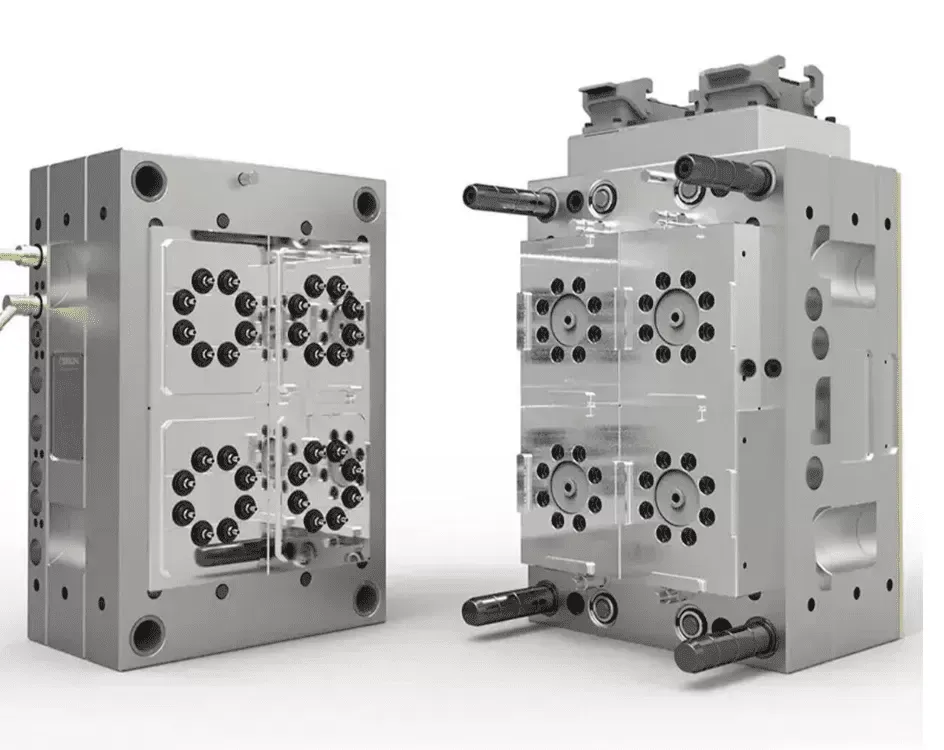
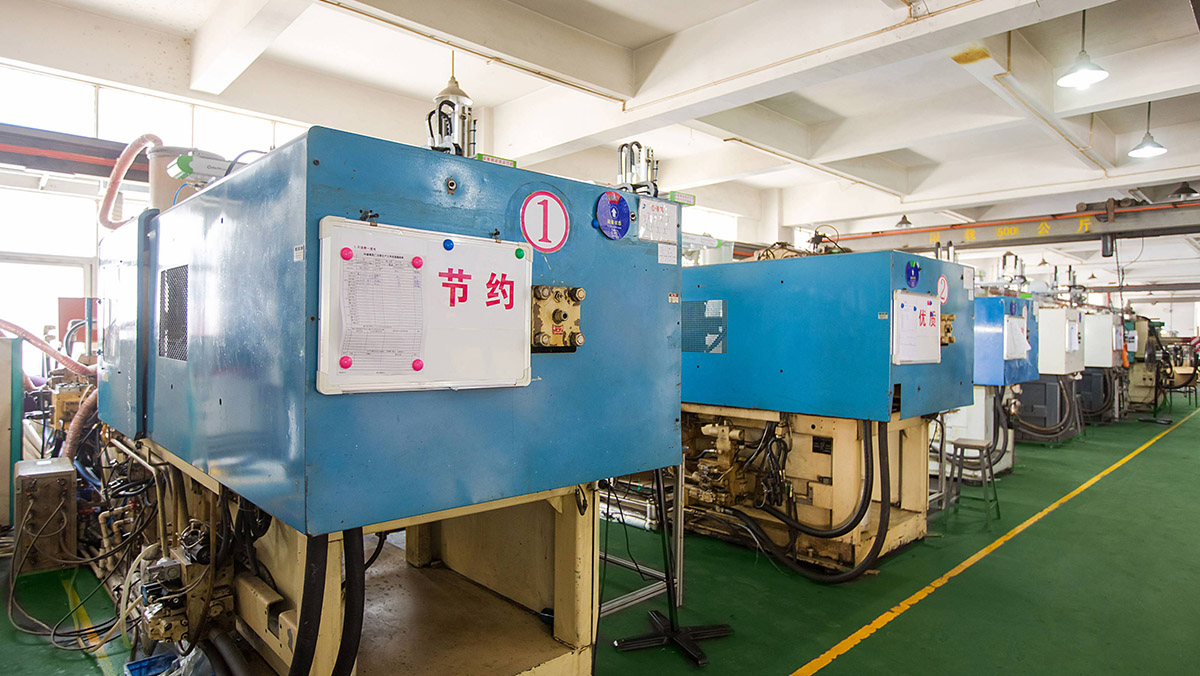
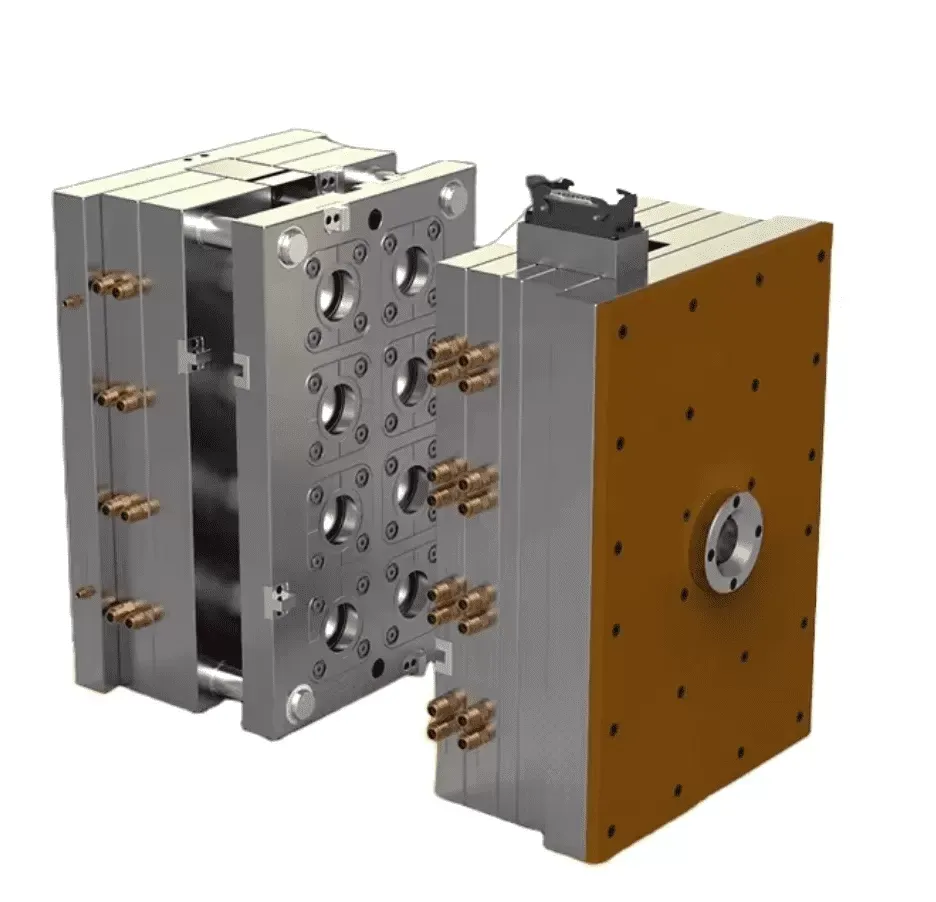
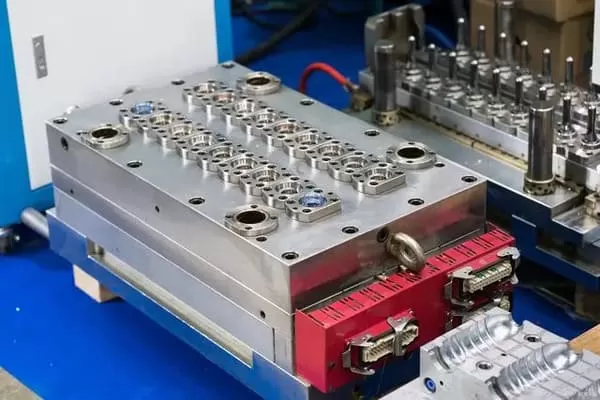
Injection Mold Building Factory
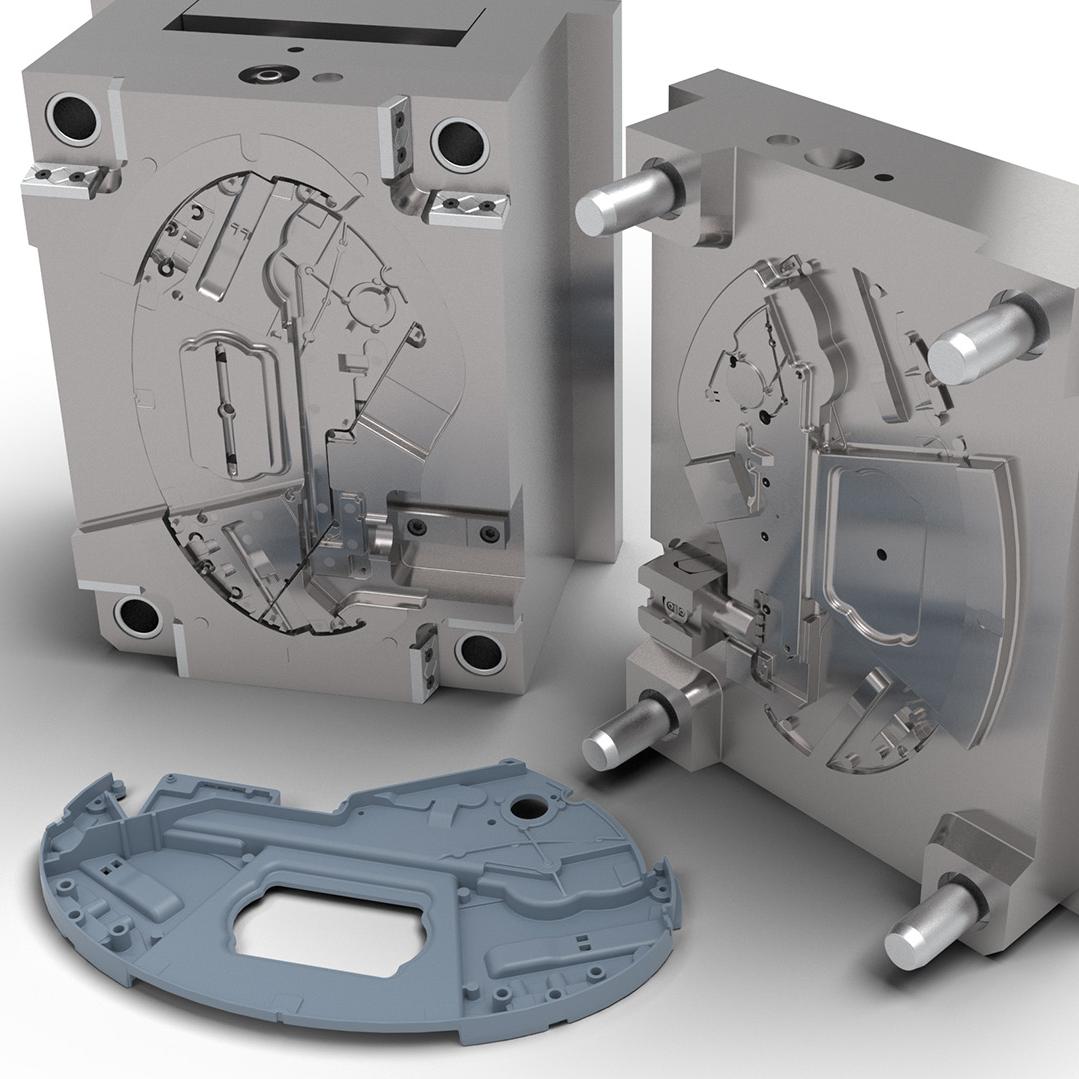
Injection Mold building Service
KingStar Mold provides full-service injection mold making, with on-site tooling capabilities to ensure fast and efficient production. Our skilled mold makers specialize in handling urgent projects, delivering rapid turnaround times to meet tight market deadlines. We excel in producing customized molds to exact specifications, using cutting-edge technologies such as VDI standards, high-polish SPI finishes, and Mold Technology. Whether you need molds for high-precision applications or complex designs, KingStar Mold ensures quality and speed in every project.
Resources for Injection Mold Steel
What fundamental features do Plastic Mold Steels have?
- Exceptional Hardness:
To withstand constant wear, preserving the mold’s form and surface integrity. - Excellent Thermal Conductivity:
Ensures efficient heat dissipation during molding, reducing the chances of warping or thermal shock. - Strong Corrosion Resistance:
Prevents damage from corrosive plastics, mold release agents, and cleaning chemicals, maintaining mold longevity. - Low Thermal Expansion:
Helps minimize distortion and warping caused by fluctuating temperatures during the molding process.

What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting Injection Mold Steel
- Hardness and Wear Resistance
- Thermal Conductivity
- Corrosion Resistance
- Machinability
- Toughness
- Cost
What Type of Steel is Used for Molds?
For non-abrasive injection mold materials, such as those without glass fibers or corrosive additives, P-20 steel is widely favored in the plastic injection molding industry. Its popularity stems from its excellent wear resistance and affordable cost, making it a go-to option for many mold applications. Several types of plastic mold steels are commonly used in the plastics industry, each offering unique properties and suited to specific purposes. Below are a few of the most frequently used mold steels:
| Mold Steel | Hardness | Suitable Plastic Materials | Property | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S136 | 48~54HRC | Molds designed for high-temperature plastics such as PTFE, PEEK, PPSU, LCP, PEI, and PAI. Production of molds for POM and PVC plastics, with requirements for mirror polishing and transparency, suitable for materials like PC and PMMA. | It offers excellent polishing capabilities and demonstrates strong resistance to acidic environments. | It provides outstanding polishing performance and shows a high level of resistance to acidic conditions. |
| 2344 | 48~52HRC | Manufacturing molds for PA+CF and PA+GF plastic materials. | This hot-working die steel boasts excellent polishing capabilities, high toughness, and good ductility, along with strong heat resistance. | Extrusion mold, die casting mold, injection mold |
| S50C | 19~22HRC | Producing molds for materials such as ABS, PP, PE plastics, rubber, and soft plastics. | Medium carbon steel is recognized for its outstanding wear resistance; however, it has lower ductility. | Medium carbon steel is acknowledged for its exceptional wear resistance, though it tends to have decreased ductility. |
| H13 | 50~54HRC | Molds designed for high-temperature plastics such as PEI, PEEK, PPSU, LCP, PAI, and PTFE. | It is a hot-working die steel known for its excellent wear resistance and heat resistance. | Molds for forging dies that can withstand significant impact loads, precision forging dies, hot extrusion dies, as well as die-casting and injection molds. |
| 2738 | 29~33HRC | Molds that require a high level of smoothness for PP, PE, ABS, PS, and PA plastic materials. | It offers outstanding processing and polishing capabilities. | Plastic molds that necessitate specific polishing capabilities. |
| P20 | 30~36HRC | Creating molds for materials such as PA, , PE, PS, PP plastics, rubber, and other soft plastics. | It offers excellent machinability and can be polished to a mirror-like finish. | It provides superb machinability and can achieve a mirror finish when polished. |
| 2083 | 48~52HRC | Production of molds for POM and PVC plastic materials | It offers strong corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and excellent cutting properties. | Injection molds for corrosive plastic materials |
| 718H | 34~38HRC | Plastic molds with mirror polishing requirements, suitable for PS, PE, PA, POM, PP, PBT, and ABS plastics. | This is a pre-hardened plastic mold steel with outstanding polishing characteristics. | Plastic product molds requiring a high surface finish, including blow molds. |
| NAK80 | 37~43HRC | Plastic molds that require mirror polishing, designed for transparent products, and suitable for PC and PMMA plastics. | This is a pre-hardened plastic mold steel that is well-suited for polishing and engraving. | Mold for mirror polishing and molds designed for transparent products. |
These are only a few examples of the many plastic mold steels available. The choice of steel alloy often depends on the specific application, the type of plastic being molded, and the desired properties of the mold.
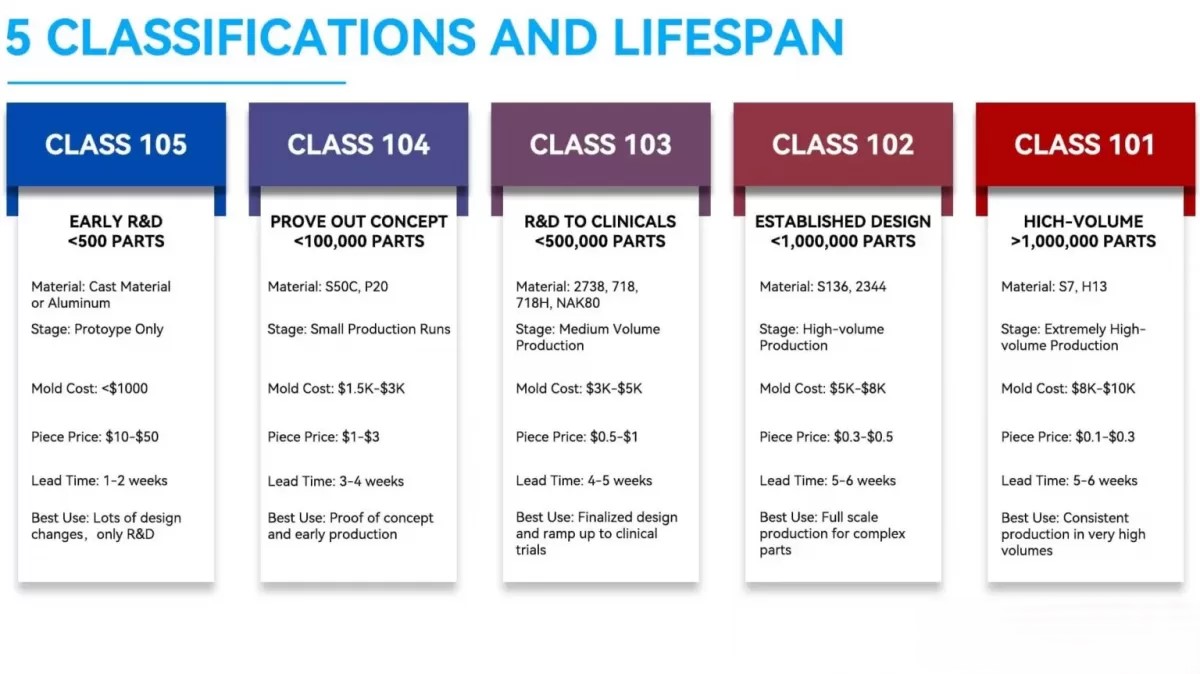
SPI Mold Classifications: 5 Injection Mold Standards
| Standards | Lifetime Cycles | Production level | Steel Hardness | Wear Resistance | Thermal Conductivity | Cavity Steel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 101 | 1 million or more | Extremely high-volume | 50~54 HRC | Very High | High | S7,H13 |
| Class 102 | Not exceeding 1 million | High-Volume | 48~52 HRC | High | Moderate | S136, 2344 |
| Class 103 | Not exceeding 500,000 | Medium Volume | 38~42 HRC | Moderate | Moderate | 2738, 718, 718H, NAK80 |
| Class 104 | Not exceeding 100,000 | Low-Volume | 15~25 HRC | Low | Low | S50C, P20 |
| Class 105 | Not exceeding 500 | Very low | Below 15 HRC | Very low | Very low | Aluminum |
Breakdown of SPI Mold Classes
Here’s an overview of each mold classification in the Society of the Plastics Industry (SPI) system, which helps guide the selection of tool steels for plastic injection molds:
- Class 101: Designed for the highest production volumes, this category is used for large-scale manufacturing. Molds are built to withstand continuous use in mass production environments.
- Class 102: Suitable for medium to large production runs, these molds are tougher and more corrosion-resistant, capable of handling significant production but with less intensity than Class 101.
- Class 103: Designed for medium production runs, these molds are built with higher precision, ideal for applications that require parts with superior accuracy and quality.
- Class 104: Used for low to mid-range production runs, these molds offer versatility, making them suitable for jobs requiring various options or adjustments during production.
- Class 105: Tailored for the smallest production runs, these molds are built with flexibility in mind, ideal for short runs or prototyping where frequent changes may be needed.
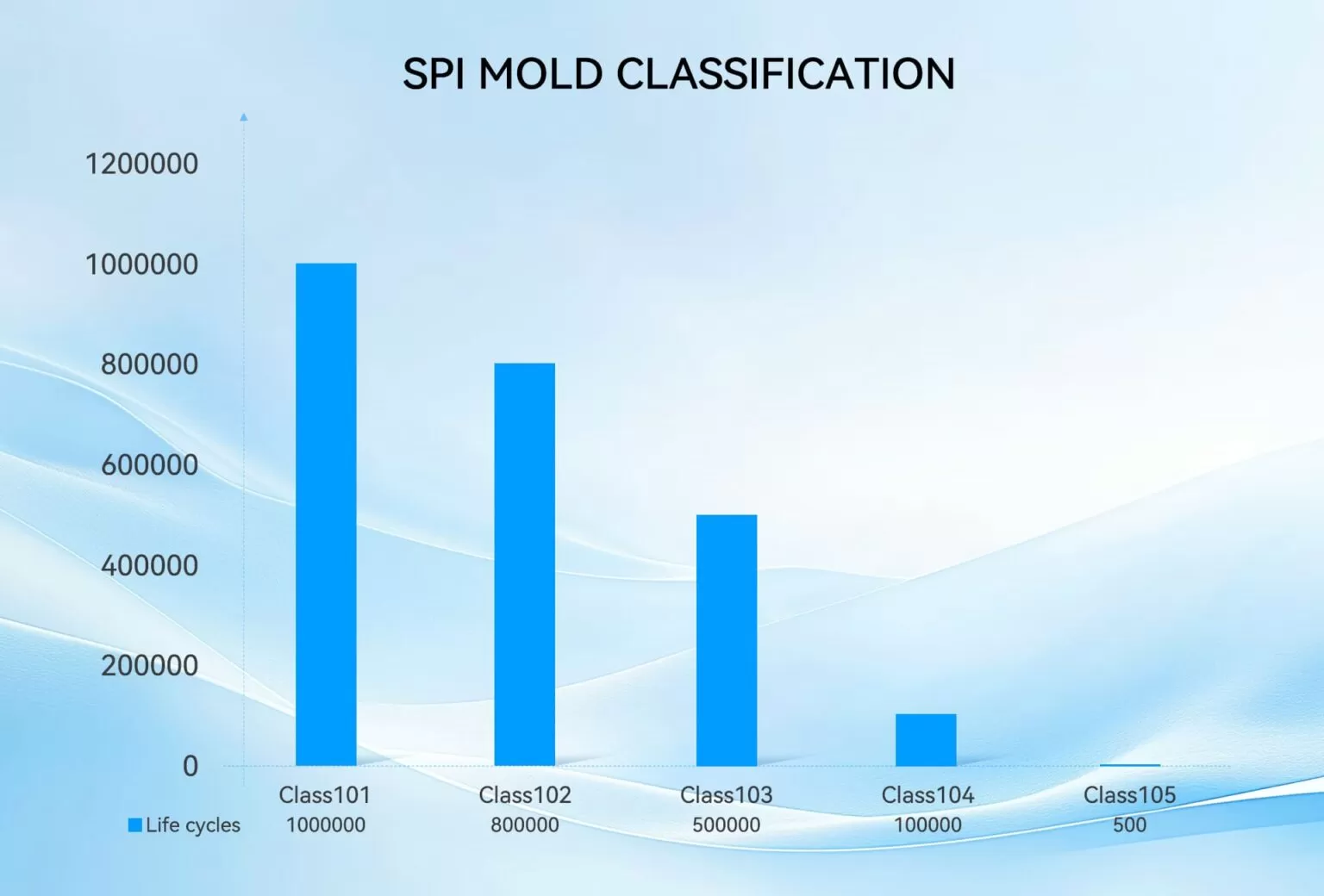
Keep in mind that the SPI classification system is a general guide, and molds may sometimes fit between categories. The choice of mold class depends on your specific requirements, including the type of plastic, mold design, and production volume.
The design requirements for different SPI mold classification




Injection Mold Cost Resources
What is the Price to Create an Injection Mold?
A basic single-cavity mold for low-volume production, for instance, usually falls within the range of $1,000 to $3,000. In contrast, molds for larger or more complex parts can exceed $10,000. Generally, a standard mold for a simple, hand-sized part averages around $5,000. Understanding these costs highlights the value of careful planning and design optimization early in the process.

How to Obtain a Precise Quote for an Injection Mold?
To get an accurate injection mold quote, follow these steps:
1. Provide Detailed Specifications
- Describe the part’s appearance, dimensions, materials, and function.
- Include production quantity and schedule to help the supplier assess timing and cost.
2. Define Mold Requirements
- Specify the mold type (e.g., hardened steel, mild steel).
- State the desired finish (e.g., polished, brushed).
- Mention special features, like cooling channels or ejector pins, if needed.
3. Share Production Volume and Schedule
- Communicate your production goals and timeline, so the supplier can estimate mold durability and maintenance needs.
4. Outline the Mold Design
- Share the design software or 3D file, if available.
- Note any specific considerations, such as spatial limitations or required materials.
5. Detail Part Dimensions and Tolerances
- Provide accurate part measurements and tolerances to ensure the mold meets design requirements.
6. Request a Detailed Quote
- Ask for a comprehensive quote covering:
- Mold design and manufacturing costs
- Tooling expenses (e.g., inserts, ejector pins)
- Production costs (labor, materials, overhead)
- Additional costs (maintenance, repairs)
7. Review the Quote
- Check each line item to ensure it aligns with your budget and needs. Ask for clarification as needed.
8. Request a Sample or Prototype
- Ensure product quality by requesting a sample or prototype to confirm the mold’s design.
9. Negotiate Terms
- Discuss any adjustments needed to ensure mutual understanding and alignment.
10. Evaluate the Supplier
- Research the manufacturer’s experience with similar products and materials to verify their reliability.
Following these steps helps you obtain an accurate, thorough quote that meets both your technical and financial requirements.
What Is a Fair Price Range for a Plastic Injection Mold?
Plastic mold costs can vary significantly based on factors such as part complexity, mold size, materials, and production volume. Typically, a basic mold might range from $1,000 to $3,000, while more complex molds can be much more expensive. If you’re unfamiliar with the industry, it’s a good idea to consult multiple mold manufacturers. Request several quotes, review the specific costs for your project, and consider selecting a supplier with a mid-range price that aligns with your needs.
How to choose an injection mold supplier?
To choose an injection mold supplier, follow these steps:
By following these steps, you can find a reasonable cost for your plastic injection mold project and choose a manufacturer that aligns with your specific needs and requirements.
Why Are Injection Molds Expensive to Produce?
Injection molds demand high precision and specialized expertise, which substantially increases their cost. Every stage in mold production—from intricate design specifications to labor-intensive fabrication—contributes to the total expense.
What Factors Affect the Cost of an Injection Mold
Injection molds can be expensive to make due to several factors. Here are some reasons why and percentage share:
| Factors | Detailed description | Percentage Share |
|---|---|---|
| Material Costs | Molds are often made from durable materials like hardened steel or aluminum. Steel is preferred for long production runs due to its durability, but it is also expensive. The material choice directly impacts the mold’s cost. | 20-30% |
| Design and Engineering | Complex mold designs require skilled engineers and advanced CAD software. Custom designs, tight tolerances, and features like cooling channels or ejector pins increase both time and cost. | 10-20% |
| Machining and Manufacturing | Precision machining processes such as CNC milling, EDM, and grinding are required to create molds with exact dimensions. The labor-intensive nature of machining, combined with the need for highly skilled operators, makes this one of the most expensive components. | 30-40% |
| Labor and Expertise | The expertise involved in mold design, assembly, and quality control requires highly trained professionals, contributing to higher labor costs. | 10-15% |
| Testing and Adjustments | Once the mold is built, it needs to be tested, adjusted, and sometimes modified to ensure it produces parts that meet specifications. This trial-and-error process can add time and cost. | 5-10% |
| Overhead and Other Costs | This includes costs for energy, facility maintenance, quality control inspections, and certifications, all of which add to the overall mold price. | 5-10% |
Look at the table above. It shows the different cost parts and percentages that make injection mold so expensive. Find ways to make some of them smaller.

Sourcing a Plastic Injection Mold Maker in China
To find injection mold manufacturers in China, it’s important to understand the key distribution of the country’s injection mold industry. The industry is primarily located in Hebei, Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, and Shanghai. Notably, Shanghai, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang together account for 70% of the production capacity of China’s injection mold industry.
Below is a table highlighting the regions, their characteristics, and the proportions of injection mold manufacturers in China.
| Regions | Characteristics | Production Capacity Proportion | Average Industry Quality | Average Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhejiang Province | Specializes in household and consumer product molds. | 20% | Medium to High | $3,000 - $10,000 |
| Shanghai | Hub for innovation and high-tech mold production. | 25% | High | $3,000 - $10,000 |
| Jiangsu Province | Strong focus on automotive and electronic molds. | High | $3,000 - $10,000 | |
| Hebei Province | Provides a mix of low to mid-range quality molds. | 5% | Low to Medium | $1,000 - $3,500 |
| Fujian Province | Emphasizes cost-effective solutions and smaller production runs. | 10% | Medium | $1,500 - $5,000 |
| Guangdong Province | Known for a large number of manufacturers and advanced technology. | 15% | Medium to High | $1,000 - $3,000 |
How to find an injection mold factory
In China, 60% of injection mold factories operate through B2B online platforms, while 30% maintain their own official websites and social media presence. Additionally, 10% of these factories participate in exhibitions. Here are some common methods to locate injection mold manufacturers:
Timeframe for Plastic Mold Production
Plastic mold production generally takes 2–8 weeks, with the timeline influenced by factors like mold complexity, chosen materials, and the manufacturer’s capabilities. Simple molds may be completed in 2–3 weeks, while more complex or large-scale molds may require up to 8 weeks.
The following chart outlines a sample 30-day mold production cycle, breaking down each step to clarify the timeline.
| Production Stage | Duration |
|---|---|
| Design & Engineering | 5 days |
| Material Preparation | 10 days |
| Polishing & Finishing | 5 days |
| Quality Inspection | 3 days |
| Final Adjustments | 2 days |
| Delivery Preparation | 2 days |
Four Key Factors Affecting Timelines of Plastic Injection Mold
| Factor | Summary | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity of Mold Design | Complex designs require more precise work and added steps. | Does the design include intricate details or tight tolerances? |
| Design Changes | Adjustments during prototyping add time to redesign and re-machine the mold. | Are design revisions anticipated during development? |
| Material Choice | Harder materials like hardened steel last longer but take more time to machine. | What materials are chosen for durability versus ease of machining? |
| Manufacturer Expertise & Capacity | Experienced manufacturers with advanced tools produce molds faster, avoiding bottlenecks. | Does the manufacturer have the capacity, expertise, and technology to complete the mold efficiently? |
What is the Injection Mold-Making Process?
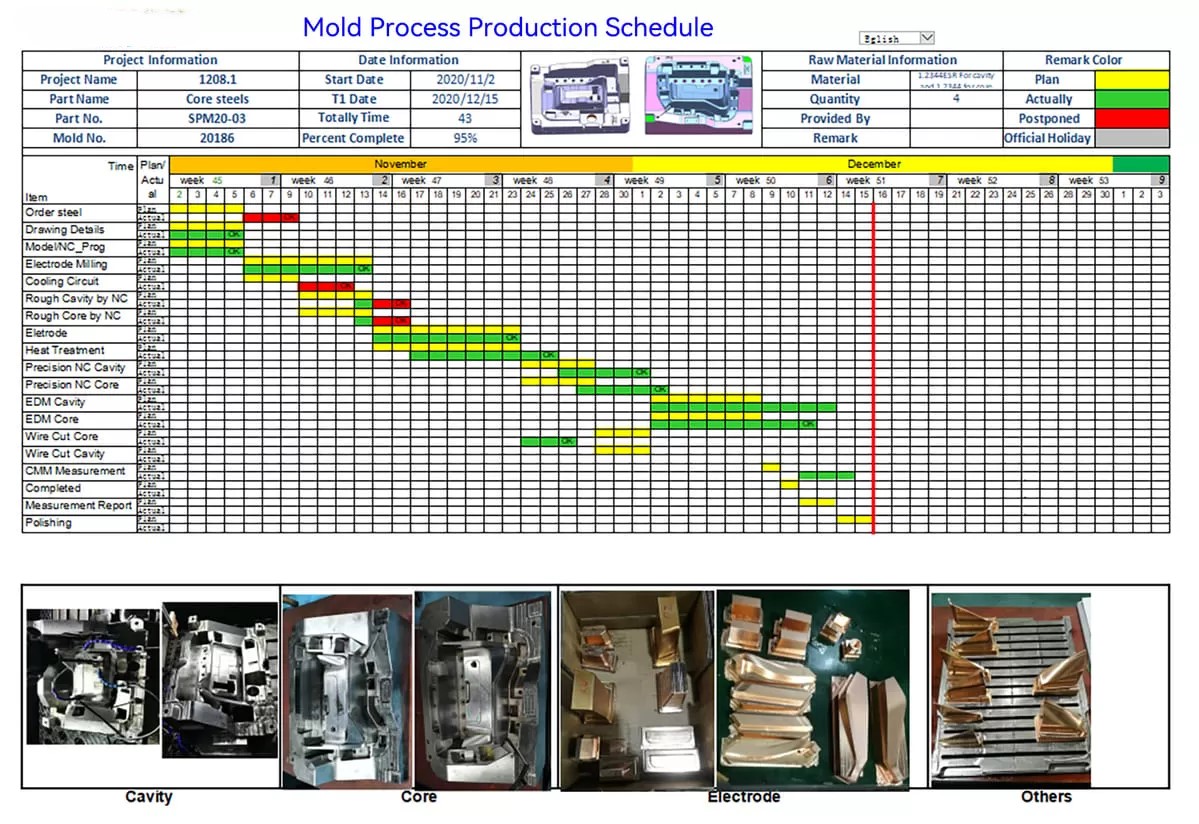
The entire injection mold creation process includes steps from initial design and prototype development through to finalizing the mold for transfer to production or packaging and shipping directly to the customer. To manage each phase, the Mold Process Production Schedule helps keep track of timelines and progress. Producing an injection mold is a detailed process with multiple stages to ensure the final mold can generate high-quality plastic parts. Here’s a summary of each step:
What Impacts the Lifespan of Injection Molds?
Several factors influence how long an injection mold will last: