Thin Wall Injection Molding

Resources for The Complete Guide to Thin Wall Injection Molding
What is thin wall injection molding?
Thin-wall injection molding is a specialized injection molding process used to manufacture parts with thin walls.
This technology is often referred to as thin-wall plastic injection molding, and it can be defined in three ways:
- The molded product has a wall thickness of less than 1 mm, with a projected area of the plastic part exceeding 50 cm².
- The wall thickness of the molded product is below 1 mm (or 1.5 mm), or the ratio of thickness (t) to diameter (d) of disc-shaped plastic parts is under 0.05. This is considered thin-wall injection molding.
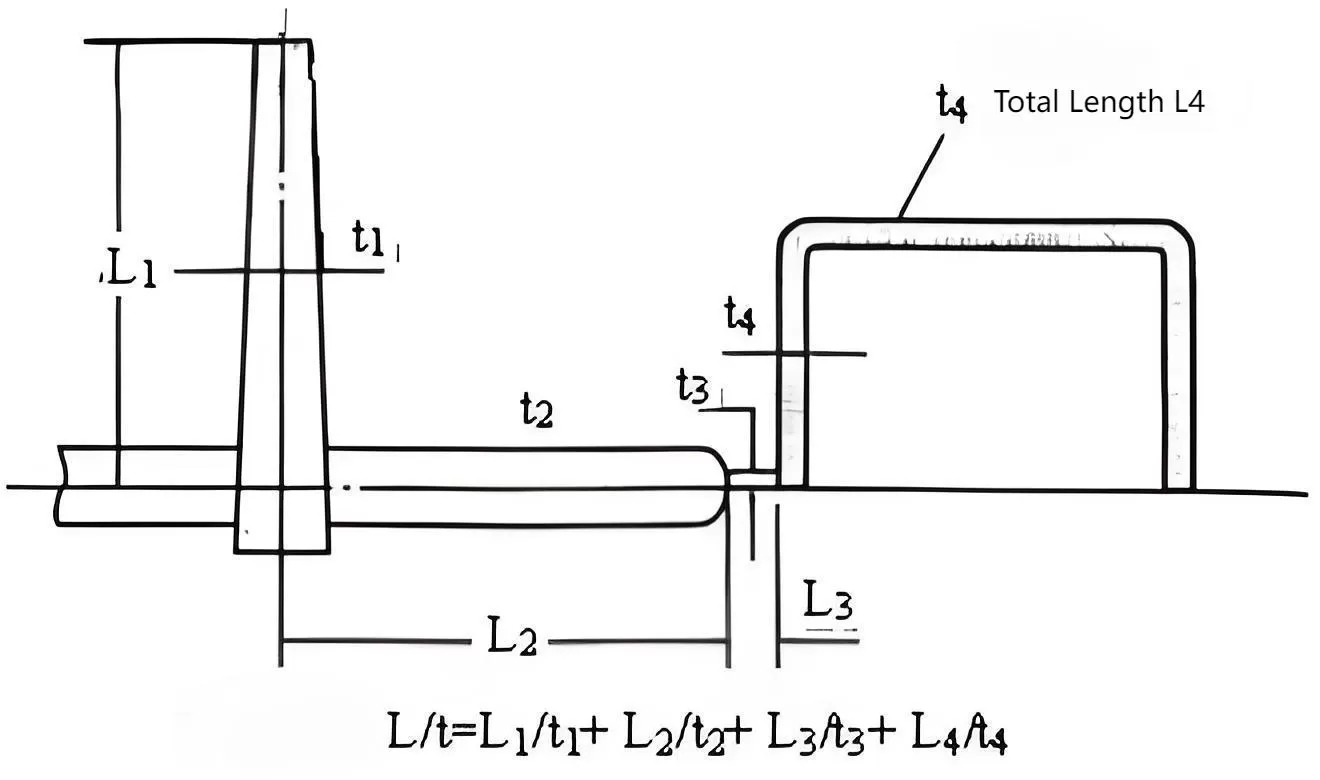
- The flow length (L) from the mold’s main channel to the furthest point of the finished product, divided by the wall thickness (t) of the product, is referred to as the flow length/wall thickness ratio. When this ratio exceeds 150 (L/t > 150), the process is categorized as thin-wall injection molding. If the thickness is not uniform, the ratio can be calculated in sections.

For example:
- For a disposable lunch box made from PP (with a viscosity factor of 1), the flow length is 135 mm and the wall thickness is 0.45 mm. The flow length/wall thickness ratio is 300 (135/0.45), which is greater than 150, qualifying it as thin-wall injection molding.
- For a mobile phone battery shell made from PC (with a viscosity factor of 2), the flow length is 38 mm and the wall thickness is 0.25 mm. The flow length/wall thickness ratio is 152 (38/0.25), and when multiplied by the viscosity factor (2), the ratio becomes 304, which is also greater than 150, thus also classified as thin-wall injection molding.
What is the principle of thin-wall injection molding?
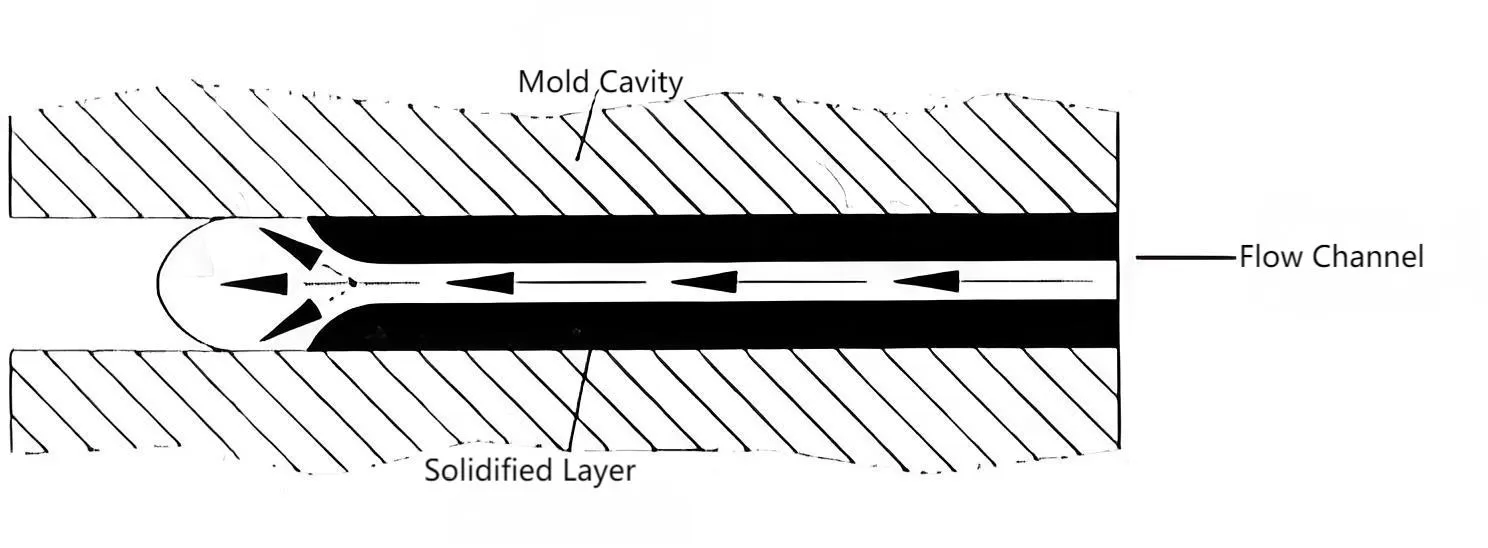
The cold mold cavity wall causes the molten metal to solidify upon contact, forming a solidified layer that reduces the thickness of the flow channel. This effect is more pronounced when the wall thickness is thinner.
The key principles of thin-wall injection molding include the following aspects:


What are the applications of thin-wall injection molding?
Thin-wall injection molding technology is widely used in various industries. Some common applications include:
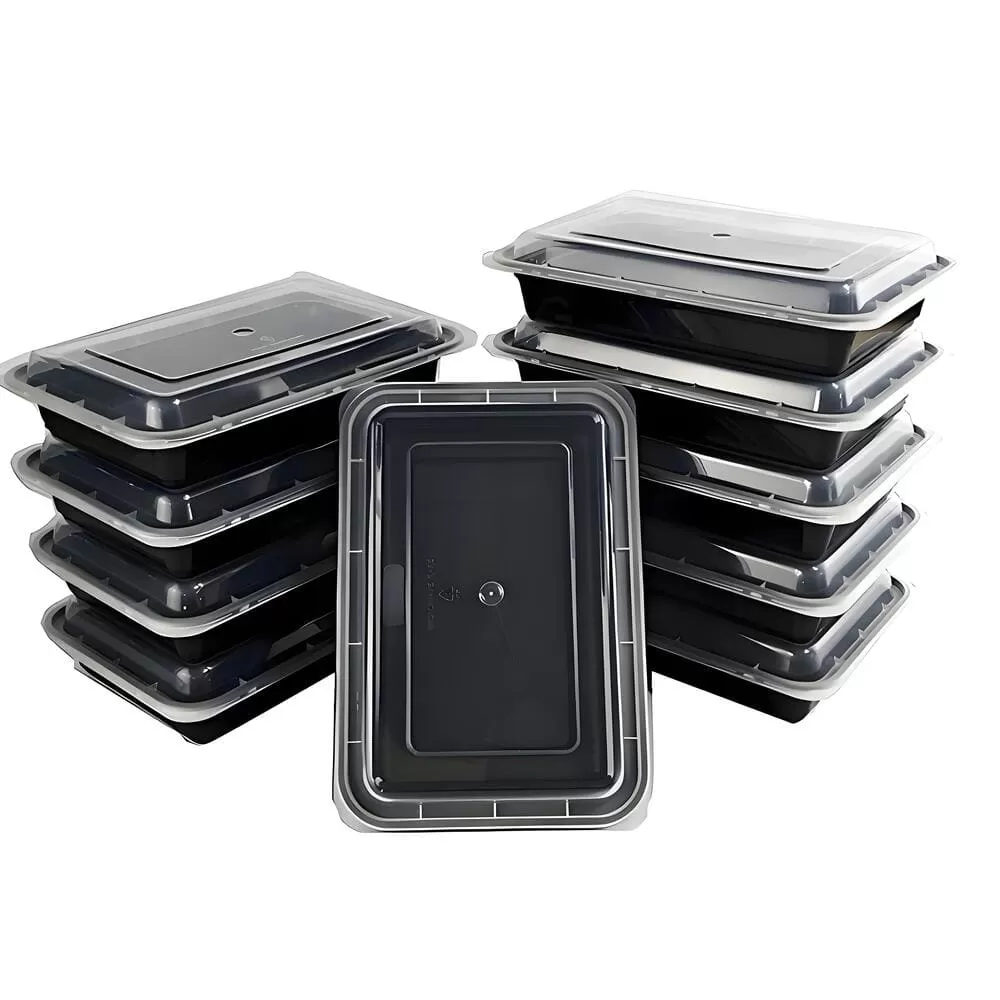

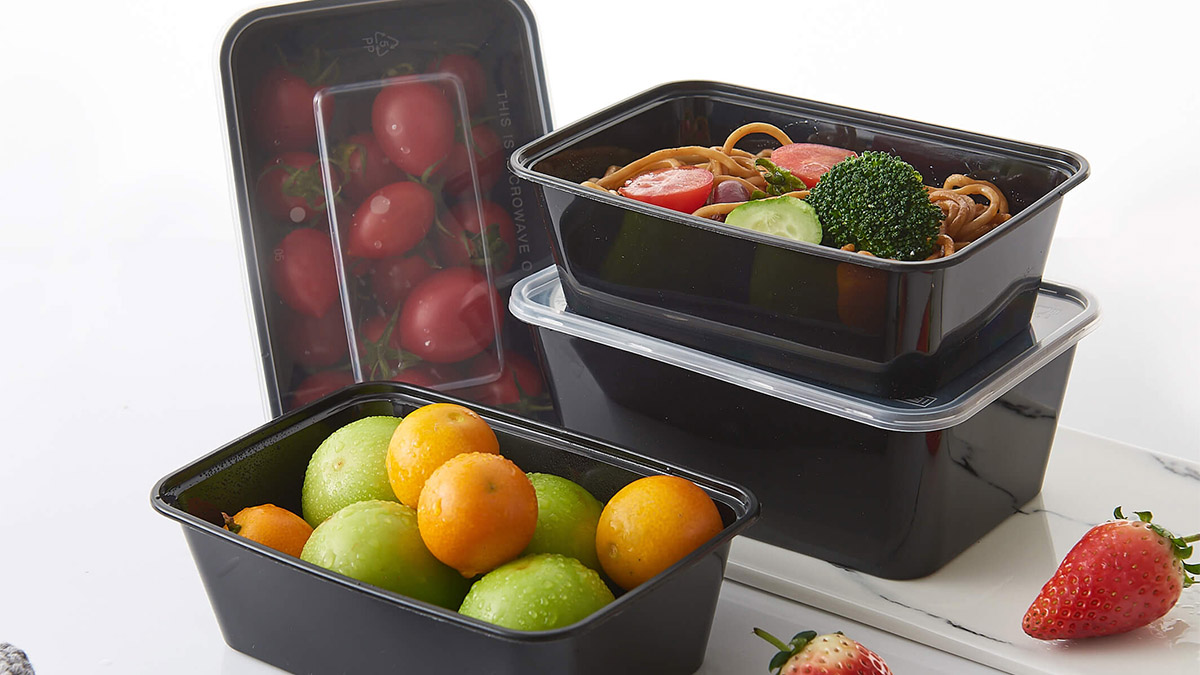
① Food Packaging: Thin-wall injection molding is extensively used in food packaging, allowing the production of containers with excellent sealing and preservation properties, such as plastic bowls and boxes. The technology’s fast production speed and high efficiency make it suitable for large-scale production, meeting the food packaging industry’s demand for both production efficiency and high-quality products.
② Electronic Product Housing: Thin-wall injection molding is commonly used in the production of electronic product housings, including mobile phone cases, TV enclosures, and other electronic devices. This technology enables the creation of thin yet durable housings, offering high precision and dimensional stability that meet the aesthetic and accuracy requirements for electronic products.
③ Auto Parts: Thin-wall injection molding is widely applied in automotive parts manufacturing, producing lightweight yet strong components such as interior parts and automotive lighting. The technology’s fast cooling and curing process, along with its high efficiency, enhance production speed and help reduce manufacturing costs for auto parts.
④ Medical Devices: Thin-wall injection molding is crucial in the production of medical devices, offering the ability to manufacture products like syringes and infusion sets with excellent biocompatibility and ease of cleaning. The precision and dimensional stability of thin-wall injection molding ensure that medical devices meet the high standards for both appearance and accuracy required in healthcare.
Thin-wall injection molding is an essential technology for producing high-performance thin-walled plastic products. By utilizing rapid injection speeds and quick cooling and solidification, it enables the production of durable and precise parts. This technology is widely used across industries such as food packaging, electronics, automotive, and medical devices. As technology continues to advance, thin-wall injection molding will expand into even more fields, further driving innovation and efficiency across various sectors.
Knowledge About Thin Wall Injection Molding