Resources for The Complete Guide to PEI Injection Molding

What is PEI?
PEI (Polyetherimide) is a durable, high-performance plastic valued for its remarkable heat resistance, strength, and chemical stability. It excels in maintaining mechanical and electrical properties under high temperatures, tolerating up to 200°C short-term and 180°C long-term. These qualities make it a preferred material for applications in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical industries.
Its molecular structure, comprising polyether and imide groups, contributes to its robust performance. The imide groups enhance its resistance to heat, chemicals, and electricity, while the polyether groups provide toughness and impact resistance.
What are the characteristics of Polyetherimide (PEI)?
PEI (Polyetherimide) offers a range of impressive qualities, making it suitable for diverse applications:

What are the properties of PEI?
| Property | Metric | English |
| Density | 0.0500 - 1.90 g/cc | 0.00181 - 0.0686 lb/in³ |
| Filler Content | 5.00 - 50.0 % | 5.00 - 50.0 % |
| Water Absorption | 0.0150 - 1.30 % | 0.0150 - 1.30 % |
| Moisture Absorption at Equilibrium | 0.000 - 1.30 % | 0.000 - 1.30 % |
| Water Absorption at Saturation | 0.100 - 2.90 % | 0.100 - 2.90 % |
| Additive Loading | 10.0 - 40.0 % | 10.0 - 40.0 % |
| Particle Size | 15.0 µm | 15.0 µm |
Viscosity | 3.00 - 87.0 cP @Temperature 220 - 360 °C | 3.00 - 87.0 cP @Temperature 220 - 360 °C |
| 3.00 - 87.0 cP @Load 2.16 - 10.0 kg | 3.00 - 87.0 cP @Load 2.16 - 10.0 kg |
|
| Maximum Moisture Content | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Linear Mold Shrinkage | 0.000 - 0.0230 cm/cm | 0.000 - 0.0230 in/in |
| Linear Mold Shrinkage, Transverse | 0.00100 - 0.0240 cm/cm | 0.00100 - 0.0240 in/in |
| Melt Flow | 1.80 - 113 g/10 min | 1.80 - 113 g/10 min |
| Tensile Strength, Ultimate | 1.00 - 650 MPa | 145 - 94300 psi |
| Tensile Strength, Yield | 20.0 - 255 MPa | 2900 - 37000 psi |
| Elongation at Break | 0.500 - 110 % | 0.500 - 110 % |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.0500 - 1.00e+18 ohm-cm | 0.0500 - 1.00e+18 ohm-cm |
| Surface Resistance | 1.00 - 5.80e+16 ohm | 1.00 - 5.80e+16 ohm |
| Dielectric Constant | 2.52 - 6.80 | 2.52 - 6.80 |
| Dielectric Strength | 4.33 - 244 kV/mm | 110 - 6200 kV/in |
| Transmission, Visible | 58.0 - 90.0 % | 58.0 - 90.0 % |
| Processing Temperature | 60.0 - 410 °C | 140 - 770 °F |
| Nozzle Temperature | 173 - 421 °C | 343 - 790 °F |
| Adapter Temperature | 270 - 335 °C | 518 - 635 °F |
| Die Temperature | 260 - 360 °C | 500 - 680 °F |
| Melt Temperature | 107 - 427 °C | 225 - 801 °F |
| Head Temperature | 290 - 360 °C | 554 - 680 °F |
| Mold Temperature | 37.8 - 399 °C | 100 - 750 °F |
| Drying Temperature | 60.0 - 152 °C | 140 - 305 °F |
| Moisture Content | 0.0200 - 0.0400 % | 0.0200 - 0.0400 % |
| Dew Point | -28.9 °C | -20.0 °F |
| Injection Pressure | 82.7 - 124 MPa | 12000 - 18000 psi |
Comparison of PEI with Other High Temperature Injection Molding Materials
Polyetherimide (PEI) is often compared to other materials with good-performance like Polyamide 46 (PA46), Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP), Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU), Polyimide (PI), Polyphthalamide (PPA), and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK). Here’s a detailed comparison of these materials to help you figure out which one is best for your specific application needs.

Can PEI Be Used As Injection Molding Material?
You can certainly use it as injection molding material.
PEI has a high melting point, which can make it tricky to injection mold. But modern injection molding machines and mold designs have come a long way to handle the special needs of PEI.PEI is a high-performance thermoplastic with outstanding characteristics ideal for injection molding, including:
What are the basic conditions for PEI Injection Molding?
PEI is a fantastic plastic known for its ability to handle high temperatures, corrosion, and fatigue. To make high-quality PEI parts, you’ll need to follow these guidelines:
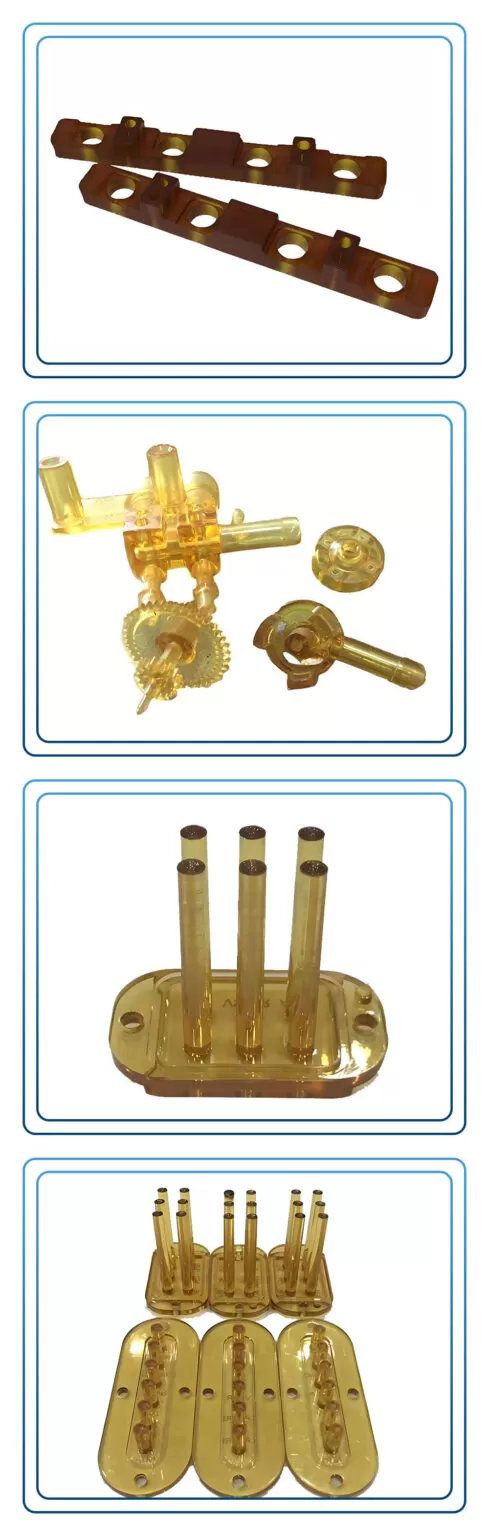
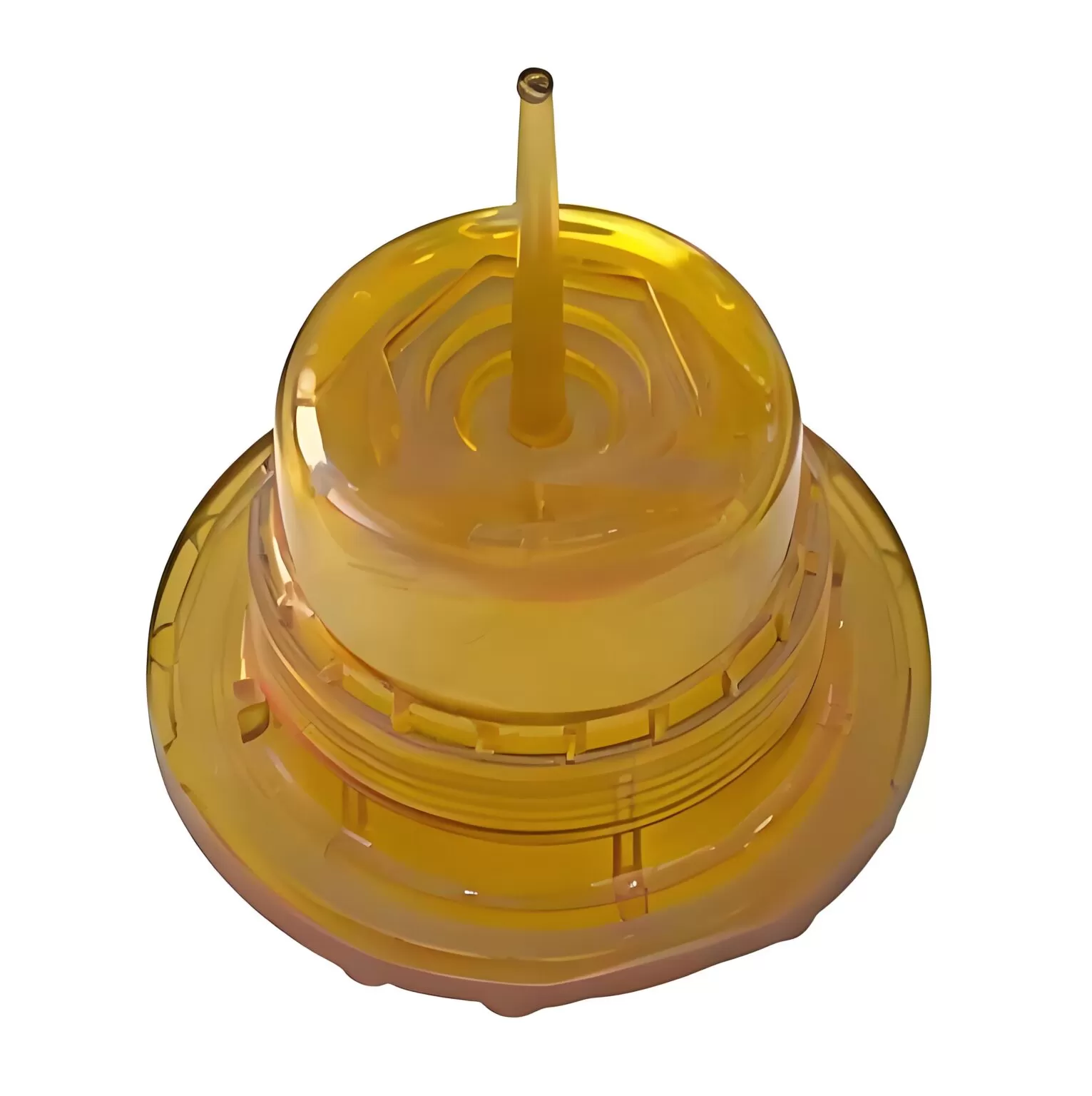


Resources for the Comprehensive Guide to PEI Injection Molding Manufacturing
What are the precautions for PEI Injection Molding?
When performing injection molding with PEI (Polyetherimide), it’s important to pay close attention to several factors due to its high-performance nature. Here are key considerations to ensure a successful molding process:


What are the advantages of PEI Injection Molding?
Thanks to its high temperature resistance and excellent mechanical properties, PEI injection molding offers several advantages. Here lists several key benefits:
Disadvantages of Using PEI (Polyetherimide) for Injection Molding Processes
Although PEI injection molding offers many benefits, it also comes with some drawbacks and challenges. Here are a few things to consider:
What are the Applications of PEI Injection Molding?
PEI injection molding is a versatile process used across various high-end industries, thanks to PEI’s exceptional properties such as temperature stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance. Common applications include: