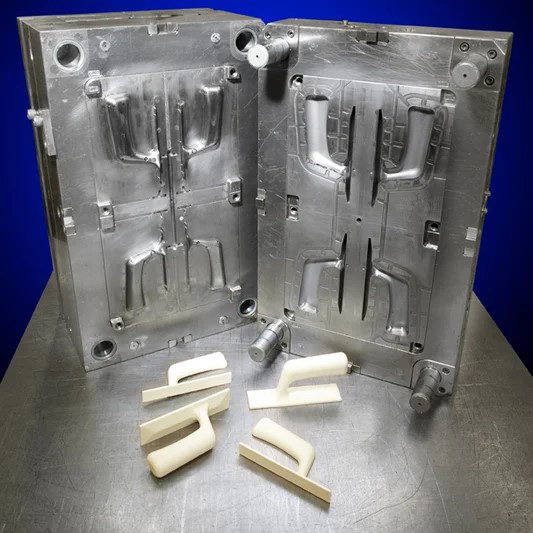
Mold Making Service
Specialized in complex mold designs with quick turnaround, as fast as 3 days.
- Comprehensive solutions: design, manufacturing, repair, and more.
- Competitive pricing with guaranteed high-quality results.
- Commitment to innovation and efficiency in every project.
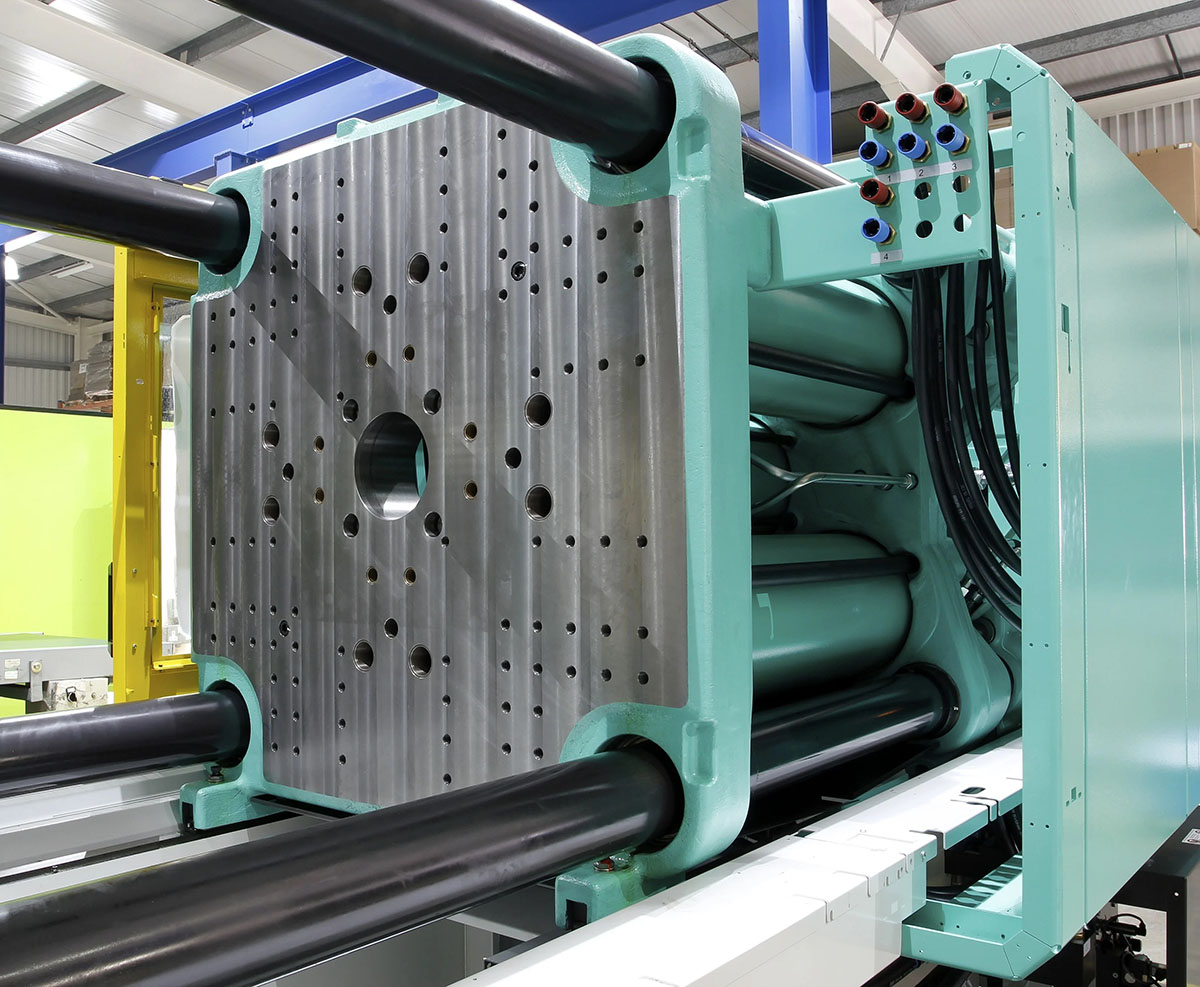
Mold Making Process
1. Initial Design & Conceptualization

2. Mold Design & CAD Modeling

3. Mold Flow Analysis

4. Material Selection

5. Mold Base Construction

6. Core & Cavity Machining
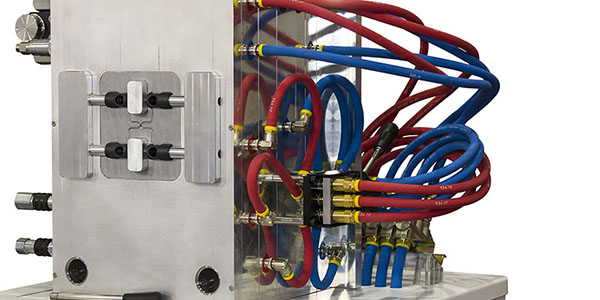
7. Cooling System Design

8. Injection System Setup

9. Assembly of Mold Components

10. Prototype Molding

11. Mold Refining & Adjustment

12. Final Inspection & Delivery
Start Your Project with a Click
Challenges You Might Be Facing
In the past, you may have encountered the following issues with your current suppliers:
Excessive Molding Defects
Defects like short shots, flow lines, burn marks, and sink marks can impact part quality and consistency.
Hidden Cost Increases
Long injection cycle times and poor communication lead to unexpected delays and rising costs, affecting your bottom line.

Frequent Mold Revisions
Frequent mold repairs and adjustments due to design or process issues often delay project timelines, leading to inefficiencies.
Missed Deadlines
Suppliers consistently push back delivery dates with numerous excuses, leaving you with delayed production and missed commitments.
How KingStar Mold Solved the Problem
At KingStar Mold, we focus on proactive communication and swift problem-solving to ensure smooth project execution and client satisfaction.
Design Process
We ensure rigorous mold design to maximize efficiency, with most molds being ready for mass production after just one trial.
- Proactive Problem Analysis: We analyze material properties and product feasibility, considering factors like wall thickness, deformation, and gate placement to identify potential issues early.
- Customer-Centric Communication: We maintain close communication with our clients to fully understand their functional needs and product requirements, including bonding lines, surface finishes, and other critical specifications.
- Comprehensive Quality Control: Our design process includes a thorough examination system: pre-design program structure discussions, self-checks by designers during the design phase using a detailed checklist, and post-design reviews with the manufacturing team.


Quality Assurance
We ensure quality at every stage of the process to proactively identify potential issues before mass production begins.
- Comprehensive Quality Inspections: Inspections are performed at each stage—raw materials, processing, and final molding—to detect and address problems early.
- Traceable Inspection Reports: Each item undergoes detailed quality checks, with complete inspection reports for full traceability.
- Premium Materials & Standards Compliance: We use high-quality raw materials and strictly adhere to SPI mold classification standards to ensure the best value and performance for your products.
Delivery Time
We ensure timely delivery by keeping you updated at every step of the process.
- Project Management: Each project is assigned a dedicated project manager who strictly monitors the schedule to ensure timely completion.
- Regular Progress Updates: Weekly progress reports and mold photos are provided to keep you informed of the status of your project.
- Real-Time Mold Trials: We offer online mold trial videos, allowing customers to see the mold’s performance and operations in real-time.

Custom Plastic Injection Mold Making Company
We are a leading custom plastic injection mold maker / tooling builder, recognized for our precision, innovation, and exceptional quality. With our state-of-the-art facility and skilled experts, we manufacture intricate plastic components using advanced molding techniques, consistently delivering top-tier solutions to meet the unique needs of our clients.
Contact Us

Frequently Asked Questions
| Mold Class | Expected Lifespan | Material Type | Production Volume | Typical Applications | Key Takeaway | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 101 | 1,000,000+ cycles | Premium-grade hardened steel | High-volume production | Automotive, industrial, consumer products | Best for large-scale, continuous production with maximum durability and minimal maintenance. | H13, 718H, STAVAX, DAC55, S-STAR, GS-767, GS-808VAR |
| Class 102 | Up to 1,000,000 cycles | Hardened steel (32–48 HRC) | Medium-to-high-volume runs | Furniture, electronic components | Ideal for frequent, mid-volume production, offering durability and cost-efficiency. | P20, NAK80, 718H, GS-711 |
| Class 103 | Up to 500,000 cycles | Pre-hardened steel or aluminum | Moderate-volume production | Industrial parts, packaging | Suitable for cost-sensitive, mid-range production with moderate wear resistance. | P20, 6061-T6, GS-738 |
| Class 104 | Up to 100,000 cycles | Pre-hardened steel or aluminum | Low-volume production | Prototypes, custom components | Best for short-term or limited production with lower durability needs. | S50C, 6061-T6, P20M |
| Class 105 | Up to 500 cycles | Soft aluminum or low-grade steel | Prototyping and very low volume | Test parts, pilot runs | Cost-effective for prototyping or small-batch production, but lacks long-term durability. | 5052 aluminum, epoxy resin |
- A carbide-tipped core pin for the central bore, hardened to 58–60 HRC to resist wear from glass-filled resin.
- A servo-driven rotary table for the mounting bosses, enabling in-mold measurement and real-time adjustment of cavity positions.
- A cam-driven side action with a 0.005mm clearance fit to form the undercut without flash.
- EDM sinking with a 0.1mm diameter electrode to machine the microchannels, achieving a positional accuracy of ±0.003mm between intersecting paths.
- A temperature-controlled cavity plate (±0.5°C variation) to avoid warpage in the PEEK material.
- A vacuum-assisted ejection system to release the thin-walled (0.4mm) part without deformation.
From our perspective the cost of building a mold is shaped by several core factors that tie directly to the tool’s intended use and performance:
The material cost typically accounts for 15% to 25% of the total cost of the mold. For instance, if a common P20 steel (whose price might be approximately $8 to $15 per kilogram) is used instead of the higher-quality S136 steel (which costs around $25 to $45 per kilogram), it will be more cost-effective. The material cost for a medium-sized mold made of P20 steel could be between $2,000 and $5,000, while that for the same mold made of S136 steel might soar to $5,000 to $10,000.
The complexity of the design also plays a significant role. For simple molds with only one cavity and a basic shape, the design cost might account for 5% to 10% of the total cost. However, for molds with complex chamfers, multiple cavities, or strict tolerance requirements, the design cost might increase by 50% to 100% compared to this benchmark value. For example, the design cost of a simple plastic box mold without chamfers might be between $500 and $1,500, while that of a medical component with a complex internal structure and high precision requirements might be between $2,000 and $5,000.
For a more detailed breakdown of these cost components and how they apply to different scenarios, you can refer to our post: How Much Does It Cost To Make A Plastic Injection Mold, which contains separate sections dedicated to discussing the costs of molds.
Ensuring precision in mold building is a practice honed through decades of hands-on work, rooted in deep technical know-how and uncompromising attention to detail. At KingStar Mold, our approach is shaped by real-world challenges—from tight-tolerance medical parts to high-wear automotive components—and built around four pillars that reflect our expertise:
1. Equipment Calibration
Our workshop runs on 5-axis CNC machines and wire EDM systems, but what matters most is how we maintain them. Every machine undergoes weekly calibration using laser interferometers, checking for positional drift down to ±0.0005mm—critical for parts like 0.3mm microfluidic channels where even a hairline misalignment ruins functionality. For EDM work, we track electrode wear in real time (down to 0.001mm increments) and replace tools mid-job if needed, a step we’ve learned prevents costly rework on intricate undercuts, especially for aerospace components.
2. Materials Verification
We don’t just check steel certifications—we test them. A batch of H13 for a automotive mold, for example, goes through Rockwell hardness tests (verified with a Mitutoyo HR-400) to confirm 48–52 HRC, then ultrasonic scans to root out internal inclusions that could warp under injection pressure. For aluminum molds (used in short-run electronics), we add stress relief annealing at 315°C for 4 hours, a process refined over 15+ years to cut post-machining distortion by 70%.
3. Processes built on lessons from past projects
Our DFM reviews aren’t just checklists—they’re collaborative: engineers and floor technicians sit down with CAD models to flag issues like “this cooling channel layout will create a 0.02mm shrinkage in the part’s corner,” based on data from 500+ similar molds. During machining, we log every parameter (spindle speed, feed rate, tool type) in a database, so if a tolerance drifts, we can cross-reference with past runs to adjust. For multi-cavity molds, we use a custom alignment jig (developed in-house) to sync cavities within ±0.002mm—vital for medical parts where even minor mismatch risks product failure.
4. Rigorous Inspections
Final checks go beyond CMM scans. We run 100 trial shots with production resin, then section samples to measure wall thickness (using a Keyence 3D microscope) and check for internal voids. For FDA-regulated parts, we document every step—from raw material lot numbers to inspection sign-offs—so clients can trace precision back to its source. Last year, this rigor helped us pass an unannounced audit for a medical device client, with zero non-conformances in 200+ checked dimensions.
This isn’t just about meeting tolerances—it’s about proving, through consistent results, that precision is built into every step.
-
P20 and 718H: Workhorse materials for general injection molds, offering a balance of hardness (28–32 HRC) and machinability. Ideal for medium-volume production of parts like consumer electronics housings, they withstand 500,000+ cycles with proper maintenance.
-
H13: A heat-resistant alloy steel (42–48 HRC) designed for high-temperature applications, such as molding glass-filled plastics or die-casting. Its resistance to thermal fatigue makes it a staple for automotive component molds.
-
NAK80: A pre-hardened steel (38–42 HRC) with excellent polishability, eliminating the need for post-machining heat treatment. We use it for molds requiring high-gloss finishes, like cosmetic packaging or medical device casings.
-
Aluminum alloys (e.g., 7075, 6061): Lighter and faster to machine than steel, these are favored for rapid tooling or low-volume runs (up to 50,000 cycles). Their high thermal conductivity speeds up cooling, reducing cycle times for prototyping.
Mold building services cater to a wide range of industries, and from the inquiries we receive and projects we’ve handled, the automotive sector stands out with the highest demand. We regularly work on molds for sensor housings—parts requiring tight tolerances of ±0.01mm to fit seamlessly with other engine components, door panel clips produced in high volumes using multi-cavity molds, and H13 steel tools designed to withstand hundreds of thousands of cycles.
In medical fields, you’ll find molds for syringe barrels, IV connectors, diagnostic device casings, pill bottle caps.
For consumer electronics, we work on molds for headphone charging cases, smartphone stand hinges, USB-C port covers, smartwatch band clasps.
Packaging industry projects often involve molds for water bottle caps, cosmetic compact shells, blister packs, food container lids.
In industrial machinery, we produce molds for plastic gears, hydraulic seals, control panel housings, conveyor belt fasteners.
Each industry has distinct needs—precision, efficiency, material compatibility—but all rely on molds that transform designs into scalable products, with tooling tailored to their specific performance requirements.