In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing and product design landscape, selecting the right material is crucial to achieving performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Traditional plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, have long been go-to choices for a variety of applications, but as industries push for higher-performance solutions, innovative plastic alternatives have emerged. These alternatives not only offer enhanced physical properties but also cater to the specific needs of specialized industries. From high-temperature resistance to superior chemical stability, materials like PPA, PSU, SPS, and Tritan are redefining what is possible in product design.
This post explores these alternative plastics in detail, highlighting their unique properties, applications, and trade names to help designers and plastic injection molding manufacturers make informed decisions.
- 1. ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate)
- 2. COC (Cyclic Olefin Copolymer)
- 3. PCT (Polycyclohexylenedimethylene Terephthalate)
- 4. PESU (Polyethersulfone)
- 5. PPA (Polyphthalamide)
- 6. PPO (Polyphenylene Oxide)
- 7. PSU (Polysulfone)
- 8. SPS (Syndiotactic Polystyrene)
- 9. Tritan Plastic
- Common Thermoplastics and Alternative Options
- Conclusion
1. ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate)
Overview:
- Chemical Composition: ASA is a copolymer made from acrylonitrile, styrene, and acrylic ester. The chemical structure combines the impact strength of styrene with the weathering resistance of acrylic esters.
- Common Names: Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate, Styrene-Acrylonitrile-Acrylate Copolymer, and Acrylonitrile-Styrene-Acrylate.
- Chemical Structure:
- Acrylonitrile contributes to chemical resistance.
- Styrene provides high-impact strength and rigidity.
- Acrylic ester contributes to UV resistance and improves outdoor weathering properties.

Properties:
- UV Stability: Outstanding resistance to UV radiation, preventing degradation from prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Weatherability: Excellent resistance to environmental factors such as rain, snow, and extreme temperatures.
- Impact Resistance: High impact strength, similar to ABS, which makes it suitable for parts subject to physical stress.
- Chemical Resistance: Resistant to a variety of acids, bases, and other chemicals.
Applications:
- Automotive: Used in exterior automotive parts such as mirror housings and grills.
- Consumer Products: Ideal for products exposed to outdoor conditions like garden furniture, electrical enclosures, and housing.
- Building and Construction: Commonly used in roofing materials and window profiles.
2. COC (Cyclic Olefin Copolymer)
Overview:
- Chemical Composition: COC is a polymer derived from cyclic olefins, such as norbornene, combined with various co-monomers to create a copolymer structure. While part of the polyolefin family, its unique molecular design results in distinct properties.
- Common Names: Cyclic Olefin Copolymer, COC.
- Chemical Structure: COC is composed of cyclic olefin monomers and potentially other co-monomers, depending on the specific grade. It has a crystalline structure that contributes to its high transparency.

Properties:
- Transparency: Offers exceptional optical clarity, rivaling polycarbonate, making it ideal for applications requiring clear, unobstructed views.
- Low Moisture Absorption: Demonstrates extremely low moisture absorption, providing excellent stability and performance in humid environments.
- Chemical Resistance: Exhibits resistance to a wide range of solvents and chemicals, which makes it well-suited for use in chemically aggressive settings.
- Biocompatibility: Non-toxic and biocompatible, making it a safe choice for medical and pharmaceutical applications.
- Dimensional Stability: Maintains its shape and integrity even in high-humidity conditions, ensuring long-lasting performance.
Applications:
- Medical Devices: Ideal for use in diagnostic disposables, drug packaging, and medical device housings, thanks to its transparency and biocompatibility.
- Optical Components: Widely used for lenses, optical fibers, and light guides due to its high clarity and precise dimensional stability.
- Packaging: Commonly used in food and pharmaceutical packaging because of its superior barrier properties, ensuring product protection and safety.
3. PCT (Polycyclohexylenedimethylene Terephthalate)
Overview:
- Chemical Composition: PCT is a high-performance polyester synthesized from terephthalic acid and cyclohexanedimethanol. This semi-crystalline polymer provides superior chemical and heat resistance compared to traditional PET.
- Common Names: Polycyclohexylenedimethylene Terephthalate, PCT.
- Chemical Structure: PCT has a rigid backbone consisting of terephthalic acid linked with cyclohexanedimethanol. This unique structure contributes to enhanced thermal and hydrolytic stability.

Properties:
- Heat Resistance: PCT boasts a high melting point of approximately 285°C, making it suitable for applications requiring exposure to elevated temperatures.
- Hydrolysis Resistance: Offers exceptional resistance to moisture and water, making it ideal for components exposed to harsh environmental conditions, particularly in automotive and electronics.
- Chemical Resistance: Demonstrates strong resistance to most solvents and chemicals, ensuring stability and durability in demanding applications.
- Electrical Properties: With excellent dielectric strength, PCT is a preferred material for electrical components that require reliable insulation and conductivity.
- Dimensional Stability: Its low moisture absorption ensures that PCT maintains consistent dimensions and performance, even in humid environments.
Applications:
- Automotive: PCT is commonly used for under-the-hood components, including connectors, relays, and switches, thanks to its excellent heat resistance and durability.
- Electronics: Frequently employed in electronic components such as circuit boards, plug connectors, and housings due to its electrical properties and resistance to harsh environments.
- Industrial Components: PCT serves as a reliable alternative to PBT in industrial applications that demand enhanced temperature resistance and chemical stability.
4. PESU (Polyethersulfone)
Overview:
- Chemical Composition: PESU is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer synthesized through the reaction of bisphenol A and diphenyl sulfone. As part of the sulfone polymer family, it is renowned for its excellent thermal and mechanical properties.
- Common Names: Polyethersulfone, PESU.
- Chemical Structure: The polymer backbone consists of repeating ether and sulfone linkages, which provide a balance of mechanical strength and chemical stability, making PESU suitable for demanding applications.

Properties:
- High-Temperature Stability: PESU can withstand continuous exposure to temperatures as high as 204°C, making it ideal for applications in high-heat environments.
- Hydrolytic Stability: It exhibits superior resistance to water and steam, which is essential for applications in the medical and food industries.
- Flame Retardant: PESU is naturally flame-retardant, eliminating the need for additional flame-retardant additives in many applications.
- Electrical Insulation: The material boasts excellent dielectric properties, which make it highly suitable for use in electrical components requiring insulation.
- Transparency: PESU offers good optical clarity, making it a versatile choice for applications that require transparency, such as medical or consumer products.
Applications:
- Medical Devices: PESU is commonly used in sterilizable medical equipment, including water filters, dialyzers, and surgical instruments, due to its biocompatibility, thermal stability, and resistance to harsh sterilization methods.
- Automotive: The polymer is widely used in automotive applications, especially for electrical components like connectors and housings, owing to its electrical insulation properties and high heat resistance.
- Food and Beverage Industry: PESU is employed in food-contact materials, such as parts in coffee machines, faucets, and beverage dispensers, as it meets the strict safety and hygiene requirements of the industry.
5. PPA (Polyphthalamide)
Overview:
- Chemical Composition: PPA is a semi-aromatic polyamide polymer synthesized from phthalic acid and diamines. It is a part of the polyamide family but offers enhanced high-temperature stability compared to traditional nylons.
- Common Names: Polyphthalamide, PPA.
- Chemical Structure: The polymer has a semi-aromatic structure, which is key to its high melting point and superior chemical resistance. This structure provides enhanced thermal stability and mechanical properties compared to aliphatic polyamides.

Properties:
- High-Temperature Resistance: PPA has a high melting point and glass transition temperature, making it well-suited for applications in extreme heat environments.
- Chemical Resistance: It offers excellent resistance to a wide variety of chemicals, including automotive fluids, oils, and fuels, ensuring its durability in challenging environments.
- Dimensional Stability: The material exhibits excellent dimensional stability even at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for high-precision components that require consistent performance under stress.
- Mechanical Strength: PPA maintains good mechanical strength and stiffness at elevated temperatures, ensuring robust performance in demanding applications.
Applications:
- Automotive: PPA is commonly used for under-the-hood components, including fuel line connectors, water pumps, and engine cover parts, due to its heat resistance and mechanical strength.
- Industrial Components: The material is ideal for use in industrial applications such as gears, bearings, and bushings, thanks to its wear resistance and strength under high-stress conditions.
- Electronics: PPA is frequently employed in electronic connectors and housings, where high-temperature resistance and dimensional stability are essential for reliable performance.
6. PPO (Polyphenylene Oxide)
Overview:
- Chemical Composition: PPO is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer synthesized from phenylene oxide. It is renowned for its exceptional electrical insulating properties and dimensional stability. PPO is often blended with other polymers, such as polystyrene (PS), to enhance its overall performance and broaden its application range.
- Common Names: Polyphenylene Oxide, PPO.
- Chemical Structure: PPO features a polymer backbone made up of phenylene groups, contributing to its strength and resistance to various chemicals. This structure provides PPO with enhanced durability and stability under stress.

Properties:
- Heat Resistance: PPO can withstand high temperatures without compromising its mechanical properties, making it suitable for demanding environments.
- Electrical Insulation: With excellent dielectric properties, PPO is ideal for electrical components that require reliable insulation, such as connectors and housings.
- Chemical Resistance: PPO exhibits strong resistance to steam, hot water, and a variety of chemicals, including both mineral and organic acids.
- Stress Cracking: Although PPO is highly durable, it is sensitive to stress cracking, which may limit its use in certain applications that involve mechanical strain.
- Dimensional Stability: PPO has low moisture absorption, ensuring that its shape and size remain stable over time, even in fluctuating environmental conditions.
Applications:
- Electrical Components: Due to its excellent electrical insulating properties, PPO is widely used in connectors, insulators, and housings in the electrical and electronics industries.
- Automotive: PPO is commonly used in automotive applications, including pump parts, fan impellers, and engine components, where high heat resistance and dimensional stability are essential.
- Consumer Goods: The material is found in household appliances and a range of consumer products that require resistance to both high temperatures and chemicals.
7. PSU (Polysulfone)
Overview:
- Chemical Composition: Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic synthesized through the nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction of bisphenol A and diphenyl sulfone. As part of the sulfone polymer family, PSU is known for its exceptional thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance.
- Common Names: Polysulfone, PSU.
- Chemical Structure: PSU has a repeating structure of ether and sulfone groups in its polymer chain, providing it with outstanding resistance to high temperatures and a variety of chemicals.
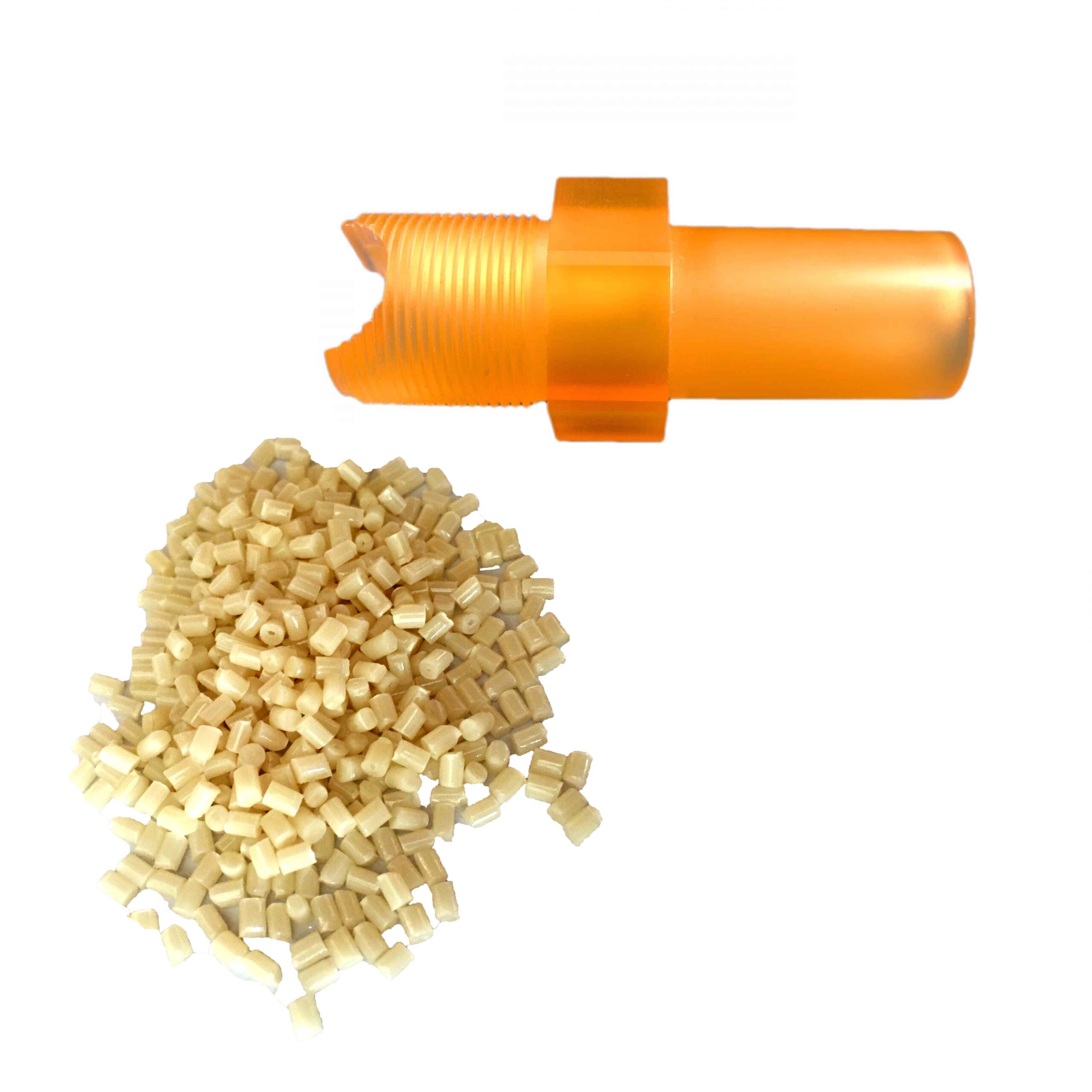

Properties:
- Thermal Stability: PSU can withstand high temperatures, typically up to 180°C (356°F), and is suitable for continuous service in high-heat environments.
- Hydrolytic Stability: The material offers exceptional resistance to water, steam, and hydrolytic attack, making it ideal for use in applications that involve exposure to high-temperature water or steam.
- Chemical Resistance: PSU resists a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents but is sensitive to certain polar solvents, such as benzene and toluene.
- Mechanical Strength: PSU provides high tensile and impact strength, comparable to polycarbonate, while maintaining excellent dimensional stability.
- Electrical Insulation: The material has good electrical insulating properties, making it suitable for various electrical and electronic applications.
Applications:
- Medical Devices: Polysulfone is widely used in sterilizable medical equipment, including components for dialysis machines, water treatment filters, and coffee machines.
- Automotive: PSU is used in automotive under-the-hood components such as electrical connectors, sensors, and manifolds due to its thermal and chemical resistance.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Polysulfone is also found in food-processing equipment, including sterilizable containers and water treatment systems, where hygiene and durability are critical.
8. SPS (Syndiotactic Polystyrene)
Overview:
- Chemical Composition: Syndiotactic Polystyrene (SPS) is a highly crystalline variant of polystyrene produced using metallocene catalysis. This process results in a unique structure with alternating benzene ring orientations, providing SPS with distinct properties compared to other forms of polystyrene.
- Common Names: Syndiotactic Polystyrene, SPS, Xarec (trade name).
- Chemical Structure: SPS features a regular arrangement of benzene rings in a syndiotactic configuration, enhancing its crystallinity and performance compared to atactic polystyrene.
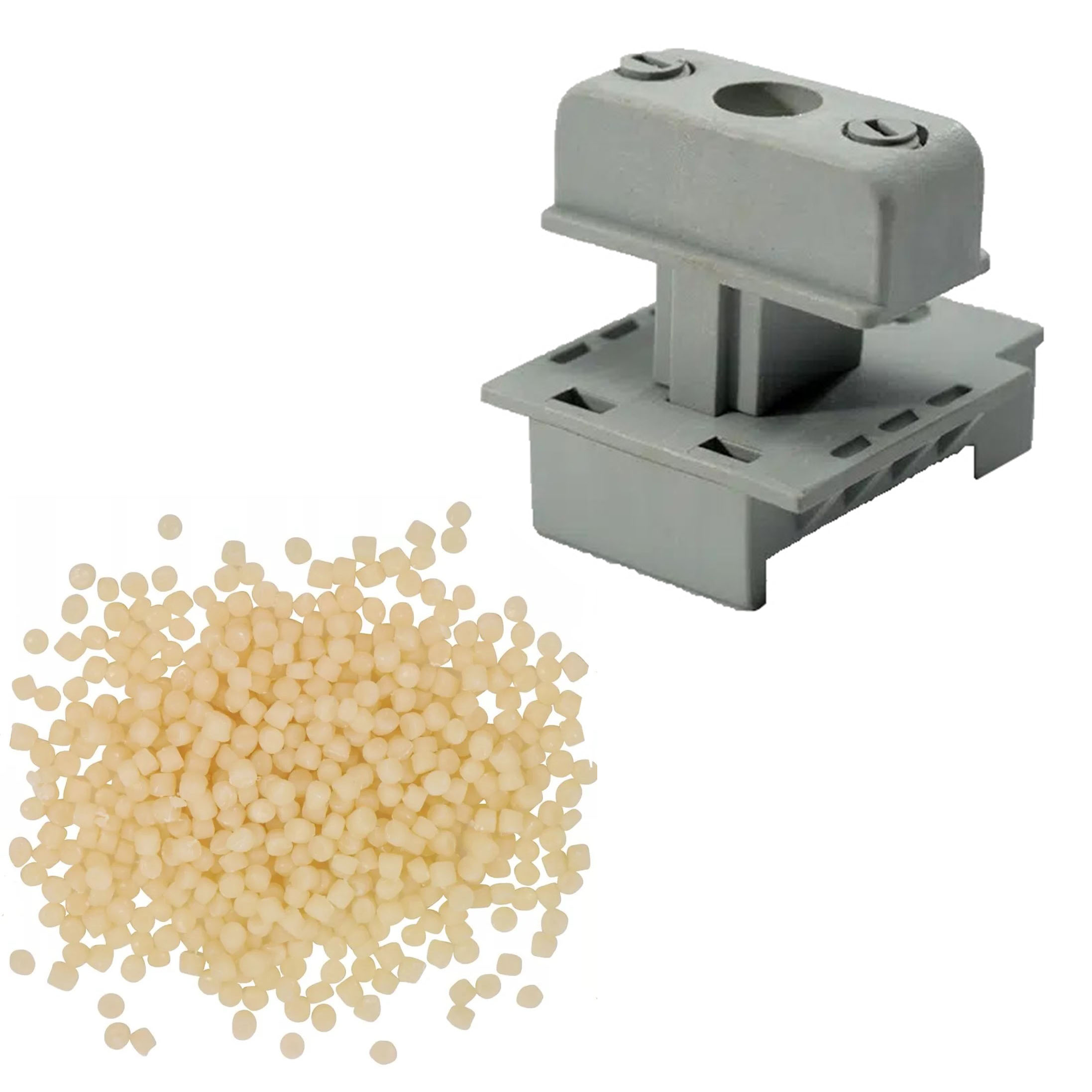

Properties:
- Heat Resistance: SPS has superior heat resistance, with a heat distortion temperature of up to 250°C (482°F), making it ideal for applications involving high temperatures.
- Chemical Resistance: It is highly resistant to corrosion from various acids, alkalis, automotive oils, and antifreeze.
- Lightweight: SPS has a low specific gravity, which helps reduce the overall weight of components, making it suitable for lightweight applications.
- Electrical Properties: The material offers excellent dielectric properties, including a low dissipation factor and dielectric constant, making it ideal for high-frequency electrical components.
- Moisture Resistance: SPS demonstrates good moisture resistance, along with excellent dimensional stability, even in humid conditions.
- Processability: SPS is highly moldable with minimal degradation and a high flow rate, making it well-suited for injection molding processes.
Applications:
- Automotive: SPS is used in parts that require high heat resistance, including wave soldered electronic components, connectors, and other automotive components.
- Electrical and Electronics: It is ideal for high-frequency electrical components and connectors, where precise dielectric properties are needed.
- Consumer Products: SPS is commonly found in household appliances, including microwave parts and dishwasher components that operate in high-temperature environments.
9. Tritan Plastic
Overview:
- Chemical Composition: Tritan is a copolymer made from bisphenol A (BPA) and other materials that do not release BPA, offering a safe alternative to polycarbonate. It belongs to the polyester family, specifically modified polyesters.
- Common Names: Tritan, Tritan Copolyester.
- Chemical Structure: Tritan’s structure is a combination of bisphenol A-based polyester and other monomers, providing enhanced strength, clarity, and safety.
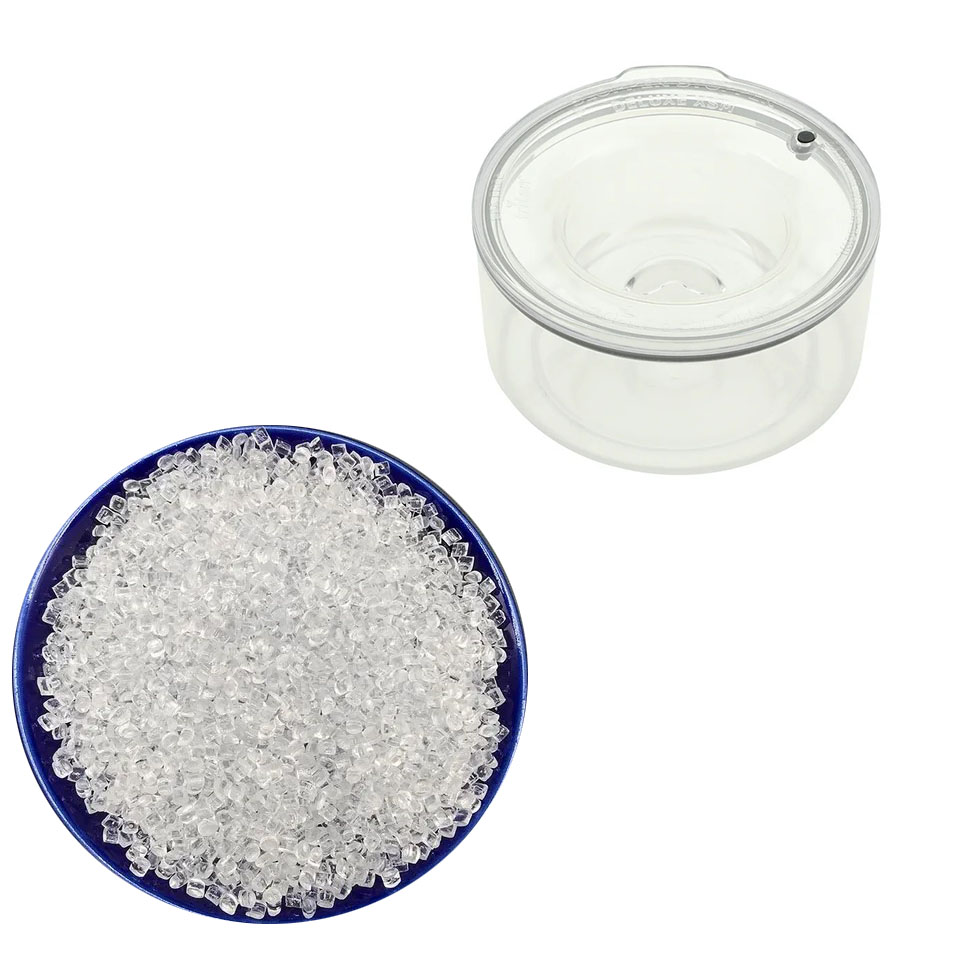

Properties:
- BPA-Free: Tritan is free from Bisphenol A (BPA), commonly found in polycarbonate plastics, making it a safer option for food and beverage containers.
- Impact Resistance: Tritan offers excellent impact resistance, similar to polycarbonate, but without the drawbacks of BPA.
- Thermal Resistance: It can withstand high temperatures of up to 100°C (212°F) without losing its shape, making it ideal for applications in hot water environments.
- Clarity: Provides superior optical clarity, making it perfect for applications requiring transparency, such as beverage containers, bottles, and lenses.
- Chemical Resistance: Tritan is resistant to a wide range of chemicals and detergents, making it well-suited for use in the medical and food industries.
- Dishwasher Safe: It is dishwasher safe, retaining its clarity and strength even after multiple washing cycles.
Applications:
- Consumer Goods: Frequently used in food and beverage containers, including reusable water bottles, baby bottles, and food storage containers.
- Medical Devices: Tritan is used in medical components that require clarity, strength, and resistance to sterilization processes.
- Household Products: Common in kitchen appliances, baby products, and various household goods requiring high impact resistance and clarity.
Common Thermoplastics and Alternative Options
| Plastic | Trade Names | Alternatives | 3DP Alternatives |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | Lustran, Cycolac, Polylac, RTP | PSU, ASA, COC, PPO | ABS-Like stereolithography |
| ABS/PC (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene/Polycarbonate) | Bayblend, Cycoloy | PSU, ASA, PPO | ABS-Like and PC-Like stereolithography |
| HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) | Marlex, Hostalen, Petrothene | PP, PPO | PP selective laser sintering |
| HIPS (High-Impact Polystyrene) | - | PMMA, ASA, PPO | - |
| LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer) | Vectra | PEEK, PEI, PCT, PPA, PPS, PESU, PPSU | - |
| PA Nylon (Polyamide) | Hylon, Minion, RTP, Stanyl, Vydyne, Zytel | SPS, PSU, PESU, PPSU, PPA, PPO | PA Nylon selective laser sintering, Multi Jet Fusion |
| PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) | Valox, Crastin | SPS, PCT, PSU, PPO | - |
| PC (Polycarbonate) | Hylex, Lexan, Makrolon, RTP | PSU, COC, PMMA | PC-Like stereolithography |
| PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | Rynite | SPS, PCT, PSU, PPO | - |
| PP (Polypropylene) | Thermylene, Polyfort, Pro-fax, Hostacom | PE, PPO | PP selective laser sintering |
| PPA (Polyphthalmide) | Amodel, Zytel, HTN | PPS, PEEK, PEI, PSU, PESU, PPSU | - |
| POM (Acetal) | RTP, Celcon, Delrin | PP | PP selective laser sintering |
Conclusion
Choosing the right material for your product is more than just a technical decision – it’s about ensuring long-term performance, reliability, and meeting the growing demands of consumers and industries. As we’ve explored, materials like PPA, PSU, SPS, and Tritan offer specialized properties that allow for a range of advanced applications, from high-temperature environments to medical and food industries. Understanding their advantages and limitations is key to selecting the most suitable material for your next project. By leveraging these innovative alternatives, manufacturers can not only improve product performance but also enhance sustainability and cost-efficiency.
KingStar Mold, as the leading custom injection molding company, we are committed to helping you find the best materials for your injection molding needs, ensuring high-quality and optimized solutions tailored to your unique requirements.