
PTFE Injection Molding Overview
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) injection molding is a specialized process used to create high-performance parts that require exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability. Ideal for industries such as automotive, electronics, and chemical processing, PTFE is known for its ability to withstand harsh environments while maintaining its integrity over time. This process involves injecting PTFE resin into a mold cavity under high pressure, which allows for the precise formation of complex shapes with tight tolerances.
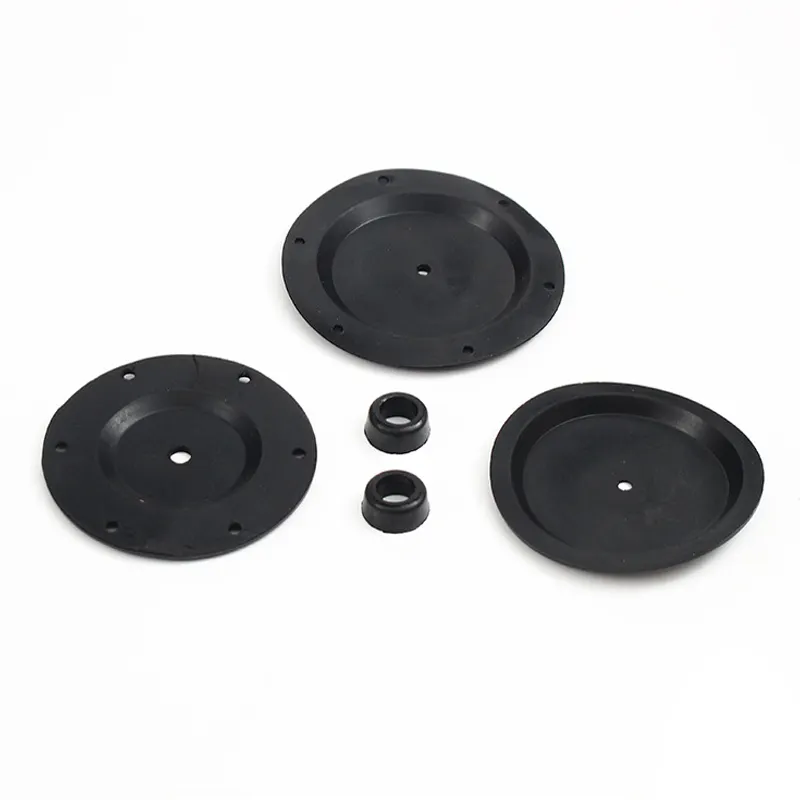
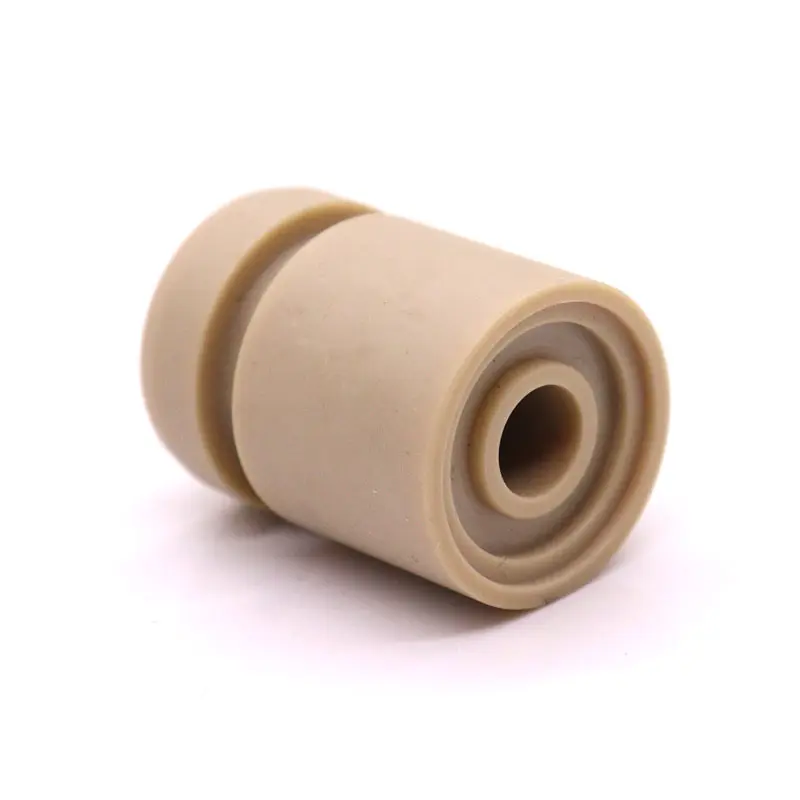
Due to PTFE’s high melting point and non-stick properties, its injection molding process requires specialized equipment and techniques. Parts made from PTFE are widely used for seals, gaskets, bearings, and electrical insulation. The material’s unique properties make it an excellent choice for applications that demand performance in extreme temperatures, exposure to corrosive chemicals, or low friction. PTFE injection molding ensures that these parts meet the rigorous demands of various industries while offering long-lasting reliability.
PTFE Material’s Characteristics
| Property/Characteristic | Value/Description | Property/Characteristic | Value/Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stability | Excellent chemical, thermal, and electrical stability. | Viscosity | Low melt viscosity, contributing to ease of flow during processing. |
| Solubility | Insoluble in almost all solvents. | Thermal Expansion | 112–125 × 10⁻⁶/K (coefficient of thermal expansion). |
| Vicat Softening Point | Approximately 327°C (621°F). | Water Absorption | Less than 0.01% (extremely low moisture absorption). |
| Tensile Modulus | 500–700 MPa (depending on grade). | Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. |
| Tensile Strength | 20–30 MPa (depending on grade and processing). | UV Resistance | Excellent UV resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications. |
| Elongation at Break | 200–400% (depending on grade). | Biocompatibility | Non-toxic and biocompatible, suitable for medical applications. |
| Density | 2.2–2.3 g/cm³. | Flammability | Non-flammable, but can produce hazardous fumes when heated to extreme temperatures. |
| Melting Point | 327°C (621°F). | Electrical Insulation | Excellent electrical insulating properties, ideal for wiring and connectors. |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.05–0.10 (low friction, ideal for sliding applications). | Compression Set | Low compression set, maintaining its shape and performance under stress. |
| Heat Resistance | Can withstand continuous use at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F). | Surface Energy | High surface energy, leading to its non-stick properties. |
| Low-Temperature Resistance | Maintains properties in temperatures as low as -270°C (-454°F). | Abrasion Resistance | Good resistance to wear and tear, making it durable for mechanical applications. |
| Dielectric Strength | 60 MV/m (excellent electrical insulation). |
Can PTFE materials be injection molded?

At KingStar Mold, we specialize in precision injection molding, and yes, we can injection mold PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene). However, due to its high melting point and non-flowing nature, PTFE requires specialized equipment and techniques for successful molding. We use fine powder or granular PTFE, which is heated and injected into molds using advanced molding technology.
Since PTFE has high viscosity and low flow properties, traditional injection molding methods are not suitable. To overcome this, we use compression molding or ram extrusion prior to the injection process, ensuring the material flows properly and forms complex shapes. PTFE injection molding is ideal for parts that demand exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and high thermal stability, such as seals, gaskets, and electrical insulation. At KingStar Mold, we ensure these parts meet the highest standards of durability and performance for industries that rely on long-lasting, high-performance components.
What’s PTFE Injection Molding’s Challenges?
Processing and Emissions Control
PTFE releases harmful gases, such as hydrogen fluoride, at high temperatures, requiring specialized ventilation and handling systems to safely manage these emissions and avoid defects like voids.
Thermal Management and Shrinkage
PTFE’s high rate of thermal expansion and poor thermal conductivity make it difficult to control during molding, leading to potential shrinkage (2-5%) and part warping if not properly managed.
High Pressure and Demolding Difficulties
PTFE requires very high injection pressures (over 10,000 psi), and due to its high surface energy, it can be challenging to demold without damaging the part, necessitating careful handling and specialized mold designs.
Post-Processing and Equipment Needs
PTFE parts often require additional processing, such as annealing or machining, and the high reactivity of PTFE with mold materials results in shorter mold life, demanding frequent maintenance or replacement of specialized equipment.
What’s PTFE Injection Molding’s Advantages?
Exceptional Durability and Resistance
PTFE offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature endurance, and UV resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments in industries like chemical processing, aerospace, automotive, and outdoor applications.
Low Friction and Easy Movement
With its low friction properties, PTFE is perfect for components requiring smooth operation and minimal wear, including bearings, seals, gaskets, and medical devices.
Biocompatibility and Electrical Insulation
PTFE’s non-toxic and biocompatible nature makes it suitable for medical applications, while its excellent electrical insulating properties are ideal for connectors, switches, and sensors.
Ease of Maintenance and Moisture Resistance
PTFE’s non-stick surface, low moisture absorption, and ease of cleaning make it perfect for moisture-sensitive and cleanliness-demanding applications like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices.
Chemical Processing Equipment

Electrical Components
Food and Beverage Equipment

Medical Devices
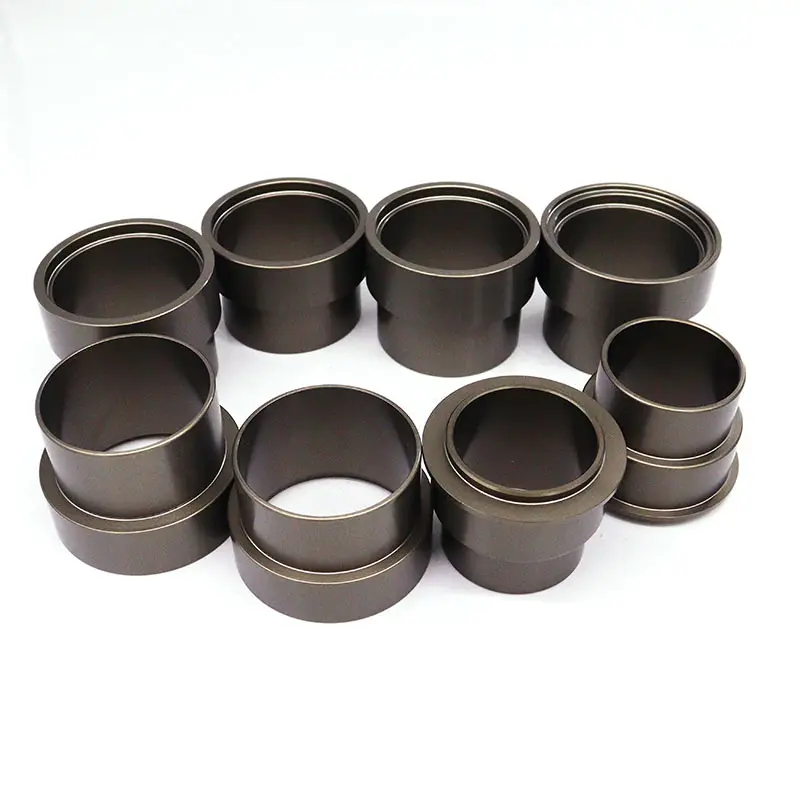
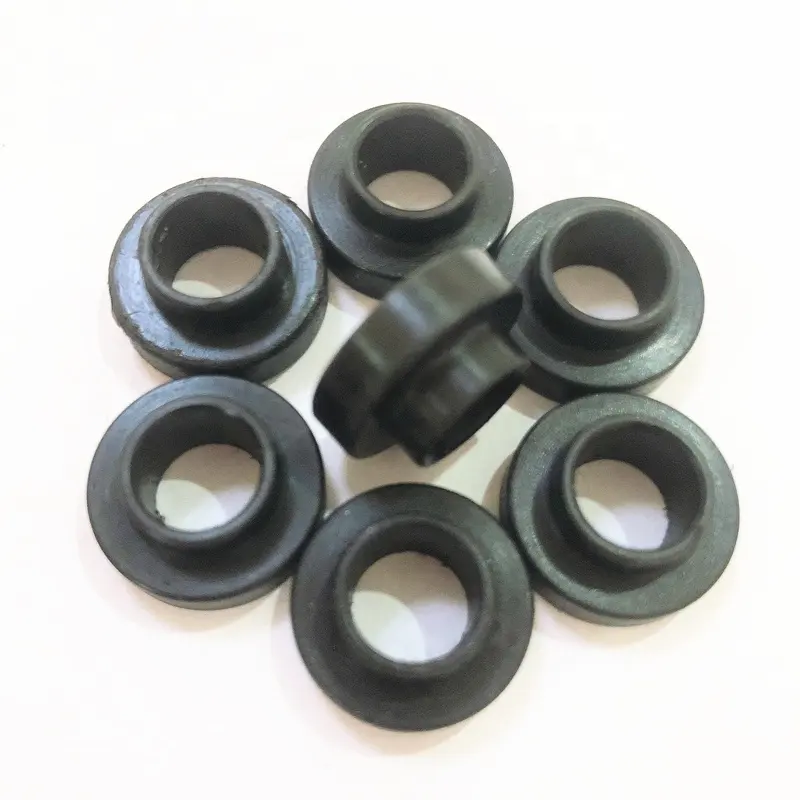
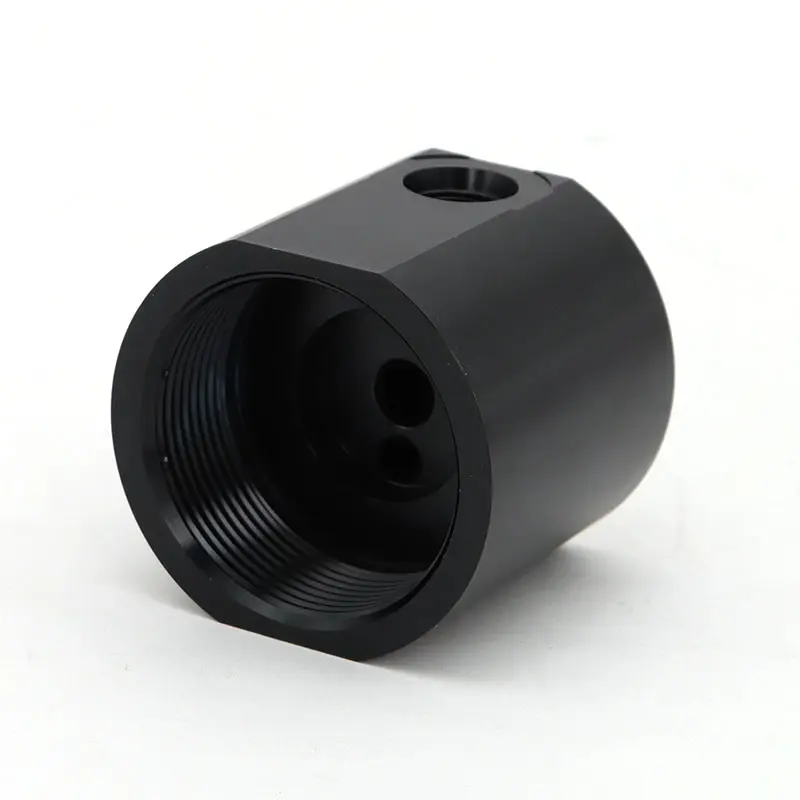






PTFE presents challenges such as high shrinkage rates, high pressure requirements, and difficult demolding due to its non-stick properties, requiring special mold designs and handling procedures.
PTFE is widely used in automotive, chemical processing, medical devices, food processing equipment, and electrical components due to its unique properties.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a high-performance plastic known for its chemical resistance, low friction, and high-temperature stability. It is ideal for injection molding in demanding applications.
KingStar Mold adheres to strict safety protocols, including advanced ventilation and handling systems, to safely manage PTFE emissions and ensure quality production.
Yes, KingStar Mold can accommodate both small batch prototypes and large-scale production runs, providing flexibility to meet diverse customer needs.
KingStar Mold has extensive experience in producing high-precision PTFE injection molded parts, utilizing advanced equipment and techniques to ensure quality and consistency in every product.
PTFE’s excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents makes it ideal for sealing components, gaskets, and linings in chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
PTFE’s low friction makes it ideal for components like bearings, seals, and gaskets that require smooth movement and minimal wear.
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, chemical processing, food and beverage, medical, and electrical benefit from PTFE’s unique properties for critical components.
Yes, PTFE is biocompatible, non-toxic, and widely used in medical devices, including implants, surgical tools, and drug delivery systems.
PTFE has a high melting point and is resistant to extreme temperatures, making it perfect for high-temperature environments in industries like automotive and aerospace.
No, PTFE requires specialized injection molding equipment that can handle the material’s high viscosity and the high pressures necessary for molding.