Plastic injection molding is a commonly employed manufacturing technique that consists of injecting heated plastic into a mold to produce various components and products. This technique is known for its efficiency and ability to produce high volumes of identical items with precision. It’s essential in industries ranging from automotive to consumer goods, allowing for intricate designs and complex geometries that would be challenging to achieve with other manufacturing methods.
Choosing the right plastic material is crucial in this process, as different materials possess distinct properties that influence the performance, durability, and cost of the final product.
Factors such as strength, flexibility, chemical resistance, and thermal stability can vary significantly among materials, making it important to select one that aligns with the specific requirements of the application. By understanding the different types of plastics available for injection molding, manufacturers can optimize their products for functionality, aesthetics, and longevity.
1. Polypropylene (PP)
-
Properties:
Polypropylene (PP) is a lightweight and versatile thermoplastic known for its excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. It has a high melting point, making it suitable for applications that require thermal stability.
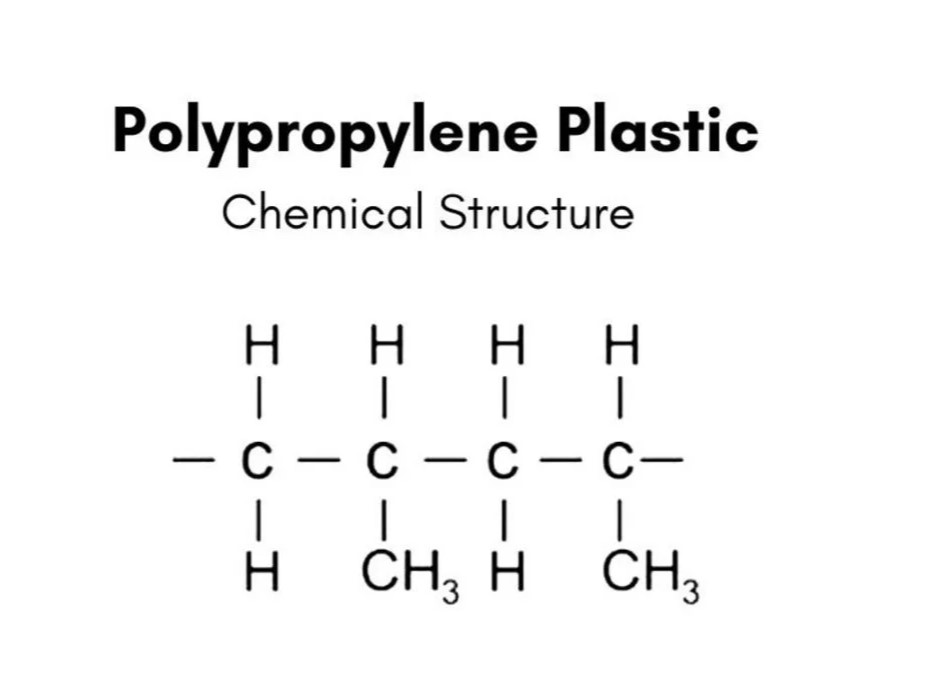
-
Common Uses:
PP is widely used across various industries, including:
- Packaging: Bottles, containers, and films due to its durability and moisture resistance.
- Automotive Parts: Components such as dashboards, interior trim, and bumpers.
- Household Goods: Items like storage boxes, furniture, and kitchenware.
-
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: PP is one of the most affordable plastics available, making it an attractive choice for high-volume production.
- Recyclable: It is recyclable, which contributes to sustainability efforts and reduces environmental impact.
- Versatile Applications: Its combination of properties allows it to be molded into a wide range of shapes and forms, catering to diverse market needs.
2. Polyethylene (PE)
-
Properties:
Polypropylene (PP) is known for its lightweight nature, making it easy to handle and transport. It offers excellent chemical resistance, allowing it to withstand exposure to a variety of substances without degrading. Additionally, PP is flexible, which makes it suitable for applications requiring some degree of bending or stretching.
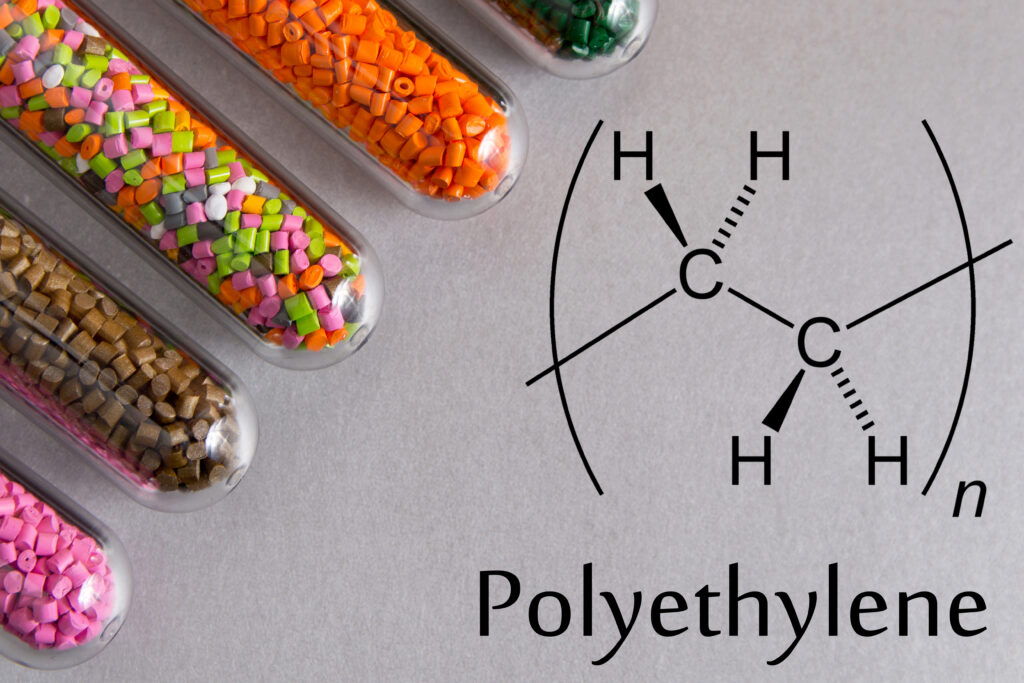
-
Common Uses:
PP is widely utilized in various industries. Its common applications include:
- Packaging: Used for containers, bottles, and food packaging due to its barrier properties.
- Automotive Parts: Found in components such as bumpers, dashboards, and interior trim.
- Household Goods: Commonly used for storage bins, furniture, and kitchen utensils.
-
Advantages:
One of the key benefits of polypropylene is its cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for manufacturers looking to keep production costs low. Additionally, PP is recyclable, which supports sustainability efforts and reduces environmental impact. Its versatile properties allow for a wide range of applications, making it a staple material in plastic injection molding.
3. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)

-
Properties:
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a tough thermoplastic known for its excellent impact resistance and durability. It exhibits good heat resistance, making it suitable for applications where temperature fluctuations may occur. Additionally, ABS maintains good dimensional stability, ensuring that molded parts retain their shape and size over time.
-
Common Uses:
ABS is widely employed in various sectors, including:
- Consumer Electronics: Used in casings and housings for devices like televisions, computers, and smartphones due to its aesthetic appeal and durability.
- Automotive Interiors: Commonly found in dashboards, door panels, and other interior components, providing a balance of strength and lightweight design.
- LEGO Bricks: The iconic building blocks are made from ABS, allowing for precise molding and vibrant colors.
-
Advantages:
One of the standout features of ABS is its excellent surface finish, which allows for high-quality visual appeal in final products. Additionally, it is highly paintable, enabling manufacturers to create customized designs and colors without compromising the material’s integrity. Its combination of toughness, heat resistance, and versatility makes ABS a preferred choice in many injection molding applications.
4. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)

-
Properties:
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) can be formulated to be either rigid or flexible, making it highly versatile. It exhibits good chemical resistance, which allows it to withstand exposure to various substances without degrading.
-
Common Uses:
PVC is widely used across multiple industries, including:
- Pipes: Commonly used in plumbing and construction for its durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Medical Devices: Employed in products like IV bags and tubing due to its safety and reliability.
- Electrical Cable Insulation: Used to insulate electrical wires, providing safety and protection against environmental factors.
-
Advantages:
PVC is known for its durability and resistance to environmental degradation, including UV light and moisture. This makes it suitable for outdoor applications and long-term use. Its versatility allows for a range of formulations tailored to specific applications, enhancing its appeal in the market.
5. Polystyrene (PS)
-
Properties:
Polystyrene (PS) is a rigid and transparent thermoplastic that is easy to mold. It has a smooth surface finish and can be produced in various forms, including solid and foamed structures.
-
Common Uses:
PS finds applications in a variety of products, such as:
- Disposable Cutlery: Commonly used for forks, spoons, and plates due to its cost-effectiveness.
- Packaging: Employed in packaging materials to protect fragile items.
- Toys: Used in many toy products, including models and figurines.

-
Advantages:
One of the primary benefits of polystyrene is its cost-effectiveness, making it an affordable option for mass production. Additionally, PS has good insulation properties, making it suitable for thermal applications and protecting sensitive items during transport.
6. Nylon (Polyamide)
-
Properties:
Nylon, also known as polyamide, is characterized by its high strength and wear resistance. It has excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for a range of challenging environments.
-
Common Uses:
Nylon is utilized in numerous applications, including:

- Gears: Often used in mechanical components due to its strength and durability.
- Bearings: Employed in various machinery where low friction and high wear resistance are required.
- Automotive Parts: Commonly found in under-the-hood components that demand high performance and reliability.
-
Advantages:
Nylon offers excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and flexibility. Its low friction characteristics make it ideal for moving parts, reducing wear and enhancing performance over time. This makes nylon a preferred choice in both industrial and consumer applications.
7. Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
-
Properties:
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are unique materials that combine the elasticity of rubber with the processing ease of plastics. They exhibit rubber-like flexibility while maintaining the ability to be molded and reshaped through standard plastic processing techniques.
-
Common Uses:
TPEs are widely used in various applications, including:

- Seals: Employed in automotive and industrial applications to provide effective sealing solutions.
- Gaskets: Used in various machinery and equipment to prevent leaks and maintain performance.
- Flexible Components: Found in consumer products like grips, handles, and soft-touch surfaces.
-
Advantages:
One of the primary advantages of TPEs is their ability to combine the benefits of both rubber and plastic. They offer excellent elasticity and flexibility, along with the ease of processing typical of thermoplastics. This versatility makes TPEs ideal for applications that require both durability and comfort, leading to a wide range of innovative products across multiple industries.
Comparison of 7 Plastic Material Types Used in Injection Molding
Here is a table containing all seven types of plastics illustrated above that tells you their characteristics, applicability, and advantages in a simple and intuitive way:
| Material | Properties | Common Uses | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Lightweight, chemical resistance, flexibility | Packaging, automotive parts, household goods | Cost-effective, recyclable |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Tough, heat-resistant, good dimensional stability | Consumer electronics, automotive interiors, LEGO bricks | Excellent surface finish, paintability |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Rigid or flexible, good chemical resistance | Pipes, medical devices, electrical cable insulation | Durable, resistant to environmental degradation |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Rigid, transparent, easy to mold | Disposable cutlery, packaging, toys | Cost-effective, good insulation properties |
| Nylon (Polyamide) | High strength, wear resistance, chemical resistance | Gears, bearings, automotive parts | Excellent mechanical properties, low friction |
| Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | Rubber-like flexibility, plastic processing capabilities | Seals, gaskets, flexible components | Combines benefits of rubber and plastic |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Durable, impact-resistant, moisture-resistant | Containers, toys, plastic bags | Versatile, available in various densities (HDPE, LDPE) |
Conclusion
Selecting the right plastic material for injection molding is crucial to the success of any manufacturing project. The properties of different materials can significantly impact the performance, durability, and overall quality of the final product. Understanding the unique characteristics of each material allows manufacturers to make informed decisions that align with their specific application requirements.
For those navigating this process, consulting with material experts can provide valuable insights tailored to individual needs. These professionals can help identify the best material options, ensuring optimal functionality and cost-effectiveness for your projects.
Contact Us
If you’re interested in learning more about plastic injection molding solutions, we invite you to explore the resources available at KingStar Mold. Our team is here to assist you in selecting the right materials and processes for your manufacturing needs.



