PLA Injection Molding
KingStar Mold’s Advice on Choosing Your PLA Product Supplier

PLA injection molding is used in a wide range of industries to create eco-friendly, high-performance products with biodegradable properties.
| PLA Category | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard PLA | Commonly used, biodegradable, made from renewable resources like cornstarch. | Packaging, disposable items, consumer goods such as custom coolers, wholesale pill organizers etc. |
| High-Heat PLA (HTPLA) | Modified for improved heat resistance, maintaining shape and strength at higher temperatures. | Automotive parts, electronics enclosures, kitchenware |
| PLA Blends | PLA mixed with other materials for enhanced properties like flexibility or heat tolerance. | Food packaging, medical devices, specialized parts |
| Toughened PLA (PLA-T) | Modified for enhanced toughness and impact resistance. | Household products, industrial parts, consumer electronics |
| PLA Composites | PLA combined with materials like bamboo, wood fibers, or carbon fiber for strength and aesthetic qualities. | Eco-friendly furniture, construction materials, decorative items |
| PLA for 3D Printing | Formulated for 3D printing, offering low warping and easy adhesion. | Prototypes, custom parts, models |
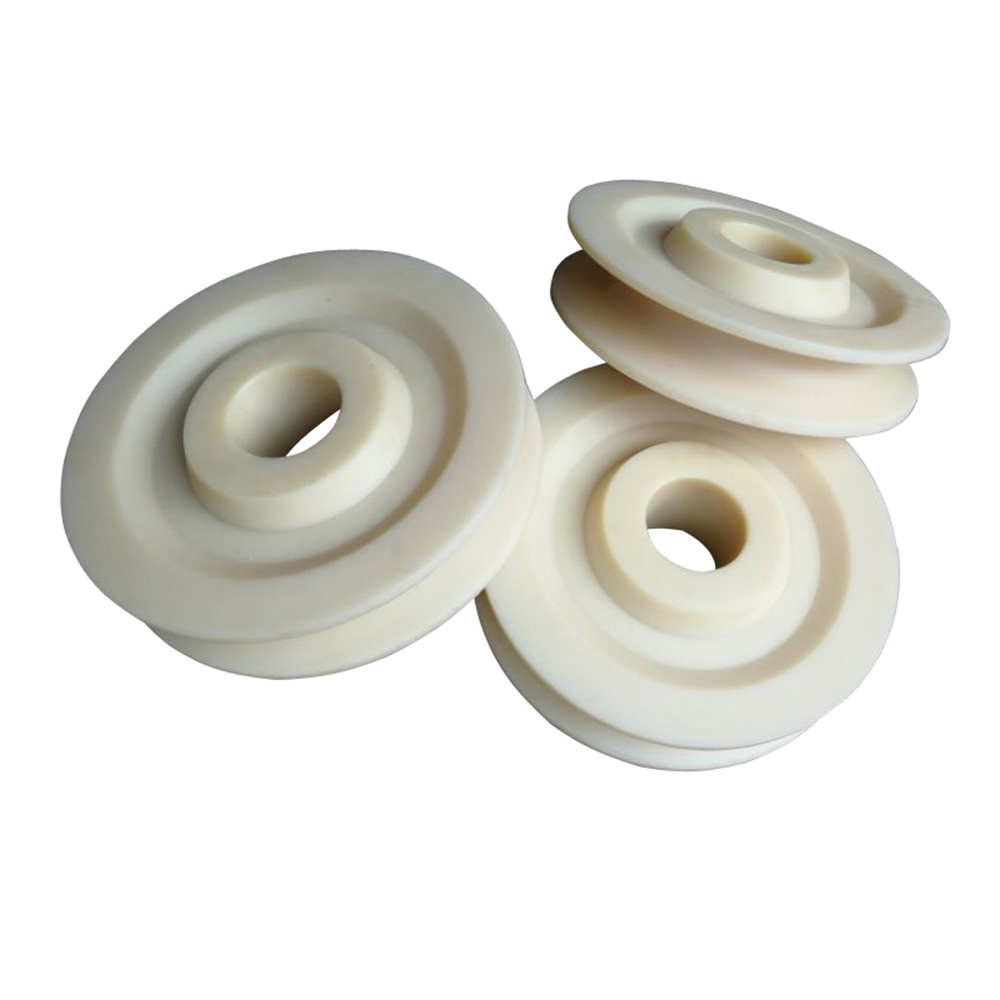
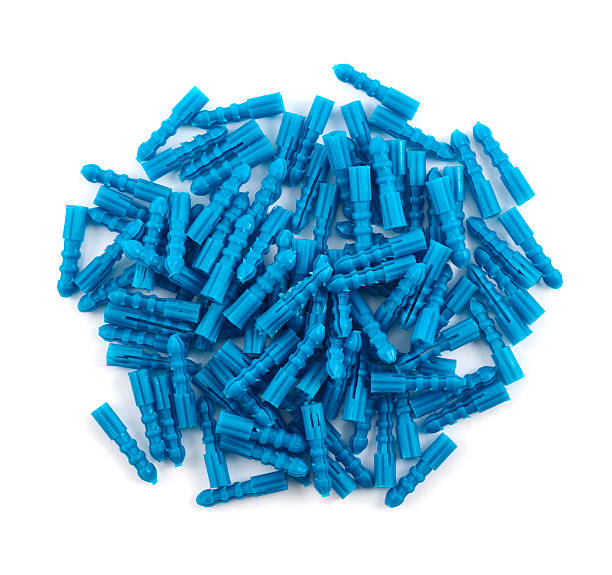
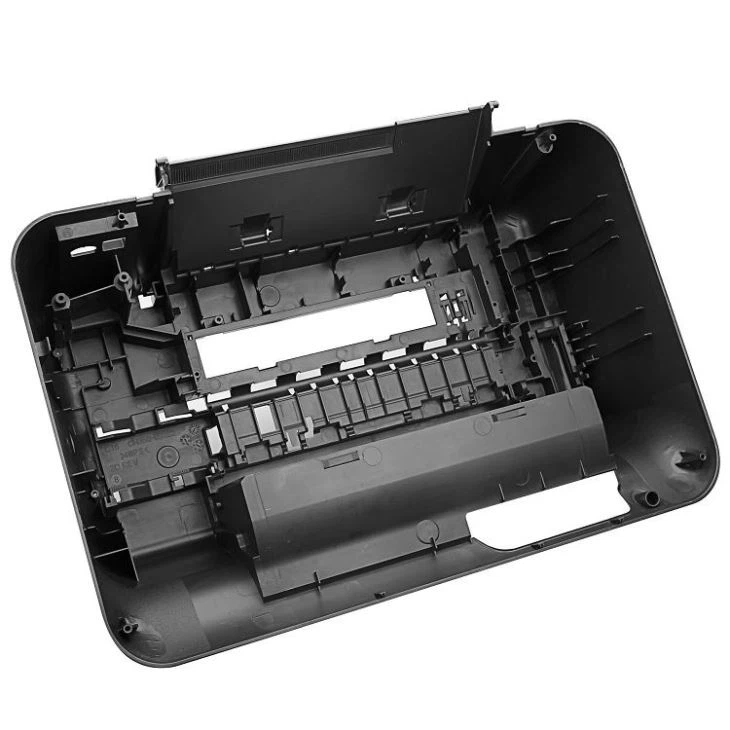




Expanding the Horizons of PLA Injection Molding
At KingStar Mold, we are committed to driving innovation in PLA injection molding by developing sustainable, high-performance solutions that meet the evolving needs of industries like packaging, medical, and consumer goods.
Sustainable Packaging Solutions
KingStar Mold is exploring eco-friendly packaging using PLA injection molding, offering biodegradable alternatives for food, cosmetics, and other products. We help clients reduce plastic waste with innovative, sustainable packaging designs.
Medical Applications
We apply PLA injection molding in the medical sector, producing biocompatible, biodegradable products like medical device housings and surgical tools. Our focus on precision ensures safe, sustainable solutions for the healthcare industry.
Benefits of PLA Injection Molding

Environmental Sustainability
PLA injection molding offers a biodegradable alternative to traditional plastics, reducing environmental impact. As PLA is derived from renewable resources like cornstarch, it helps minimize plastic waste and supports eco-friendly production.
Cost-Effective Manufacturing
PLA injection molding is an affordable solution for both small and large production runs. Its ease of processing and quick turnaround times help lower production costs, making it an attractive option for sustainable product development.
Versatile Applications
PLA is highly versatile and can be molded into a wide range of shapes and sizes for various industries. From packaging to medical devices, PLA’s flexibility makes it suitable for numerous applications, meeting both functional and aesthetic needs.
Frequently Asked Questions

Yes, KingStar Mold specializes in PLA injection molding for a variety of industries, including consumer goods, packaging, and medical applications.
No, PLA has a relatively low melting point and can deform or lose strength under high heat. It is better for low-heat applications like packaging and consumer goods.
PLA is environmentally friendly, biodegradable, and cost-effective for small runs. It is also easy to process and produces less greenhouse gas during manufacturing.