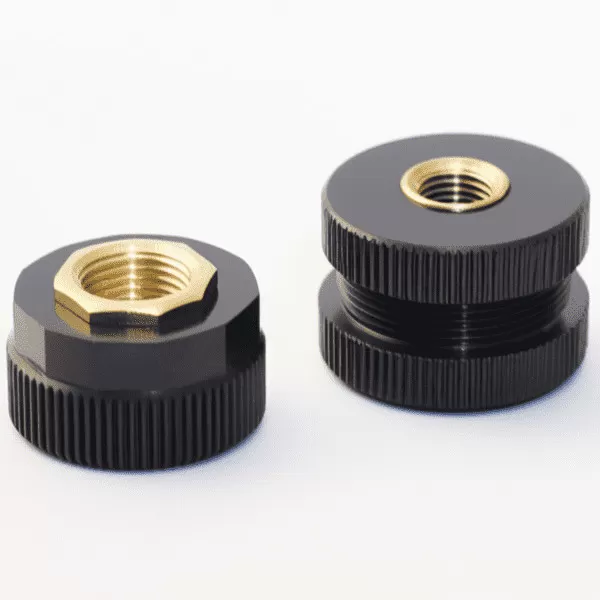
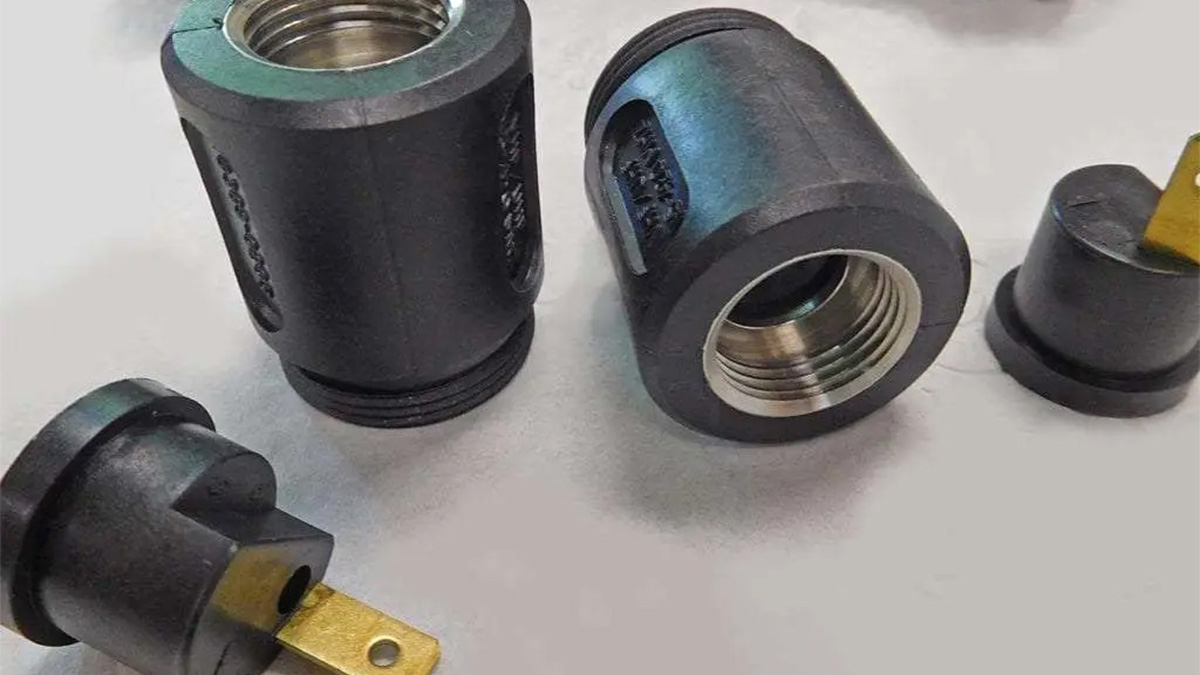
Insert Molding Service
What is Insert Molding?
Insert molding is a specialized injection molding process that combines metal and plastic materials. First, a metal insert is placed into the mold cavity, followed by injecting plastic around it. Once the plastic cools, the metal insert is securely held in place by the plastic, resulting in a finished part that seamlessly integrates both materials.
This process creates a strong bond between metal and plastic, reducing assembly time. Common inserts include components such as thread nuts, rods, blades, and knobs.
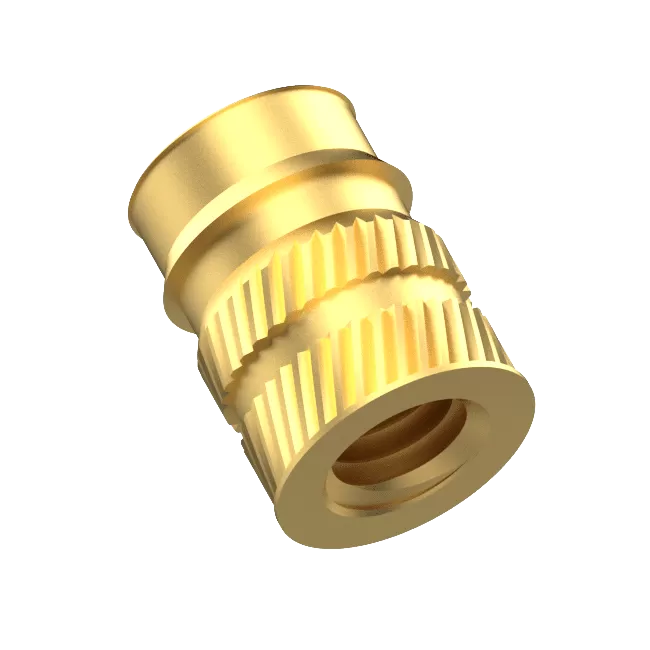
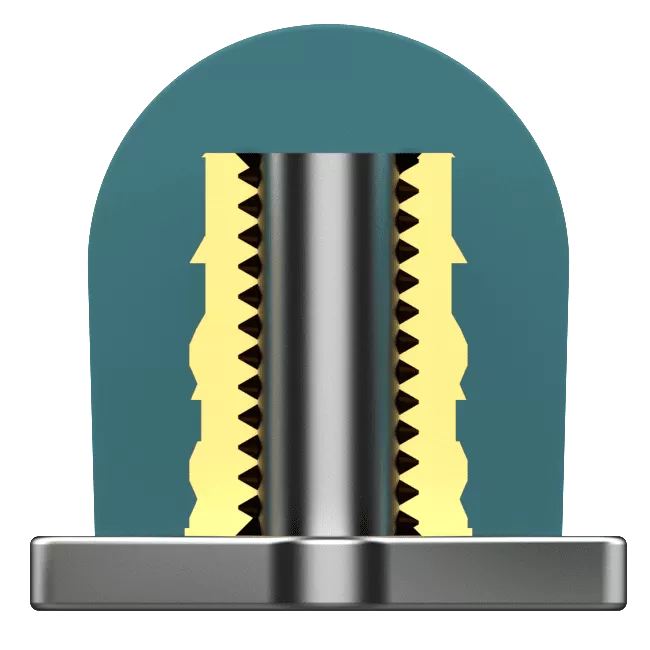

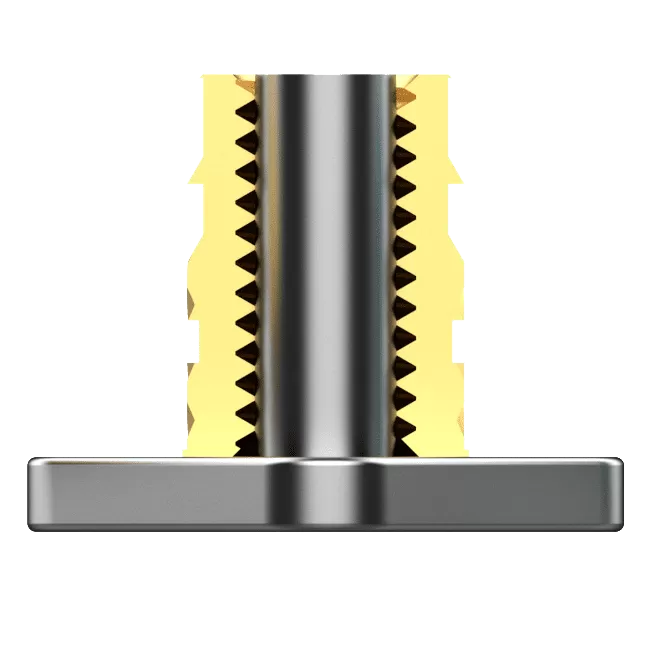

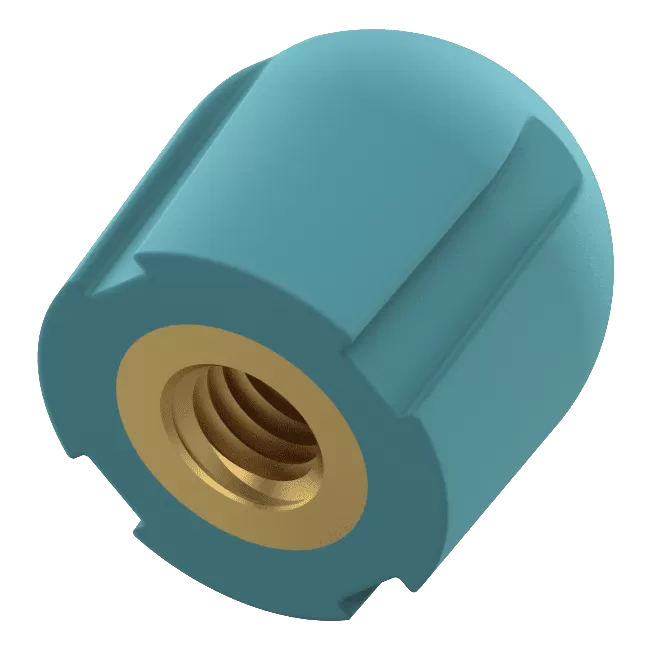
How Does Insert Molding Work?
Insert molding is a manufacturing process that merges the benefits of injection molding and insert molding to create complex, high-precision parts. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
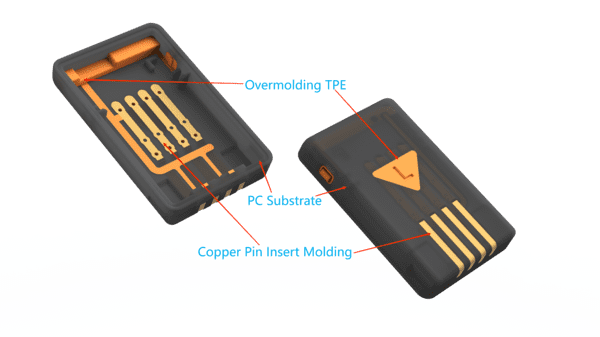
Insert Molding vs Overmolding
Insert molding and overmolding are two methods for creating plastic parts with multiple components. While they are similar in that both combine different materials, they differ in process, application, and benefits.
What are the Applications of Insert Molding?
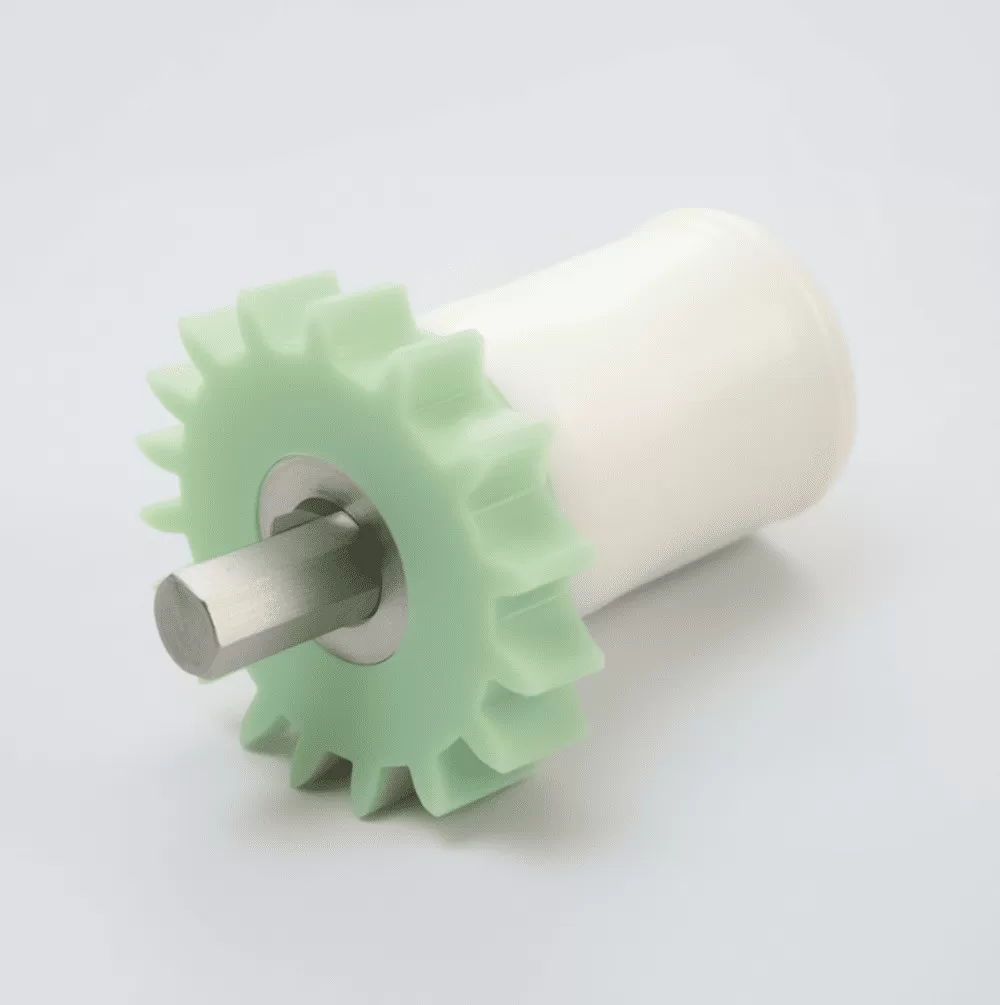

Insert molding involves injecting plastic into a mold around an insert (made of metal or plastic) to form a unified, single component. This process has various applications, with some of the most common being:
- Electronic Devices: Insert molding integrates electrical components like circuit boards, plugs, and sensors into plastic parts, improving functionality and reducing assembly costs.
- Medical Devices: This technique helps produce lighter, more hygienic medical instruments such as tube valves, needle hubs, and surgical tools.
- Automotive Parts: Insert molding is used to manufacture automotive components, including dashboard trims, door handles, and other interior parts.
- Aerospace Components: The aerospace industry benefits from insert molding for creating parts like aircraft seats, instrument panels, and other interior elements.
- Consumer Products: Insert molding is employed in the production of various consumer goods, including toys, appliances, and household items.
- Industrial Equipment: Insert molding is essential for manufacturing parts used in industrial equipment, such as pumps, valves, and other machinery.
- Sports Equipment: This process is applied in producing parts for sports gear, including bicycle frames, golf clubs, and other athletic equipment.
- Furniture: Insert molding is used to create furniture components such as chair legs, table frames, and decorative elements.
- Musical Instruments: Musical instruments plastic components are produced using insert molding, including drum shells, guitar bodies, and other essential parts.
- Medical Implants: Medical implants plastic components are manufactured through insert molding, such as joint surgical instruments, replacements, and other implantable devices.
- Fasteners: Insert molding is used to create aerospace fasteners, such as nuts, bolts, and other fastening components.
Why is insert molding so great for these applications? Well, it’s all about the benefits. Insert molding gives you stronger parts, more reliable attachment points, cost savings, and the ability to combine different materials (like plastics and metals) into a single part.
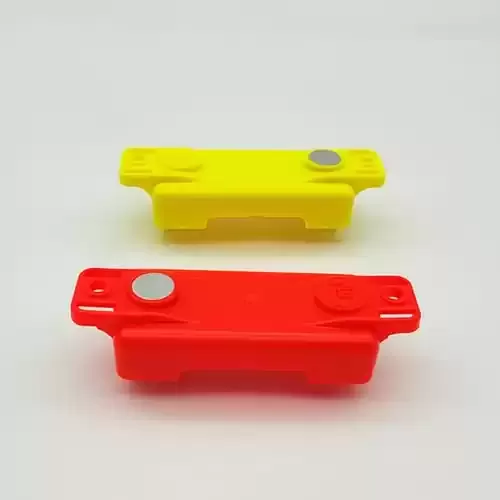
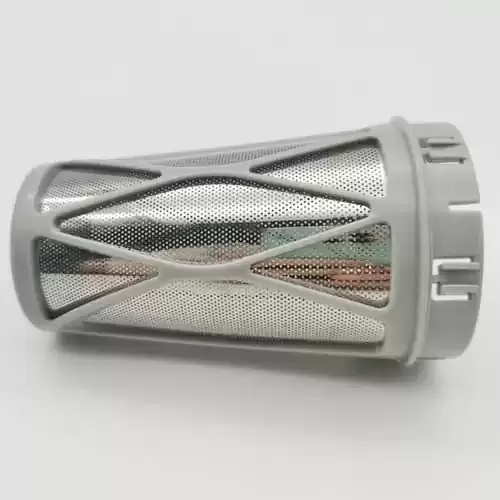


What are the Considerations for Insert Molding Design?
Before proceeding with insert molding, it’s important to plan your process carefully. Here are the key design considerations to keep in mind:
- The Structure: The metal and plastic components must be designed to ensure a strong mechanical bond between them.
- The Inserts: When molten plastic is injected into the mold, it directly contacts the insert, so the insert material must withstand the high pressure and temperature. Common insert materials include copper, aluminum, and steel, which can endure heat and resist wear.
- Insert Location: The mold should be designed for easy placement of the insert, typically positioning it at the center to facilitate smooth plastic flow.
- The Compatibility: It’s essential to consider the compatibility of metal inserts with plastic materials to avoid issues such as warping, cracking, sinking, or poor adhesion.
- The Production: Inserts can be loaded manually or automatically. It’s important to assess your production needs and conduct a cost-benefit analysis to determine the most suitable method for your process.
- Insert Shape and Size: Complex shapes or oversized inserts may cause molding issues or defects after injection. Therefore, when designing inserts, it’s best to choose simple, regular shapes and ensure the size is appropriate, staying within the mold’s maximum capacity.
Knowledge About Insert Molding & Parts With Metal Inserts

