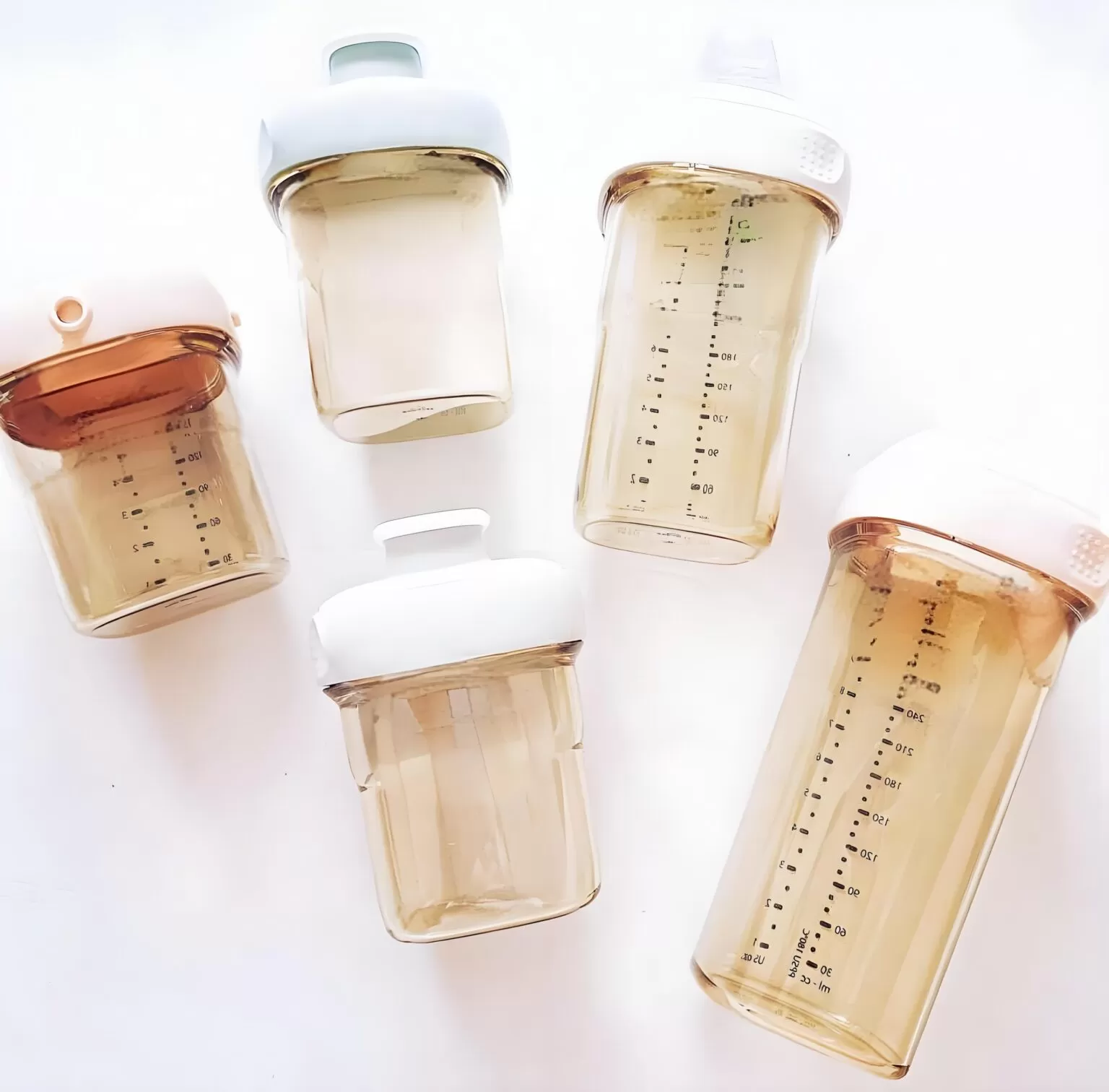
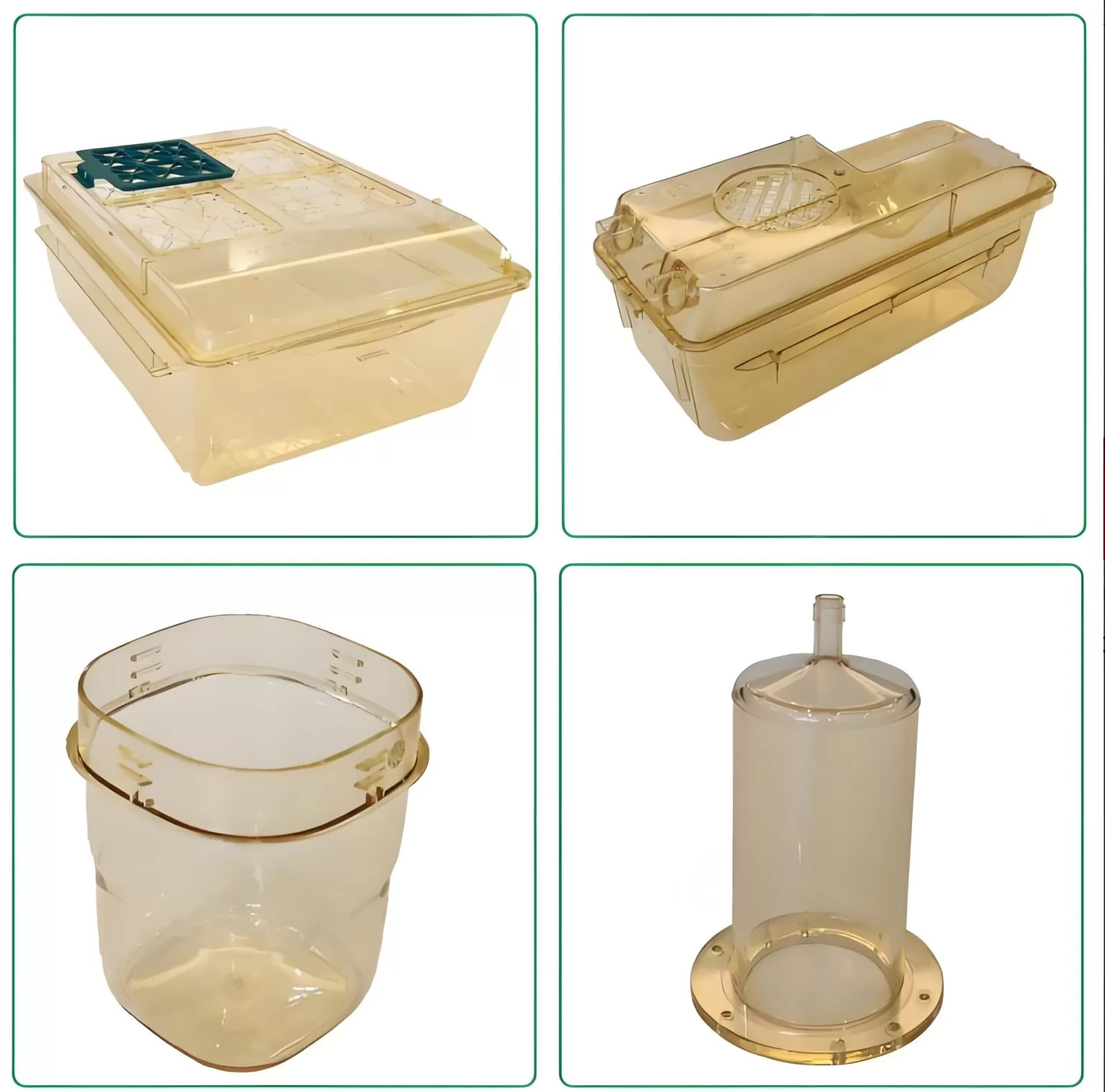
PPSU Injection Molding
KingStar Mold is a leading PPSU injection molding manufacturer, focused on PPSU and other superior thermoplastics. We partner with innovators in the medical, food & beverage, infant care, and aerospace industries to create components that ensure safety, durability, and uncompromising performance.
Your challenges demand materials that can withstand sterilization, high temperatures, and strict regulatory standards. We deliver with expert material science, rigorous quality controls, and a full-spectrum service—from DFM and prototyping to high-volume production.
We help you create safer infant products, reliable medical devices, and durable food-contact components.
Let’s build a safer, higher-performance product together. Contact us for your project.
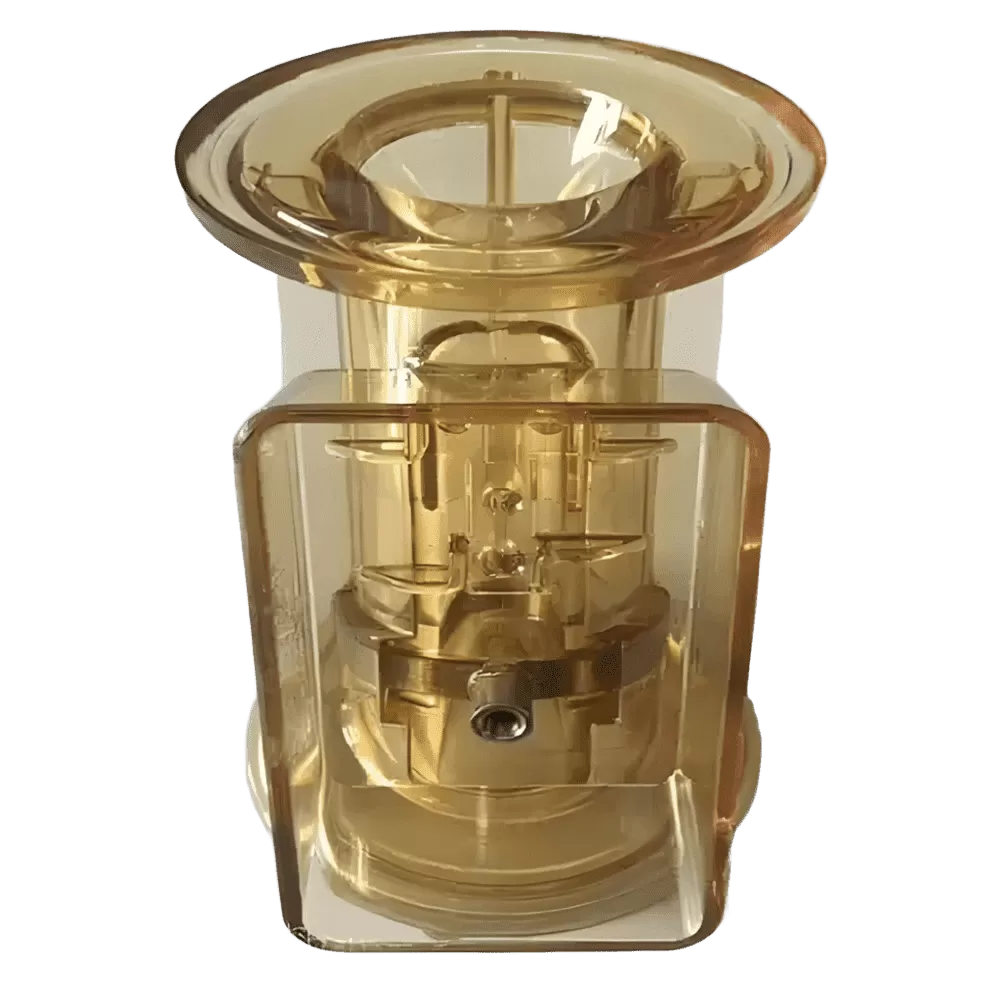

Resources for The Complete Guide to PPSU Injection Molding

What is PPSU?
What Types of PPSU Materials Are There?
PPSU is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical resistance properties. There are several variations of PPSU materials, each designed for specific applications and offering unique characteristics. Some of the most common types of PPSU materials include:
- Flame-retardant PPSU
This type of PPSU meets specific flame-retardant standards like UL94 V-0 or IEC 60695-11-5, making it ideal for electrical components, wiring, and cable insulation where fire safety is a priority. - UV-stabilized PPSU
Designed to resist degradation from UV light, this type is perfect for outdoor equipment, automotive components, and medical devices exposed to sunlight or harsh weather conditions.
- Low-temperature PPSU
Built for applications in extreme cold (below -50°C or -58°F), it offers enhanced flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for cryogenic storage tanks, low-temperature sensors, and refrigeration systems. - Conductive PPSU
Incorporates conductive materials such as carbon fibers or metal powders to improve electrical conductivity. It is commonly used in EMI shielding, antennas, and various sensor applications. - High-temperature PPSU
Engineered to perform in high-temperature environments above 250°C (482°F), this PPSU is perfect for heat exchangers, combustion systems, and high-temperature filtration applications. - Radiation-crosslinked PPSU
Crosslinked through radiation, this PPSU type offers enhanced resistance to chemicals, fuels, and harsh environments, making it suitable for use in fuel cells, batteries, and chemical processing equipment. - General-purpose PPSU
A versatile, all-around material with a balance of mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. It is widely used in medical devices, aerospace components, and industrial applications. - Antistatic PPSU
Designed to reduce static electricity buildup, this PPSU type is essential in applications like electronics, textiles, and pharmaceuticals where electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a concern.

What Are the Characteristics of Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU)?
Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU) is a high-performance plastic known for its exceptional blend of properties, such as:
- Low Water Absorption:
PPSU is highly resistant to water absorption, maintaining its shape and structural integrity even when exposed to moisture. - High Dielectric Strength:
With impressive dielectric strength, PPSU can withstand high electrical voltages before breaking down, making it suitable for electrical applications. - Minimal Outgassing:
PPSU emits fewer volatile compounds compared to other plastics, preventing the release of unwanted chemicals in sealed environments. - Excellent Fuel and Chemical Resistance:
PPSU is highly resistant to fuel and chemicals, including gasoline, diesel, and aviation fuel, making it ideal for tough applications in harsh environments. - Low Thermal Expansion:
PPSU maintains its size even under extreme temperature changes, thanks to its low thermal expansion properties. - Biocompatibility:
Due to its biocompatibility, PPSU is a reliable choice for medical devices and healthcare applications. - Electrical Insulation:
With strong electrical insulation capabilities, PPSU is ideal for use in applications that require protection from electrical currents. - Versatile Processability:
PPSU can be processed through various methods such as injection molding, extrusion, and machining, making it adaptable to diverse industrial needs. - UV and Radiation Resistance:
PPSU is resistant to both ultraviolet (UV) light and radiation, making it suitable for outdoor, aerospace, and nuclear applications. - Impact Resistance:
PPSU’s superior impact resistance makes it a durable choice for environments where parts are subject to physical stress.
What Are the Properties of PPSU?
PPSU is an amorphous thermoplastic that is typically categorized into three types based on its properties: PSU/PSF, PPSU, and PES.
Property | Polyphenylsulfone (BPA Type) | Polyphenylsulfone | Polyethersulfone |
| PSU/PSF | PPSU | PES | |
| Heat Distortion Temperature (℃) | 174 | 207 | 204 |
| Relative Density | 1.24 | 1.29 | 1.37 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 70 | 94 | 86 |
| Elongation (%) | 50–60 | 60–120 | 40–80 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 280 | 150 | 130 |
| Flexural Strength (MPa) | 107 | 127 | 136 |
| Impact Strength (Notched) (KJ/m²) | - | 690 | 23 |
| Hardness (Rockwell) | M69 (R120) | M110 | M88 |
| Flexural Modulus, 23℃ (GPa) | 2.7 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
| Tensile Modulus, 23℃ (GPa) | 2.2 | 2.4 | - |
| Specific Heat (J/Kg·K) | 1004.83 | - | - |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient 10cm/cm (℃) | 1.7 | - | - |
| Heat Distortion Temperature (1.86 MPa) (℃) | 174 | 207 | 203 |
| Heat Distortion Temperature (0.45 MPa) (℃) | 181 | - | 210 |
| Maximum Continuous Service Temperature (℃) | 140 | 180 | 180 |
| Electrical Resistivity 23℃ (Ω·cm) | 5×10 | 3.2×10 | 10 |
| Dielectric Strength (KV/mm) (Short-term) | 3 | 6.3 | 16 |
| Dielectric Constant 60Hz | 3.07 | 3.94 | 3.5 |
| Dielectric Constant 1000Hz | 3.06 | 3.24 | 3.5 |
| Dielectric Loss 60Hz | 0.0008 | - | - |
| Dielectric Loss 1000Hz | 0.001 | - | - |
| Water Absorption 24h, 3.2mm Sample (%) | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.43 |
What Are the Advantages of PPSU Injection Molding?
PPSU (Polyphenylsulfone) is a high-performance thermoplastic recognized for its outstanding thermal and mechanical properties, making it a top choice for injection molding across various industries. Here are the key reasons why PPSU is so highly valued for injection molding:
- High Mold Cost: Since PPSU is a high-performance material, it demands specialized molds to achieve the desired properties in the final parts. This means significant upfront costs for molds, which can be a barrier for some manufacturers.
- High Difficulty in Processing: PPSU injection molding’s high viscosity makes it challenging to produce high-precision or complex parts, often necessitating the use of additives or specific molding methods to improve fluidity.
- High Material Cost: PPSU is relatively expensive due to its high-performance characteristics and production challenges. While it offers excellent mechanical properties, it is not as widely available as materials like ABS or PC, which limits material options and increases overall production costs.
- High Melting Point: PPSU has a very high melting point, which requires precise heating before injection molding to ensure it flows properly. This high-temperature requirement adds complexity and demands careful temperature control during processing.
- Limited Post-Molding Operations: Due to its sensitivity to heat, moisture, and chemicals, PPSU can be easily damaged after molding. This limits post-molding processes like machining, grinding, or assembly, making it more difficult to work with once formed.
- High Warpage: PPSU tends to warp significantly during cooling, making it challenging to control during the molding process. This warpage may require design adjustments or additional steps to mitigate.
- Limited Recycling Options: PPSU’s complex chemical structure and high molecular weight make it difficult to recycle. This results in environmental concerns and adds to material waste.
- High Viscosity: PPSU’s high viscosity makes it difficult to perform complex molding operations. The material resists flowing smoothly, making precision molding and processing a challenge.
- Long Cycle Time: The high viscosity of PPSU means it takes longer to flow during the injection molding process. This increases production time and costs, slowing down the overall manufacturing process.
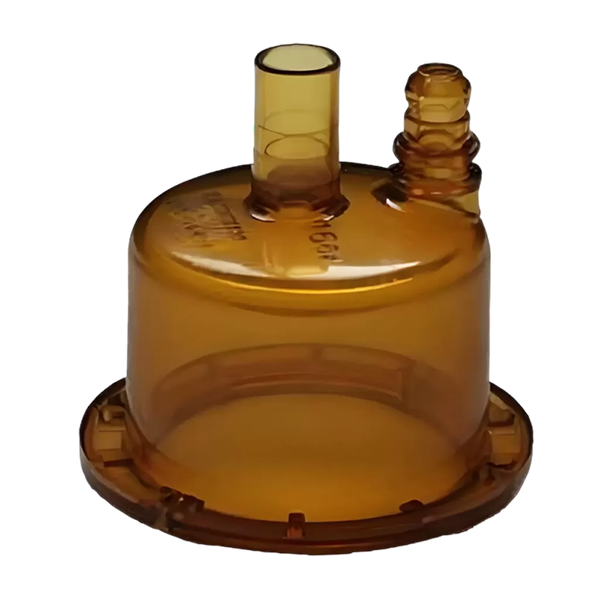

Can PPSU be Injection Molded?
PPSU (Polyphenylsulfone) can be successfully injection molded with the right equipment and processing conditions. Known for its superior thermal stability, mechanical strength, and high chemical resistance, PPSU is ideal for demanding applications across industries like automotive, medical devices, and electronics.
In the injection molding process, molten PPSU is injected into a custom-designed mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies, taking on the desired shape. This process enables the production of highly durable parts with precise dimensions and excellent performance in challenging environments.
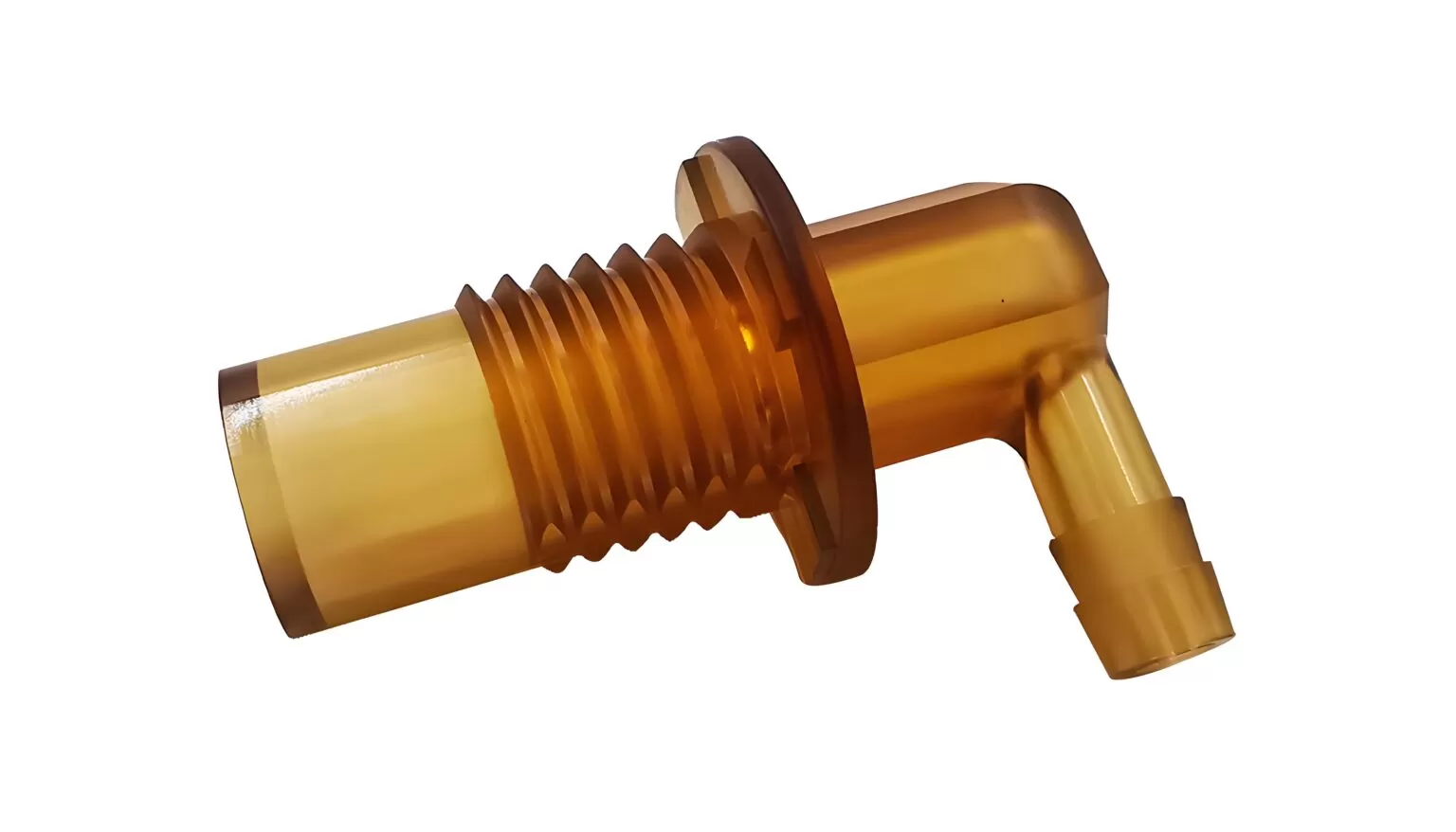

How to Perform PPSU Injection Molding: A Step-by-Step Guide

PPSU injection molding is a widely used method for creating durable, high-performance parts from thermoplastic materials. This guide will walk you through the entire process, from preparation to completion, ensuring you achieve optimal results with PPSU.
- Injection Molding Process:
a. Machine Setup: Use standard injection molding machines with a clamp tonnage around 5.5 kN/cm² (4 T/in²). The screw should have a compression ratio between 1.8:1 and 2.4:1, with a length-to-diameter (L/D) ratio of 18:1 to 22:1. Opt for a ring-check valve instead of a ball-check valve for improved performance.
b. Injection Parameters: Set appropriate injection speed, pressure, and temperature. For PPSU, typical melt temperatures range from 350°C to 400°C (662°F to 752°F). Injection cycle times typically range from 15 to 60 seconds, depending on the part size and complexity.
c. Mold Filling: Ensure the injection speed is controlled to avoid issues like splay or short shots. Monitor the melt flow and adjust settings to ensure the mold cavity is completely filled. - Cooling and Ejection:
a. Allow the part to cool slowly and evenly to minimize warping and distortion.
b. Use a controlled ejection process to avoid part damage and ensure smooth removal from the mold.
c. Consider incorporating a demolding system to reduce the risk of part damage during ejection. - Post-Molding Processing:
a. Inspect the molded parts for any defects or quality issues.
b. Clean and dry the parts thoroughly to remove any residual material or dirt.
c. Consider applying a surface finish, such as painting or chemical treatment, to enhance the part’s appearance and performance. - Quality Control:
a. Perform regular quality control checks to ensure the parts meet the required specifications and standards.
b. Continuously monitor the processing conditions and make adjustments as needed to maintain consistent part quality.
c. Implement a quality control program to track and analyze part performance, ensuring high-quality standards are met throughout production.
What Are the Challenges of PPSU Injection Molding?
PPSU is a polymer known for its high temperature resistance, chemical stability, rigidity, and dimensional stability. These features make it a popular choice for industries such as medical equipment, electronics, automotive, and food-grade products. However, despite its many advantages, the injection molding of PPSU presents certain challenges, as outlined below:
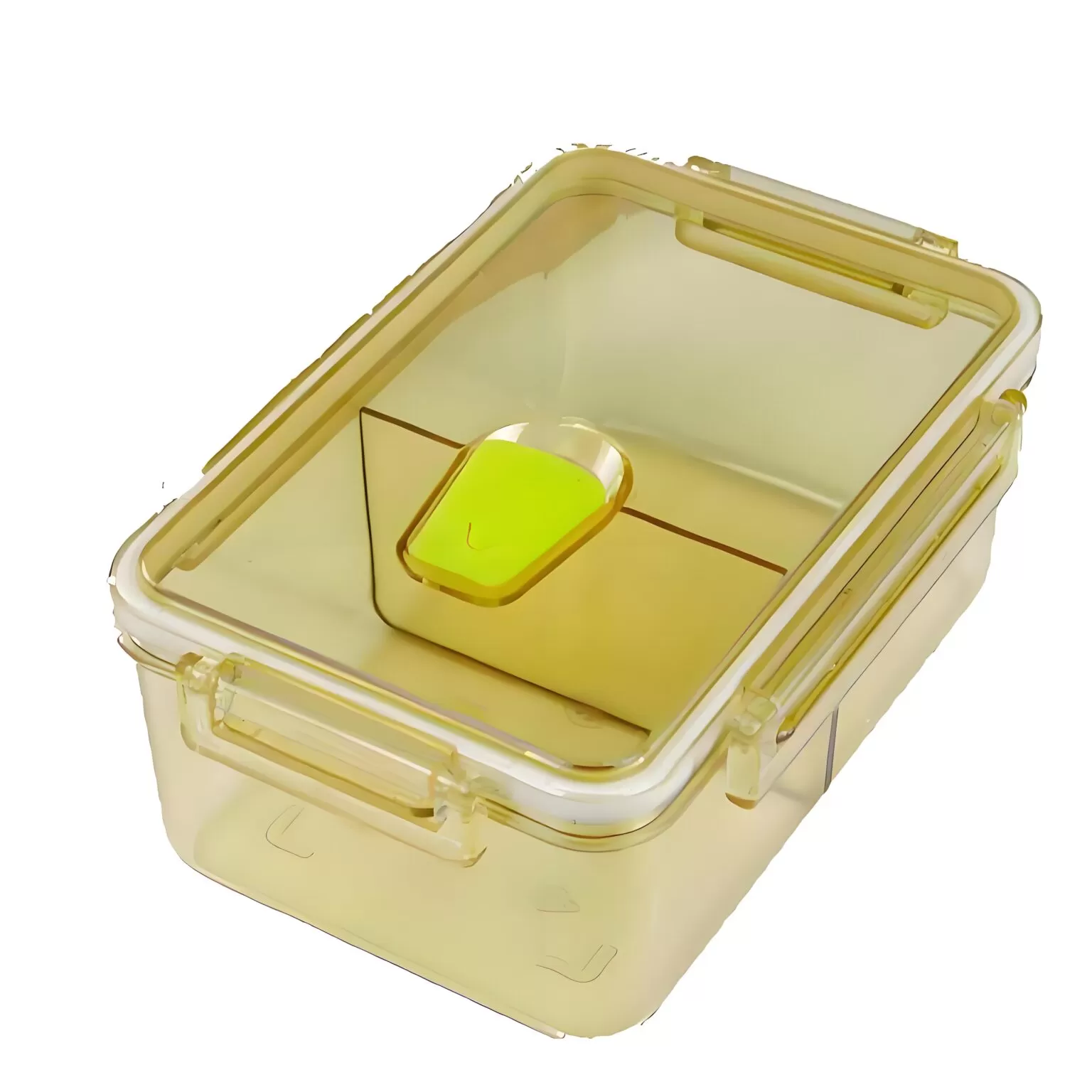

What are the Applications of PPSU Injection Molding?
PPSU (Polyphenylsulfone) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional heat and pressure resistance, making it ideal for injection molding. It’s used across various industries because of its ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh chemicals.

Here are some of the most common applications of PPSU injection molding:
- Food Processing: PPSU is widely used in food processing equipment such as valves, pumps, and pipes due to its ability to resist corrosion, withstand high temperatures, and handle chemicals without degradation.
- Aerospace: In the aerospace sector, PPSU is utilized to produce lightweight, high-performance parts, including components for airplanes, satellites, and engines, thanks to its durability and resistance to extreme conditions.
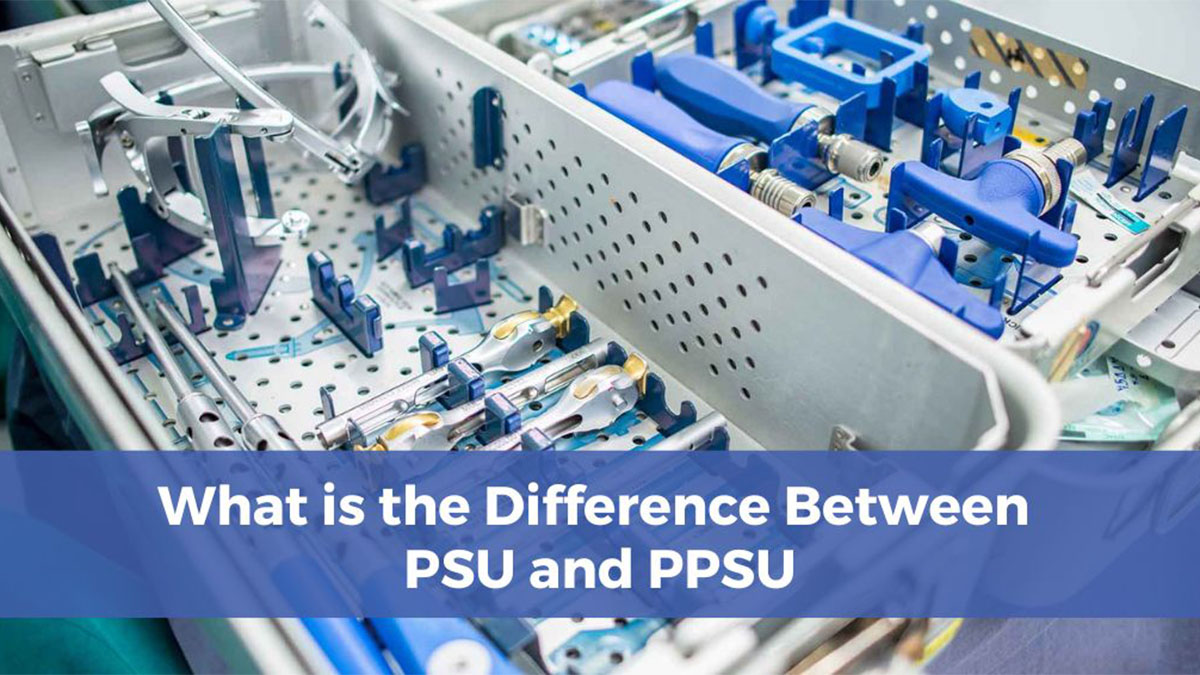
- Medical Devices: PPSU’s biocompatibility and resistance to chemicals make it a top choice for medical devices, including surgical instruments, diagnostic tools, and implantable devices that require sterilization and long-term performance.
- Automotive: The automotive industry relies on PPSU for high-performance parts like fuel injectors, engine components, and brake parts, where its heat resistance and mechanical strength are essential.
- Industrial Equipment: PPSU’s resistance to chemicals, high temperatures, and mechanical stress makes it ideal for industrial applications such as pumps, valves, and gears that need to perform under tough conditions.
- Consumer Products: From household appliances to electronics and sporting goods, PPSU is favored for its toughness, chemical resistance, and appealing aesthetic qualities, making it a versatile material for a range of consumer products.
- Chemical Processing: PPSU is commonly used in chemical processing equipment such as reactors, tanks, and pipes due to its excellent resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and high temperatures, ensuring long-term durability and performance.
- Oil and Gas: In the oil and gas industry, PPSU is employed in parts like pumps, valves, and pipes, where its ability to resist corrosion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures makes it ideal for challenging environments.
- Pharmaceutical: PPSU is used in pharmaceutical equipment, including reactors, tanks, and pipes, because of its resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and high temperatures, making it a reliable choice for this demanding industry.
- Biomedical: PPSU is favored in biomedical applications, including surgical instruments, implantable devices, and diagnostic equipment, due to its biocompatibility, resistance to chemicals, and sterilizability, ensuring safety and effectiveness in medical environments.
- Hydrogen electrolyzer: PPSU is widely used in hydrogen electrolysis due to its excellent chemical resistance against corrosion, high temperature stability, and good mechanical strength, making it ideal for components like seals and membranes.