while products with thin wall sections require faster speeds. The screw speed should be set at a low shear rate, with a conventional range of 20~80r/min and a preferred range of 20~40r/min.
4. Special Processes and Post-Processing
(1) Shutdown Processing
TPU is prone to degradation when left at high temperatures for a long time. After shutdown, it is necessary to clean the equipment with PS, acrylic plastics, PE, or ABS. When the shutdown exceeds 1 hour, the heating system should be turned off to avoid material degradation.
(2) Post-Processing of Products
Due to uneven plasticization or differences in cooling rates, TPU products are prone to internal stress, especially in thick walled products or products with metal inserts. This may lead to decreased mechanical properties, surface silver steaks(splay), deformation and cracking. Annealing treatment is required to solve the problem:
- Products with hardness below Shore A85: Anneal at 80 ℃ for 20 hours;
- Products with hardness above Shore A85: Anneal at 100 ℃ for 20 hours;
- Products with lower hardness can also be left at room temperature for several weeks.
Annealing can be carried out in a hot air oven to avoid local overheating and deformation of the product. It also promotes TPU phase separation, forming micro areas, and improving mechanical properties.
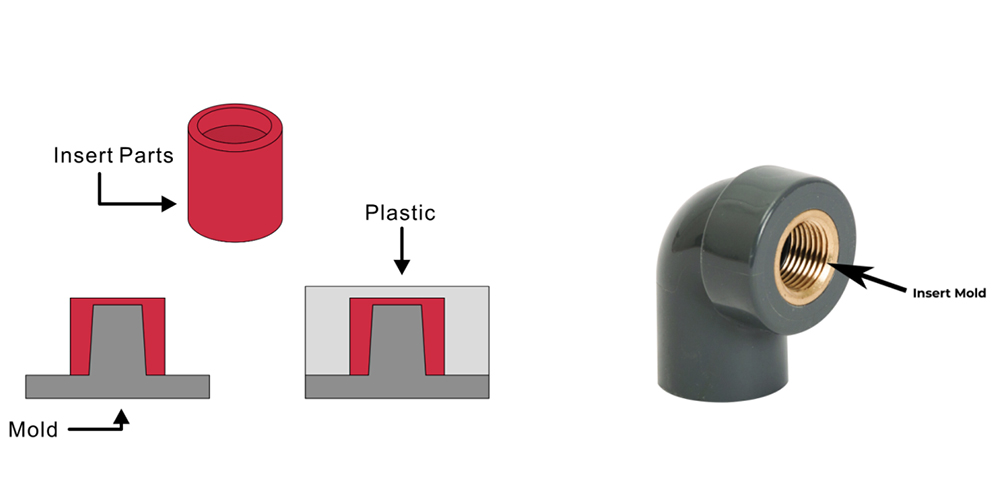
(3) Insert Injection Molding Process
To meet assembly and strength requirements, TPU parts often need embedded metal inserts. Due to the significant differences in thermal properties and shrinkage rates between metal and TPU, metal inserts require pre-treatment: after degreasing, heat them at 200-230 ℃ for 1.5-2 minutes can achieve a peel strength of 6-9kg/25mm. If a stronger bonding effect is required, the surface of the insert can be coated with adhesive and heated at 120 ℃ before injection. Note: the TPU raw materials used must not contain lubricants.
(4) Recycling Materials for Reuse
The waste materials and unqualified products generated during the TPU processing can be recycled and reused. Mechanical properties of 100% recycled materials do not significantly decrease and can remain usable. However, to ensure optimal performance and injection conditions, it is recommended to use recycled materials at a ratio of 25% to 30%. Recycled materials should be consistent with the specifications of new materials, avoiding the use of contaminated or annealed recycled materials. They should be granulated and dried as soon as possible before use, and the molding conditions should be adjusted according to changes in melt viscosity.
Conclusion
TPU injection molding process and mold design is a systematic engineering, from injection machine selection, mold structure design to molding parameter control and post-processing, each link directly affects product quality and production efficiency. KingStar can provide customers with comprehensive TPU injection molding solutions, helping companies optimize production processes and enhance product competitiveness.
If you have any requirements in TPU injection molding process optimization, or would like to explore a reliable custom part manufacturer in depth, please feel free to contact KingStar at sales@kingstarmold.com or leave online message to get free support!



