Electric Chopper Bicycle Aluminum Components
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Milling, Turning, EDM, Rapid Prototyping |
| Surface treatment | Anodizing(oxidation), sandblasting, brushing, painting, etc. |
| Color | Customized colors |
| Tolerance | +/- 0.01 mm |
| Certification | ISO 9001:2015 |
KingStar Mold’s Small-Batch Project: Custom Aluminum Parts for Electric Chopper Bikes
Back in 2023, we took on a project with a clear, specific ask: crafting three unique aluminum components for electric chopper bicycles, all in small batches. What made it stand out? Each part had a distinct role, but they shared a key trait—plus a color twist. Here’s how we nailed it.
What the Client Needed
It boiled down to three parts, each with tight specs:
Surface feel: All three needed a smooth finish—no rough edges, but not mirror-shiny. Think “satin-smooth” to the touch, with a soft sheen that avoids glare.
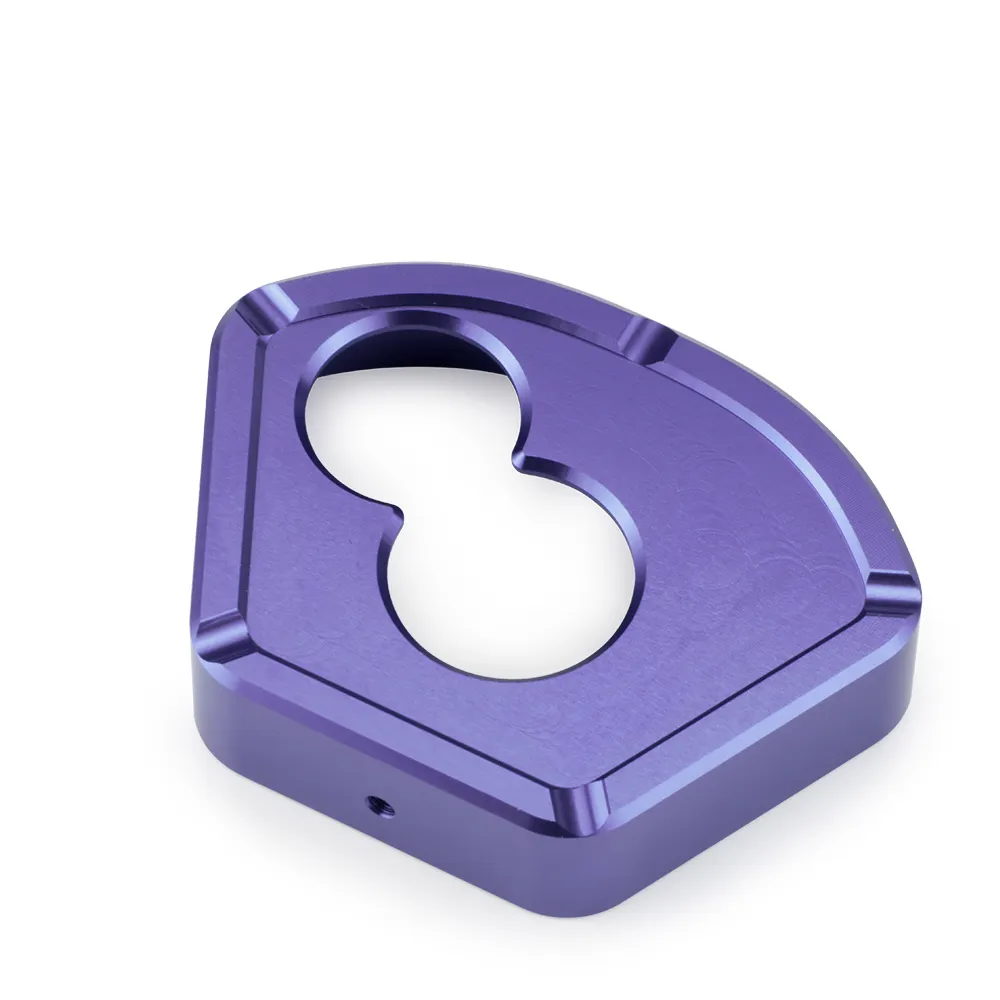
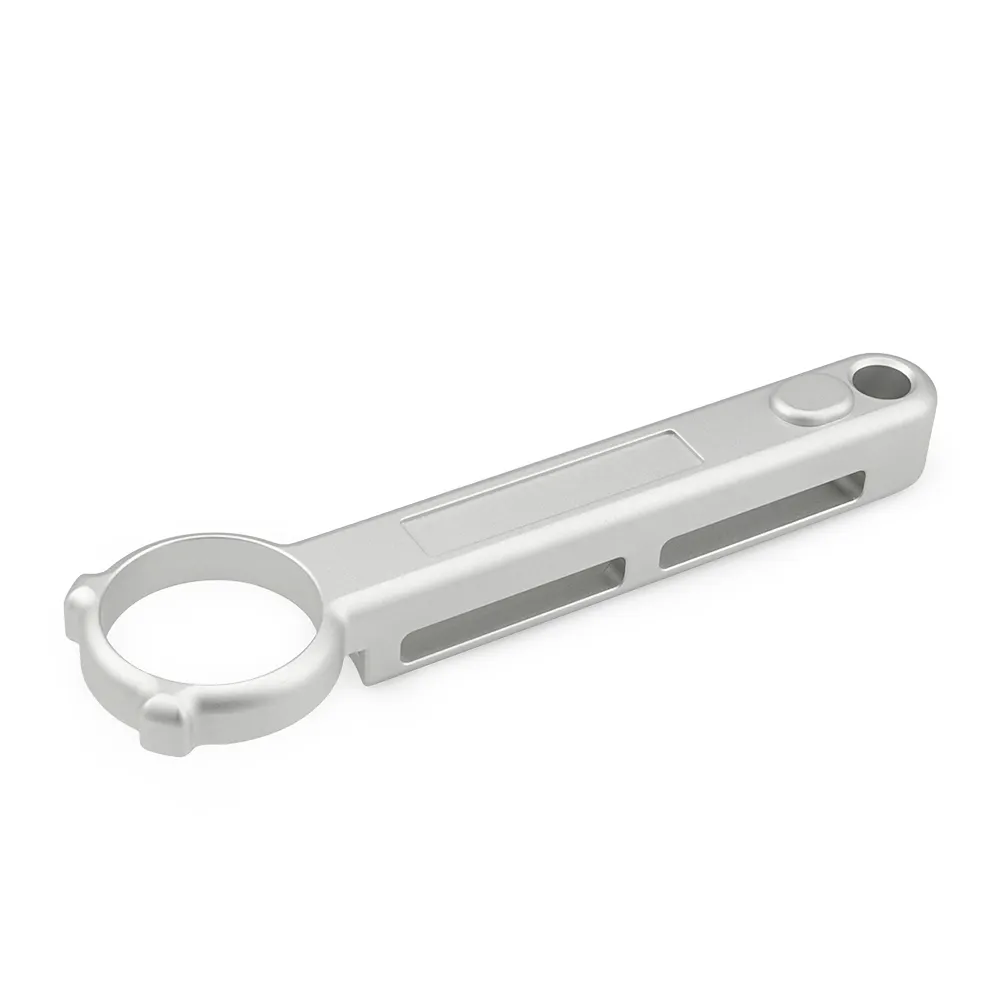
Colors: Two parts had to be a consistent silver (not too bright, not too dull), and the third a light, elegant purple—all matching the bike’s design language.
Precision: Every part needed to hit +/- 0.01 mm tolerance.
ISO 9001:2015 compliance: Traceable processes to prove quality, since these parts sit close to the bike’s motor and electrical components.
The Hurdles We Faced
Small runs (50 units per part) with specific surface and color demands? Trickier than it sounds:
Nailing the “smooth but not shiny” sweet spot: Too much polishing, and we’d get unwanted glare; too little, and the surface felt rough. We needed a consistent texture across all three parts.
Silver consistency: The two silver parts had to look identical—no slight tone shifts when mounted next to each other on the bike.
Purple precision: The colored part’s purple needed to pop but not fade; aluminum can be finicky with color adhesion, especially on a smooth surface.
Waste in small batches: With only 50 units per part, scrapping even one due to a surface flaw or color mismatch hurt costs.
How We Pulled It Off
We leaned into testing and tweaks:
Surface prep: We settled on a fine-grit sanding (400-grit) followed by a light anodizing pass—enough to seal the aluminum and create that smooth, non-reflective finish. We tested 10 sample pieces first, adjusting sanding pressure until the texture felt consistent across all.
Silver matching: For the two silver parts, we mixed a custom anodizing solution with a touch of matte additive to tone down the shine. We ran side-by-side tests: sat two parts under the same light, and we tweaked the solution until their tones matched—no visible difference.
Purple perfection: The purple part’s got a base layer of adhesion primer (key for color hold) before a specialized powder coat in the client’s exact purple shade. We sprayed 5 test pieces, baked them, and compared to the client’s swatch—adjusting the powder mix by 3% to get the depth right.
Waste reduction: By prepping materials to exact part sizes (no excess aluminum) and testing finishes on scrap pieces first, we cut material waste by 15%. We also lightened each part by 10% (thinning non-structural edges, for example) without losing strength—making the bike lighter, too.
ISO checks: Every step was logged: sanding grit used, anodizing time, powder coat temperature. We even kept a “master sample” of each part’s finish to reference for future runs.
Checking Quality
We tested like the parts were on the bike:
Surface smoothness: A profilometer measured roughness at 0.8 Ra (well within the “smooth but not shiny” range).
Color checks: A spectrophotometer confirmed the two silvers had a Delta E (color difference) of less than 1.0—imperceptible to the eye. The purple hit the client’s swatch with a Delta E of 0.7.
Fit tests: We mounted all three parts on a mock bike frame—no gaps, and the smooth surfaces meant no snags during assembly.
Durability: The purple powder coat passed a 1,000-cycle rub test with a dry cloth; no chipping or fading.
What Came Next
The client loved it: the parts fit perfectly, the finishes looked consistent, and the 15% waste reduction kept costs in line. They’ve since re-ordered two more batches, and we’re using those master samples to keep the finish and color spot-on.
Need custom aluminum parts with specific finishes or color matches? Let’s talk—we’ll nail the details.
| Item | Specification Requirements |
|---|---|
| Application Field | Electric chopper bicycle components |
| Number of Components | 3 units |
| Production Batch | Small batch (50 units/component) |
| Material | Aluminum |
| Surface Treatment Requirements | Smooth (no rough edges), non-mirror reflective, satin texture, low gloss, roughness up to 0.8 Ra |
| Color Requirements | 2 units in silver (consistent tone, neither too bright nor too dull); 1 unit in light purple (elegant, matching design language) |
| Tolerance | ±0.01 mm |
| Quality Certification | Compliant with ISO 9001:2015 standards, with traceable process records required |
| Specific Component Names | Confidential |
| Detailed Dimension Parameters | Confidential |
| Other Specific Requirements | Color adhesion must be ensured (especially for the purple component), no surface defects, good fit (no assembly gaps) |
Frequently Asked Questions
No worries—our case studies focus on the usual kinds of problems, but we deal with unique or tricky challenges all the time. Even if your specific issue isn’t featured, the problem-solving approach and technical skills you see in the case studies still apply. Send us a note with what you’re up against, and we’ll walk through how we’d tackle it for you.
We keep our case studies fresh—they show the methods we actually use right now. When we start using new tools, materials, or process fixes (like better mold simulation software or greener plastics), we update the case studies to include those too. That way, what you’re seeing matches how we work in today’s manufacturing landscape.
If a case study clicks with what you’re working on, just get in touch with our team. Share the details of your project, and we’ll talk through how the strategies highlighted—like material pairing, mold tweaks, or process adjustments—might fit your goals. If needed, we can also craft custom solutions that match what you need.
Feel free to reach out at sales@kingstarmold.com to start the conversation.
Yes, all our case studies are based on real client collaborations. To protect our clients’ rights, we only share details that have been approved for disclosure—including specific timelines, challenges, solutions, and measurable outcomes, all backed by data from client production records or third-party testing.
Each case study delves deeply into specific issues, such as how to extend the lifespan of components or how to accelerate production speed, and shows you how we solved these problems. Even if your project is not exactly the same as them, these cases can help you clearly understand how we handled the issues: breaking down the problem, adjusting the method, and achieving results. This enables you not only to see the outcomes we have achieved, but also to understand how we think about solutions – so you can roughly judge whether we can meet the requirements of your project.
Simply upload your CAD files and project details through our website (click here to go to contact page or click the “request a quote” button at the top right corner of the page, and fill in the form that appears) or contact our team() directly. We’ll respond quickly with a detailed quote, lead time, and suggestions to optimize your design for cost and manufacturability.
We accept common 3D and 2D file formats including STEP, IGES, STL, and DWG. To ensure the best results, it’s helpful to include both 3D models and detailed 2D drawings with tolerances and surface finish requirements. There are 2 ways to send them to us: click here to the contact page to directly upload the files or send them via email: sales@kingstarmold.com
Note:
We maintain pre-market confidentiality agreements and sign NDA/NNN with all our customers. Every case you see has been shared with client approval. To protect sensitive information, some details have been blurred or modified. All photos were taken internally by KingStar Mold. Thank you for your support and cooperation.
One-Stop Manufacturing Service that Fits Your Product Life Cycle
Our Custom Manufacturing Services
Your one-stop solution for enhancing your product’s market potential.

Injection Molding
We offer comprehensive services of injection molding, producing a wide range of parts through two-shot molding, overmolding and custom molding techniques.

Mold Making
At KingstarMold, we develop and produce precision die-casting molds, injection molds, stack molds, and two-color molds using state-of-the-art equipment.

Sheet Metal Fabrication
We provide precise sheet metal fabrication solutions, offering custom-made parts with exceptional durability, tailored to meet the specific requirements of your project.
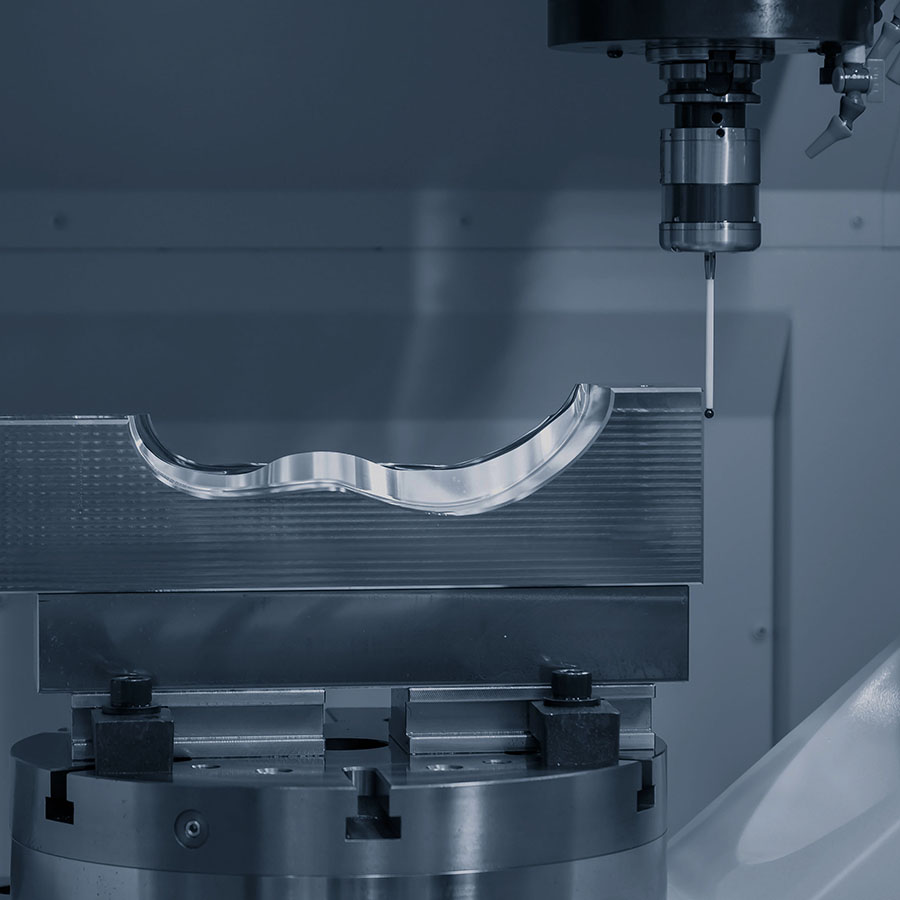
CNC Machining
Our CNC machining includes both 4-axis and 5-axis capabilities, with a focus on optimizing equipment arrangement to enhance efficiency.
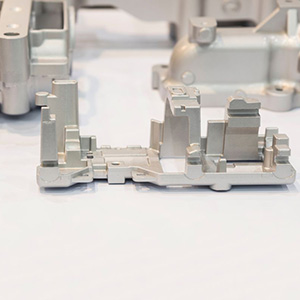
Die Casting
Our die casting service ensures high-precision, high-volume production of metal parts with excellent surface finishes and tight tolerances.
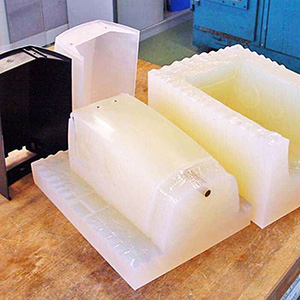
Vacuum Casting
With vacuum casting, we produce high-quality, detailed prototypes and low-volume parts with exceptional accuracy.





