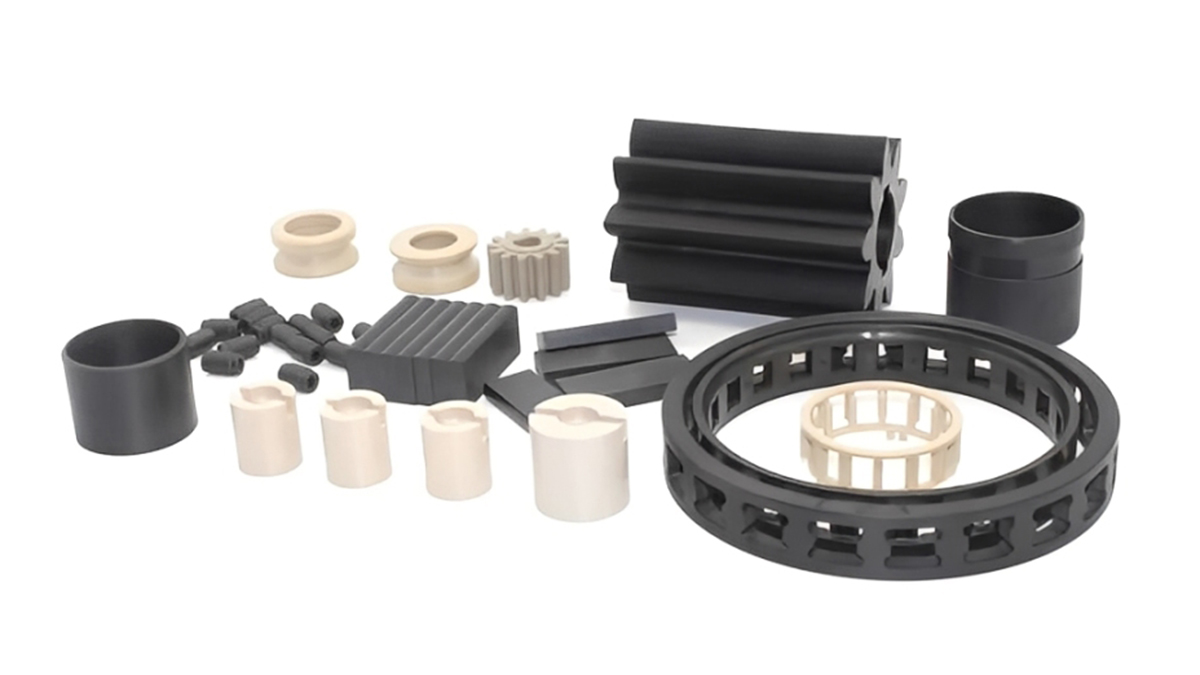
1. Introduction
With the development of society and the improvement of living standards, people’s taste for life has also been continuously elevated. Plastic products, being common and indispensable in daily life, require quality assurance to achieve good sales. This necessitates attention to every production step, with wall thickness design being a crucial aspect that impacts both the quality and aesthetics of the final product. Therefore, special care must be taken in this regard. KingStar, a leading plastic injection molding company in China, we have rich experience in the design of plastic product. Here comes the detailed design introduction.
2. The Function of Product Wall Thickness
(1) To give the product a definite structure and certain strength and stiffness, meeting the usage requirements of the product;
(2) The molding process should ensure good flow conditions (e.g., walls should not be too thin) and effective filling and cooling (e.g., walls should not be excessively thick);
(3) A reasonable wall thickness ensures that the product can be smoothly ejected from the mold;
(4) Meet the strength requirements for insert fixation and part assembly;
(5) Prevent warpage and deformation of the product.
3. Factors Affecting the Design of Plastic Part Wall Thickness
The basic structure of plastic products is specified according to the usage requirements of the products. The design of product wall thickness is determined based on the selected raw materials. Therefore, in general, when designing wall thickness of plastic products, two major factors should be considered: usage conditions and molding conditions. The usage conditions include structure, weight, strength, insulation performance, and dimensional stability. The molding conditions include factors such as material flowability, cooling time, ejection strength, and assembly strength dimensional accuracy. There is a close relationship between various factors, which can be summarized into the following three points:
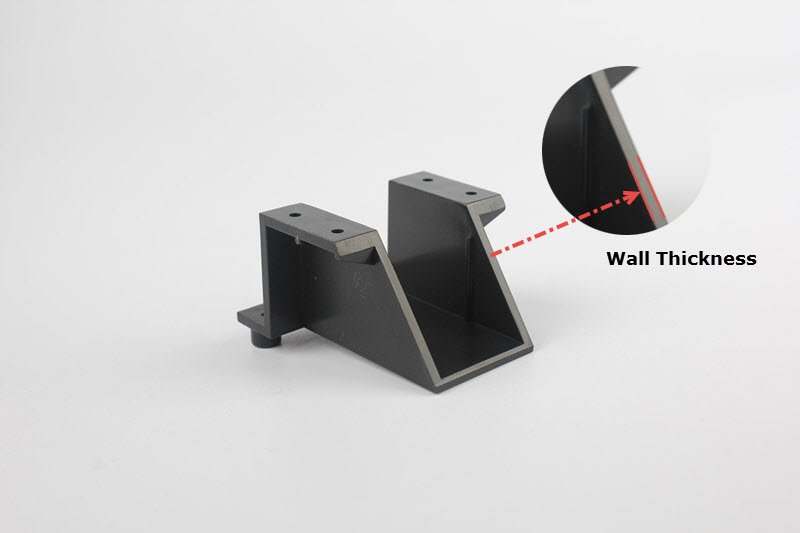

3.1 Structural Factors
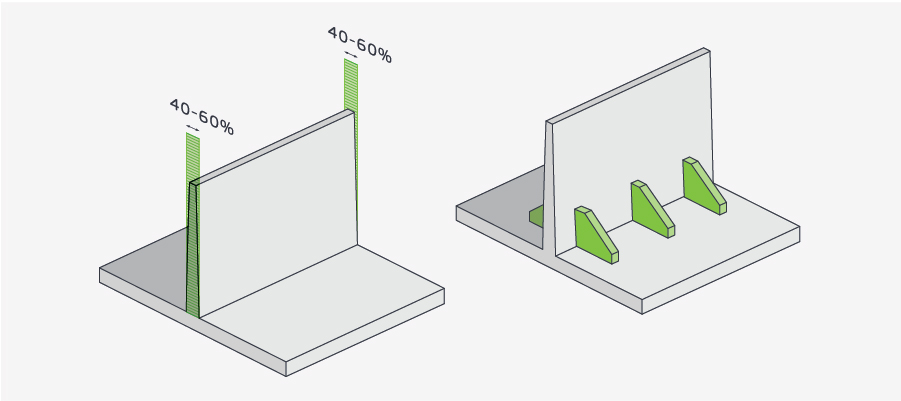
Structure determines the shape and size of the product, and by considering other factors, an ideal wall thickness product can be obtained. The wall thickness should be uniform, which is an important principle in product design. If the wall is too thin or too thick, the difference is significant, which will inevitably cause uneven shrinkage during the cooling process of the product. This will not only cause bubbles, dents, and warpage, but also generate significant internal stress inside the product, affecting its appearance and quality. This is particularly evident for thicker products made from crystalline plastics such as polypropylene, polyethylene, nylon, polyamide, etc. So in the design of wall thickness, the thick wall part needs to be hollowed out or modified to achieve uniform wall thickness. In actual production, it is impossible to design plastic products with completely uniform wall thickness. It is generally believed that the unevenness of product thickness should not exceed 50%.
3.2 Strength Factor
The strength of plastic products is determined by the physical and mechanical properties of the raw materials used. Plastic is different from metal in that it has lower impact strength, brittleness, and light weight, so the design of plastic product wall thickness should meet the strength requirements. Although sometimes the strength required for the product during use is very small, the product must withstand the impact and vibration of the demolding mechanism when demolding from the mold cavity, and must ensure a certain demolding strength. At the same time, it is necessary to consider that the product assembly should be able to withstand the fastening force, and the corresponding product wall thickness should be designed to meet the requirements of demolding and assembly strength.
3.3 Factors Affecting the Fluidity of Plastics
Plastic products have a certain degree of fluidity during the molding process. Depending on the type and grade of plastic, their fluidity also varies. The fluidity of plastic can generally be compared using the melt index and Archimedes spiral flow test method. The higher the melt index, the better the fluidity. Therefore, the wall thickness of products made of different materials should consider the design that is most conducive to flow. It can not only fill the mold cavity, but also make the plastic flow velocity consistent in all directions, and minimize the resistance encountered in the flow direction. For plastics with good fluidity such as nylon, polyethylene, polypropylene, etc., the wall thickness can be thinner. For plastics with poor fluidity such as polycarbonate, polysulfone, etc., the wall thickness can be thicker. Both thin and thick wall thickness designs are unreasonable.
4. Design Principles for Product Wall Thickness
The wall thickness of plastic parts has a significant impact on their quality. If the wall is too thin, it is difficult to meet the requirements of strength and stiffness, and it is difficult to fill the mold cavity for large and complex parts; Excessive wall thickness not only wastes materials (usually the cost of raw materials accounts for 50%~70% of the cost of plastic parts), but also easily produces defects such as bubbles on the inner wall of the plastic part and dents on the outside. At the same time, it also increases the cooling time (the cooling time of plastic is approximately proportional to the square of the wall thickness of the plastic part). Therefore, from an economic perspective, the thinning of plastic parts is very important. In addition, the wall thickness of the same plastic part should be uniform to avoid warpage or crack resulted by inconsistent shrinkage.
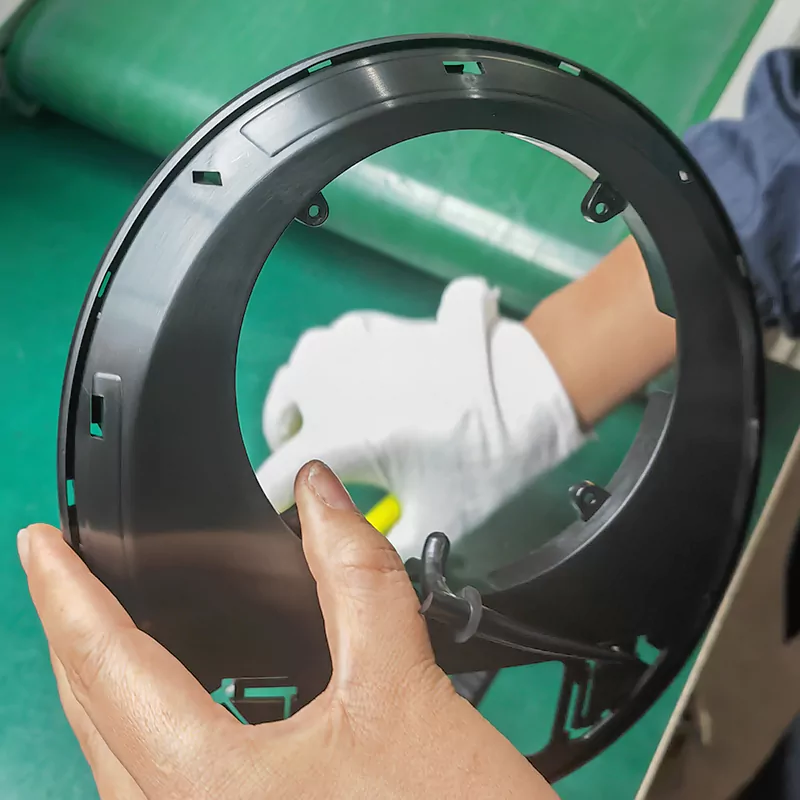

So when designing plastic parts, the wall thickness of the parts should pay attention to the following points:
1) Minimize wall thickness as much as possible while meeting usage requirements;
2) The wall thickness of each part of the component should be as uniform as possible to reduce internal stress and deformation;
3) The part that bears fastening force must ensure compressive strength;
4) Avoid shrinkage and depression in areas with excessive thickness;
5) Capable of withstanding the impact force during molding and ejection;
6) The wall thickness should be as uniform as possible to avoid sudden changes.
The wall thickness of plastic parts generally ranges from 1 to 6mm, with a maximum of 8mm. The most commonly used wall thickness values are 1.8 to 3mm, which depend on the type and size of the plastic part. However, the wall thickness of precision plastic parts is not limited by the above range. For lightweight electronic products such as portable audio players, the wall thickness can be less than 1mm, and some can even reach 0.6mm. Tables 1 and 2 respectively list the minimum or recommended wall thickness values for thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic parts.
Table 1 Minimum and Recommended Wall Thicknesses of Common Thermoplastic Parts (mm)
| Plastic Material | Minimum Wall Thickness | Recommended Wall Thickness for Small Plastic Parts | Recommended Wall Thickness for Medium-Sized Plastic Parts | Recommended Wall Thickness for Large Plastic Parts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyamide | 0.45 | 0.75 | 1.60 | 2.40~3.20 |
| Polyethylene | 0.60 | 1.25 | 1.60 | 2.40~3.20 |
| Polystyrene | 0.75 | 1.25 | 1.60 | 3.20~5.40 |
| Organic Glass (372) | 0.80 | 1.50 | 2.20 | 4.00~6.50 |
| Polyoxymethylene | 0.80 | 1.40 | 1.60 | 3.20~5.40 |
| Polypropylene | 0.85 | 1.45 | 1.75 | 2.40~3.20 |
| Polycarbonate | 0.95 | 1.80 | 2.30 | 3.00~4.50 |
| Polysulfone | 0.95 | 1.80 | 2.30 | 3.00~4.50 |
| Rigid Polyvinyl Chloride | 1.15 | 1.60 | 1.80 | 3.20~5.80 |
Table 2 Wall Thickness of Thermosetting Plastic Parts (mm)
| Plastic Material | Plastic Part Height | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic Plastic With Powdered Filler | 0.7~2.0 | 2.0~3.0 | 5.0~6.5 |
| Phenolic Resin With Fibrous Fillers | 1.5~2.0 | 2.5~3.5 | 6.0~8.0 |
| Amino Plastic | 1.0 | 1.3~2.0 | 3.0~4.0 |
| Plastic Filled With Polyester Glass Fiber | 1.0~2.0 | 2.4~3.2 | >4.8 |
| Polyester Inorganic Filler Plastic | 1.0~2.0 | 3.2~4.8 | >4.8 |
With the development of the electronic information industry and various consumer electronics markets, various plug-in molding applications are constantly expanding. There is also a minimum wall thickness requirement for the corresponding plastic material during plug-in molding.
For example, when pre forming detachable screw assembly threaded holes on the workpiece, it is necessary to pre install inserts in the mold during molding, and there is a minimum wall thickness requirement for the base of the corresponding threaded hole. Table 3 recommends the base size of the threaded hole. The insert should be smooth without sharp corners, and when using high shrinkage resin, the insert should be clean and preheated. This will reduce the stress on the resin around the insert and eliminate the possibility of stress cracking during use. All designed product assemblies must undergo injection molding and testing to ensure that these products meet the requirements during actual use.
Table 3 Minimum Wall Thickness for Insert Molding
| Plastic Material | Insert Diameter /mm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | 6.4 | 9.5 | 3.2 | 12.7 | 19.1 | 25.4 |
| Polyoxymethylene (POM) | 3.2 | 4.7 | 1.6 | 6.4 | 9.5 | 12.7 |
| Acrylic (Acrylate Resin) | 3.2 | 4.7 | 2.4 | 6.4 | 9.5 | 12.7 |
| Celluloid | 6.4 | 9.5 | 3.2 | 12.7 | 19.1 | 25.4 |
| EVA(Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate) | 2.2 | NR | 1.0 | NR | NR | NR |
| FEP(Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) | 1.5 | NR | 0.6 | NR | NR | NR |
| Nylon | 6.4 | 9.5 | 3.2 | 12.7 | 19.1 | 25.4 |
| Noryl (Modified PPO) | 3.2 | 4.7 | 1.6 | 6.4 | 9.5 | 12.7 |
| Polyolefin Elastomer | 6.4 | 9.5 | 3.2 | 12.7 | 19.1 | 25.4 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 3.2 | 4.7 | 1.6 | 6.4 | 9.5 | 12.7 |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | 6.4 | 9.5 | 3.2 | 12.7 | 19.1 | 25.4 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 6.4 | 9.5 | 3.2 | 12.7 | 19.1 | 25.4 |
| Polystyrene (PS) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Polysulfone (PSU) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Surlyn (Ionomer) | 2.4 | 3.2 | 1.6 | 4.7 | 6.4 | 7,9 |
5. How to Design the Wall Thickness of Plastic Parts?
The wall thickness of the plastic part should meet the requirements for strength, rigidity, insulation, weight, dimensional stability, and assembly compatibility with other components during use, while ensuring smooth filling of the entire mold cavity with molten plastic.
When designing the wall thickness of plastic parts, the thickness should be minimized as much as possible. The minimum allowable wall thickness of plastic parts is related to the type of plastic and the dimensions of the part. During the design process, efforts should be made to maintain uniform wall thickness, with the wall thickness difference generally kept within 30%. For cases where the wall thickness difference is excessively large, measures such as hollowing out the over-thick sections or decomposing the part into multiple components before reassembling can be taken to reduce the wall thickness difference.
The wall thickness of plastic parts is closely related to the flow length. Thicker wall sections allow for longer flow lengths, while thinner walls result in shorter flow lengths. The relationship between wall thickness and flow length can be estimated using the formulas provided in Table 4.

Table 4 Relationship Between Plastic Part Wall Thickness (δ) and Flow Length (L)
| Plastic Type | Empirical Formula |
| Good flowability (e.g., PE, Nylon, etc.) | δ=0.6(L/100+0.5) |
| Medium flowability (e.g., PMMA, POM, etc.) | δ=0.7(L/100+0.8) |
| Poor flowability (e.g., PC, PSU, etc.) | δ=0.9(L/100+1.2) |
6. Case Study
The wall thickness of the same plastic part should be as uniform as possible. If inconsistencies exist, measures to improve wall thickness can be taken. When optimizing the wall thickness of plastic parts, the following aspects should be considered:
1) It shall meet the strength requirements for plastic parts during assembly, transportation, and use;
2) Fully consider the fluidity of plastic during the molding process to ensure that thin-walled and edge areas are also fully filled;
3) The plastic part must withstand sufficient demolding force to prevent damage during the demolding process.
Example of Improved Wall Thickness in Plastic Parts:
(1) Uneven wall thickness of plastic parts often leads to additional internal stress due to different cooling or fixing speeds, resulting in shrinkage or warpage in thicker parts;
(2) When the wall thickness change in plastic parts is inevitable, in order to avoid the adverse effects of local wall thickness, a transition zone must be set up when the wall thickness transitions to the thinner part;
(3) When using side gate feeding for flat top plastic parts, in order to avoid leaving weld marks on the flat surface, it is necessary to ensure that the flat feeding is usually done;
(4) Uneven wall thickness plastic parts can be covered or eliminated by using corrugated forms on surfaces prone to dents or by opening process holes in thick walls.
Conclusion
Plastic products play a very important role in today’s society and have become indispensable to people. The development of society and people’s higher demands for life require better quality products. This requires strict production, and the wall thickness design is a crucial aspect that needs to be taken seriously in order to produce high-quality products that meet people’s needs.
As a top custom manufacturing company, KingStar Manufacturing brings decades of specialized expertise in precision wall thickness design and material engineering. We deliver end-to-end technical partnerships—from structural optimization to volume production—enabling brands to achieve superior product performance, manufacturing efficiency, and sustainable cost control.
We invite you to explore further industry perspectives and technical breakdowns through our upcoming publications. Let our engineering-driven approach become the foundation of your next product success. Reach out to our team at sales@kingstarmold.com to begin the conversation.