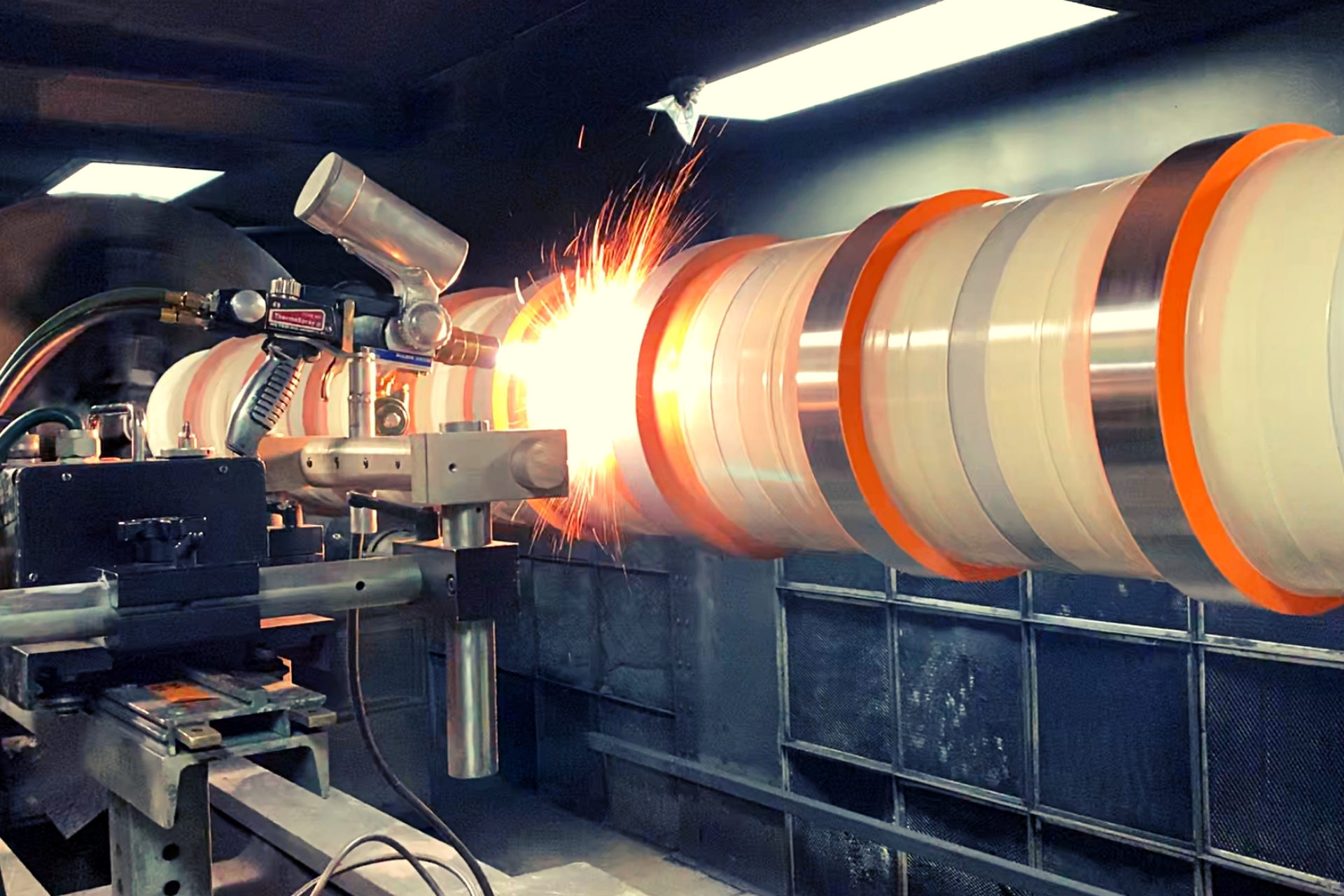
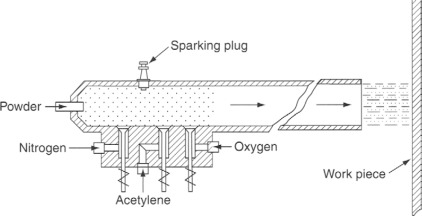
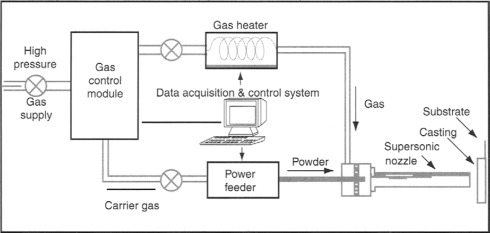
Properties of Various Sealants for Thermally Sprayed Coatings
| Sealant | Base Polymer | Curing Conditions | Wetting Angle on γ-Alumina (°) | Viscosity η (mPa·s) | Curing Shrinkage (Weight %) | Curing Shrinkage (Volume %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Inorganic aluminum phosphate | 200 °C for 7 h | 97 | 505 | 48 | – |
| B | Methacrylate¹ | 60 °C for 1 h | 15 | 6.5 | 3.8 | 17.6 |
| C | Methacrylate¹ | 60 °C for 1 h | 15 | 8.6 | 2.6 | 5.3 |
| D | Phenol¹ | Room temperature | 10 | 1.5 | 79.6 | 8 |
| E | Epoxy | 80 °C for 2 h | 39 | 162 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| F | Methacrylate¹ | UV curing | 26 | 28 | 0.5 | <2 |
| G | Epoxy | 60 °C for 2 h | 42 | 179 | 1 | 0.1 |
| H | Furan | 60 °C for 1 h → RT | 67 | 626 | 2 | 2 |
| I | Vinyl ester | 60 °C for 1 h → RT | 83 | 319 | 0.6 | 2.4 |
*Online Source: sciencedirect.com
Comparative Analysis of Key Metrics
| Spraying Technology | Most Prominent Characteristics | Advantages | Disadvantages | Cost | Applicable Scenarios | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paint Spraying | Liquid paint application using compressed air or high-pressure systems | - Low cost - Easy to apply - Wide color range | - Poor adhesion - Volatile solvents - Environmental impact | Low | Interior decoration, small-batch production | 5–10 years |
| Powder Coating | Powder coating using electrostatic spraying and heat curing | - High durability - No solvent pollution - Eco-friendly | - High cost - Color matching is difficult | Medium to high | Industrial equipment, automotive parts | 30 years |
| Abrasive Blasting | Surface cleaning and preparation using abrasive media | - Thorough surface preparation - Suitable for complex shapes | - High cost - Dust pollution | Medium | Metal surface pre-treatment | 5–10 years |
| Arc Spraying | Metal wire melted by electric arc and sprayed | - Strong bonding strength - Suitable for metal coatings | - High equipment cost - High cost | High | Metal structure repair | 30+ years |
| CGDS (Cold Gas Dynamic Spraying) | Cold gas dynamic spraying without high-temperature heating | - Suitable for high-melting materials - No thermal damage to the substrate | - High cost - Technical complexity | High | Ceramics, metal coatings | 10–20 years |
| Plasma Spraying | High-temperature plasma arc to melt and spray materials | - High-quality coatings - Suitable for high-temperature materials | - High equipment cost - Complex operation | Very high | Ceramic and metal coatings | 10–20 years |
| Flame Spraying | Flame heating of metal wire to form coatings | - Strong bonding strength - Suitable for metal coatings | - High cost - Flame pollution | High | Metal structure repair | 10–20 years |
| Air Spraying | Liquid paint atomized by compressed air | - Easy to operate - Suitable for large-area coating | - Poor adhesion - Solvent evaporation | Low | Interior decoration | 5–10 years |
| Airless Spraying | High-pressure pump to atomize paint | - Uniform coating - Suitable for high-viscosity paints | - Requires maintenance - High cost | Medium | Industrial equipment | 5–10 years |
| Electrostatic Spraying | Electrostatic charge to attract powder or liquid paint | - Uniform coating - Suitable for complex shapes | - Requires special equipment - High cost | Medium | Industrial equipment, automotive parts | 5–10 years |
Cases of Spraying Coating

Aluminum Rocker Panel

Automotive Component

Switch Kit

Drop Leveling Lowering Shackles Kit
Handrail Bracket Square

Mounting Bracket

Post Caps

Solid Telescopic Stabilizer
Guidelines for Inspection Standards of Spray-Coated Parts
| Test Item | Inspection Standard |
|---|---|
| Salt Spray Test | Continuous saltwater spray of 5% concentration at 35°C, with duration as specified by the customer. |
| No formation of bubbles or rust should be observed. | |
| Appearance | 1. Color should match the color card and have a glossy finish within sample limits. |
| 2. The surface must be free of scratches, fingerprints, or particles. | |
| 3. No rust or signs of corrosion are allowed. | |
| 4. There should be no uneven spraying or discoloration. | |
| 5. Cut edges must be smooth without sharp burrs or jagged edges. | |
| Cross-cut Test | No more than 5% of the paint should peel off the tested surface. |
| Coating Hardness | Sharpen the pencil tip to a right angle, then apply a 1KG force to draw an 8CM straight line on the paint surface at a 45-degree angle. |
| The pencil hardness should be above H, with no damage or scratches visible on the paint surface. | |
| Paint Compliance | The paint used must be accompanied by a relevant report and comply with ROHS regulations. |