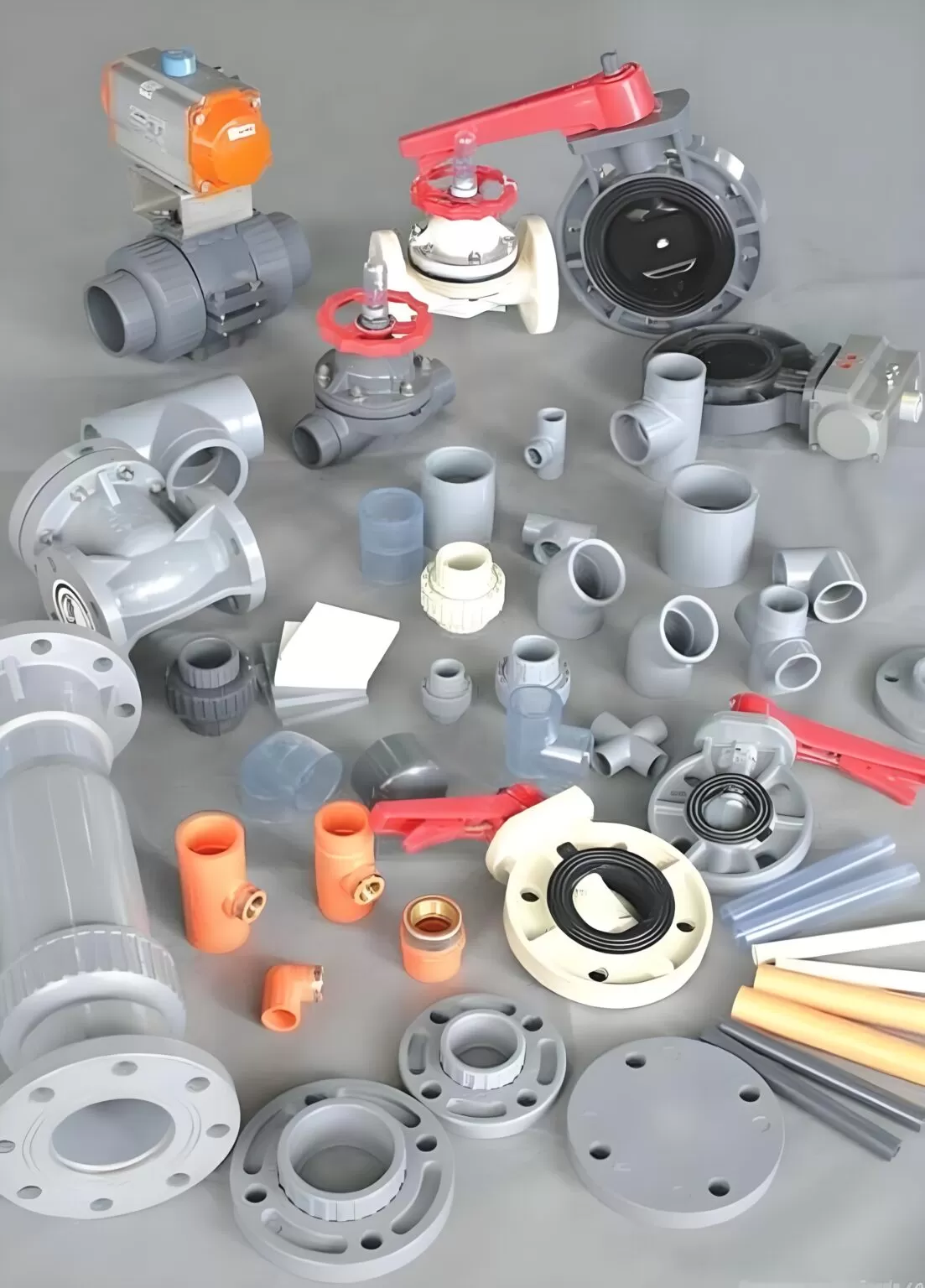
Custom PVC Injection Molding Service
We are committed to delivering cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality. From prototyping to high-volume production, we are your trusted partner for custom PVC molding. Contact us today to discuss your project and receive a personalized quote.

Resources for The Complete Guide to PVC Injection Molding

What is PVC?
PVC, or Polyvinyl Chloride, was first created in the 1800s but became widely used in the 1920s after it was made more flexible. This synthetic plastic polymer is made from vinyl chloride, which is derived from petroleum. PVC is the third most commonly used plastic globally, following polyethylene and polypropylene, with around 40 million tons produced annually. There are two types of PVC: rigid and flexible. Rigid PVC is used for products like pipes, doors, and windows, while flexible PVC is commonly used for plumbing, electrical cables, flooring, and inflatable items. PVC is a white, brittle solid available in both powder and granule forms. Known for its resistance to chemicals, weather, and corrosion, it is a durable and versatile material.
Plasticizers can be added to make PVC more flexible. It also has excellent electrical insulation properties, self-extinguishes if ignited, and is inexpensive to produce. PVC is widely used across various industries, including construction, healthcare, automotive, and packaging. It is commonly found in products such as pipes, window frames, electrical cables, medical devices, clothing, and much more.
What types of PVC materials are there?
They are many types of PVC(Polyvinyl chloride), the main types are:
Rigid PVC (UPVC or Unplasticized PVC):
This type of PVC offers high mechanical strength, weather resistance, and fire resistance. It is commonly used for pipes, window frames, and building materials. PVC-U is hard and rigid, with an ultimate tensile stress of around 52 MPa at 20°C, and is resistant to most chemicals. It is typically used at temperatures up to 60°C, though the actual limit depends on stress and environmental conditions.
Flexible PVC (Soft PVC):
Flexible PVC, or plasticized PVC, contains 30-70% plasticizers, making it elastic and moldable into complex shapes. It is commonly used for electrical cable insulation, flooring, medical tubing, and automotive interiors. The properties of plasticized PVC vary more than those of rigid PVC, and it is not used for pressure pipes.
Chlorinated PVC (CPVC):
CPVC is PVC that has been further chlorinated, increasing the chlorine content to 65-72%. This type offers better heat resistance, aging resistance, corrosion resistance, and chemical stability. It is often used in plumbing and piping, with higher temperature resistance, functioning up to 95°C.
PVC-M (Modified PVC):
PVC-M, or impact-modified PVC, includes modifiers such as acrylic and rubber to improve impact resistance. It has lower tensile strength and yield stress compared to rigid PVC.
PVC-O (Biaxially Oriented PVC):
PVC-O is created by stretching PVC to align the molecular chains, increasing strength and pressure resistance. This process enhances the material’s durability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including construction, plumbing, electrical, and automotive sectors.


What characteristics does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) possess?
PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a widely used and versatile plastic known for its durability, chemical resistance, and affordability. Here are some key points about PVC:
Electrical Properties
- Insulation: PVC is an excellent insulator due to its high dielectric strength.
Durability
- Weather Resistance: PVC is highly resistant to weathering, chemical degradation, corrosion, shock, and abrasion, making it ideal for long-lasting and outdoor applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: PVC’s resistance to corrosion ensures its durability in various environments, providing a long service life.
Flame Retardancy
- PVC is self-extinguishing, meaning it stops burning once the fire source is removed. This is due to its high chlorine content, which helps prevent the spread of fire.
Mechanical Properties
- Abrasion Resistance: PVC is tough, lightweight, and highly resistant to abrasion, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
- Strength: Rigid PVC has a yield strength ranging from 4,500 to 8,700 psi (31-60 MPa), while flexible PVC ranges from 1,450 to 3,600 psi (10.0-24.8 MPa).
Chemical Resistance
- Resistance to Inorganic Chemicals: PVC is resistant to most inorganic chemicals, including weak acids, bases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons.
- Resistance to Organic Chemicals: Some types of PVC can be damaged by ketones, esters, aromatic hydrocarbons, and nitro compounds.
Cost/Performance Ratio
- Cost-Effective: PVC is an affordable material that offers long-lasting durability with minimal maintenance.
Additives
- Plasticizers: These additives make PVC easier to work with and enhance its toughness and strength.
- Heat Stabilizers: Heat stabilizers protect PVC from degradation during manufacturing and prevent breakdown when exposed to sunlight.
What are the properties of PVC?
PVC is a thermoplastic polymer, and its properties are generally categorized into two types: rigid PVC and soft PVC.
| Property | Unit of measurement | Rigid PVC | Soft PVC |
| Density | g/cm3 | 1.3–1.45 | 1.1–1.35 |
| Thermal conductivity | W/(m·K) | 0.14–0.28 | 0.14–0.17 |
| Yield strength | psi | 4,500–8,700 | 1,450–3,600 |
| MPa | 31–60 | 10.0–24.8 | |
| Flexural strength | psi | 10,500 | — |
| MPa | 72 | — | |
| Compression strength | psi | 9,500 | — |
| MPa | 66 | — |

What are the advantages of Injection Molding PVC?
Injection molding PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) possesses several advantages, including:
- Cost-Effective: PVC injection molding is a cost-efficient method for producing large quantities of products, such as pipes, fittings, and other plastic components.
- High-Quality Products: PVC injection molding produces high-quality products with precise dimensions, smooth surfaces, and consistent wall thickness.
- Consistent Quality: The injection molding process ensures uniform quality by injecting molten PVC into the mold under high pressure.
- Fast Production: PVC injection molding enables high-volume production with quick turnaround times, making it a fast and efficient process.
- Low Labor Costs: Automation of the injection molding process reduces labor costs, benefiting manufacturers.
- Wide Range of Applications: PVC injection molding is versatile, used to create products like pipes, fittings, tubing, and other plastic components.
- Resistance to Corrosion: PVC’s resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for applications exposed to chemicals, acids, or other corrosive substances.
- Fire-Resistant: PVC is fire-resistant and produces minimal smoke, making it a good choice for applications requiring fire safety.
- Easy Installation: PVC products are easy to install using solvent cement or heat fusion, making them popular for plumbing and piping.
- Recyclable: PVC is recyclable, making it an environmentally-friendly option for both manufacturers and consumers.
- Wide Temperature Range: PVC can withstand a broad range of temperatures, making it suitable for applications with extreme temperature conditions.
- Chemical Resistance: PVC is resistant to many chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for applications exposed to chemicals.
What are the shortcomings of Injection Molding PVC?
While injection molding PVC offers numerous advantages, it also comes with certain shortcomings, including:
- Higher Up-Front Costs: PVC material is highly corrosive, and the molds are prone to rust during injection molding. Stainless steel materials like 4Cr13 or S136 are required for the molds, making the initial cost higher than for other plastic materials.
- Environmental and Health Concerns: Burning PVC releases harmful dioxins and chlorine, which are detrimental to both the environment and human health. Additionally, PVC products do not break down easily, contributing to plastic waste.
- Toxicity: PVC emits toxic fumes when burned or melted, which are hazardous to health.
- Limited Heat Resistance: PVC has lower heat resistance compared to other plastics. It can degrade during injection molding at high temperatures, releasing harmful gases.
- Limited Flexibility: PVC is a rigid material, making it difficult to form complex shapes or create products that require flexibility.
- UV Degradation: PVC can degrade when exposed to UV light over time, leading to discoloration and reduced functionality.
- Softening: PVC softens at high temperatures, which can cause it to lose its shape and performance.
- Difficult to Bond: PVC is challenging to bond with other materials, making it harder to create multi-part products.
- Limited Recyclability: Although PVC is recyclable, it is difficult to process due to its complex composition.
- Limited Color Options: PVC is difficult to color, which limits the options for achieving specific hues during injection molding.
- Moisture Absorption: PVC can absorb moisture, which may cause it to deform and negatively affect its performance over time.


Resources for The Complete Guide PVC Injection Molding Manufacturing
Can PVC be Injection Molded?
Indeed, PVC can be injection molded, and PVC injection molding is a popular manufacturing process used to create a wide range of plastic products and parts.
PVC is a versatile material, suitable for molding both flexible items, such as soft toys, and rigid structures like pipes. It is cost-effective, easily recyclable, dense, and offers high strength.
For successful PVC injection molding, it’s important to carefully consider factors such as moisture content, temperature control, injection pressure and speed, and mold design.


How to Perform PVC Injection Molding: A Step-by-Step Guide
PVC injection molding is a detailed process that turns raw PVC material into durable plastic parts. Whether you’re a beginner, professional, or student, understanding the step-by-step procedure is essential for achieving the best results. This guide will walk you through everything, from temperature settings to injection speeds, to help you master PVC injection molding.
Mold Design & Mold Material Selection:
- Mold Design: The mold should have a draft angle between 0.5° and 1° to ensure proper venting within the mold cavity.
- Vent Hole Sizes: Typically, vent hole sizes are 0.03-0.05mm deep and 6mm wide, or alternatively, a gap of 0.03-0.05mm around each ejector pin.
- Mold Material Selection: Due to PVC’s corrosive nature, it’s essential to use stainless steel materials such as 4Cr13, 2344, or S136 for the mold, depending on the production volume.
Runners and Gates:
- Regular gates can be used for most parts, but for smaller parts, needle-type or submarine gates are preferred, while fan gates are suitable for thicker sections.
- The smallest diameter for needle-type or submarine gates should be 1mm.
Injection Machine Type:
- Screw Design: A general-purpose low compression screw with a compression ratio of 2.0-2.2 should be used. The screw speed should be adjusted just enough to fill the shot before the mold opens.
- Injection Machine: Reciprocating screw injection molding machines are typically used for PVC. These machines require plasticating screws and a clamp force of 1.5 to 2.5 tons per square inch.
Drying the PVC Material:
- PVC absorbs moisture, so it must be dried at 75-90°C for 1.5 to 2.5 hours before use.
Temperature Settings:
- Barrel Temperature: Set 20°C lower than the recommended stock temperature.
- Nozzle Temperature: Set 10-20°C lower than the barrel temperature.
- Mold Temperature: Keep the mold temperature below 20°C, ensuring it doesn’t exceed 70°C.
- Melt Temperature: Maintain the melt temperature between 170°C and 190°C. Adjust the nozzle temperature to ensure the melted PVC remains in the injection cylinder.
Injection Pressure and Speed:
- Use 20-40% of the maximum allowable injection pressure, with a back pressure of 0.4-0.7 MPa.
- Set the injection speed to medium, but reduce it for thicker parts.
Processing Time:
- Processing PVC parts typically takes 30-60 seconds, depending on factors like part size, dimensions, and mold temperatures.
Injection Molding PVC Specifications
Here are some common specifications for injection molding PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride):
Material Properties:
| PVC Resin | UPVC (unplasticized) or CPVC(plasticized) depending on the application |
| Density | 1.35-1.45 g/cm³ |
| Melt Flow Index (MFI) | 3-15 g/10 min (depending on the grade) |
| Vicat Softening Point | 70-120°C |
| Tensile Strength | 40-60 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 100-300% |
| Flexural Strength | 60-100 MPa |
Tooling and Mold Design:
| Mold Material | Stainless steel mold materials(4Cr13, 2344, S136) Choose different mold materials according to product quantity |
| Mold Temperature | 50-100°C |
| Cooling System | Water or air cooling |
| Gate Type | Sub-gate, edge gate, or corner gate |
| Ejection System | Mechanical or hydraulic ejection |
Injection Molding Process:
| Melt Temperature: | 180-220°C |
|---|---|
| Injection Pressure | 50-150 bar |
| Injection Speed | 10-50 mm/s |
| Cooling Time | 10-30 seconds |
| Ejection Force | 5-20 kN |

Design Guidelines for PVC Injection Molding
Here are some design guidelines for PVC injection molding to ensure your parts meet the required specifications and standards while being produced efficiently and cost-effectively.
- Wall Thickness: The ideal wall thickness for PVC is between 1.2-3.5mm. Too thick walls can lead to sink marks, warping, and longer cycle times, while too thin walls may result in weak parts or incomplete filling.
- Ribs: Ribs should be 0.5-0.7 times the nominal wall thickness. To prevent sink marks, the height of the ribs should be no more than three times the rib thickness.
- Draft Angles: Ensure a minimum draft angle of 1-2 degrees on all vertical surfaces to aid in easy part ejection. If the surfaces are textured, consider a draft angle of 3-5 degrees.
- Corners and Edges: Avoid sharp corners. Use rounded corners with a radius at least 0.5 times the wall thickness to reduce stress concentrations and improve material flow.
- Bosses and Threads: For threads, use threaded inserts instead of molding threads directly into the part. Integral bosses should have a draft angle and rounded corners to ensure ease of production and proper material flow.
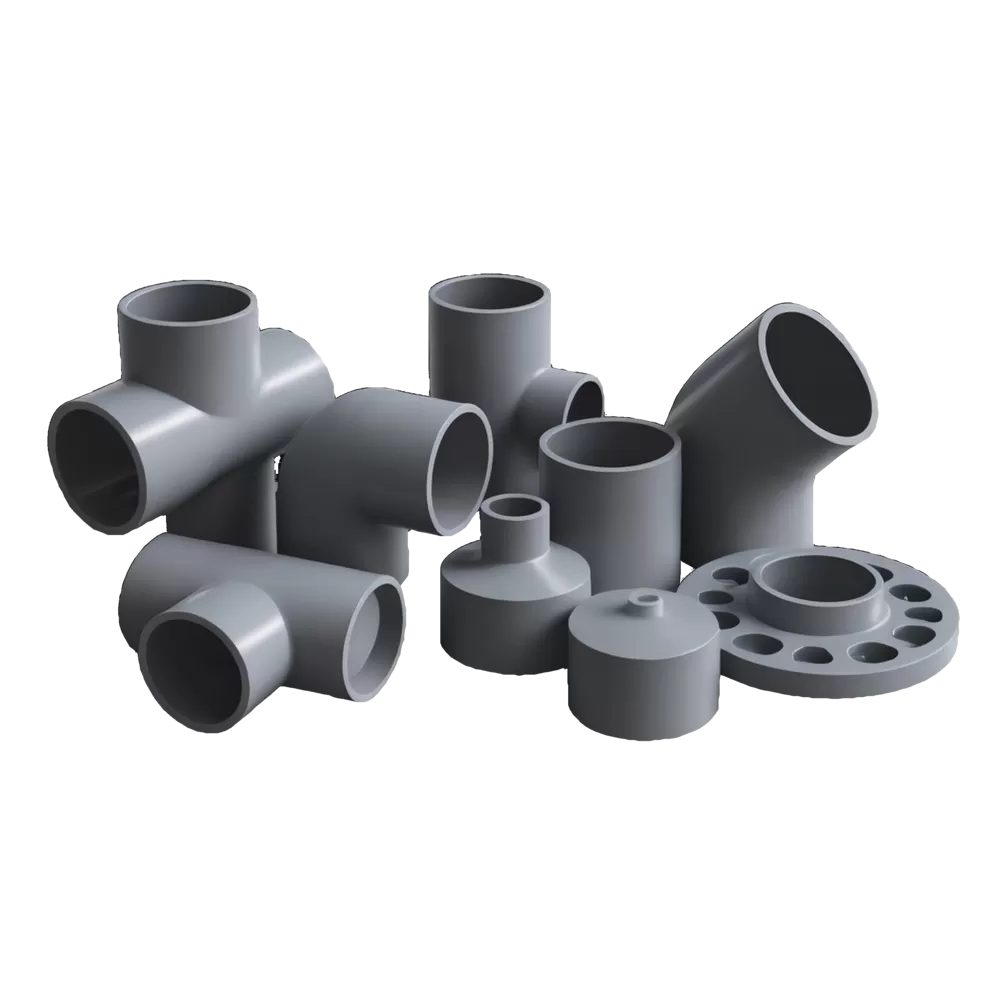
What are the Applications of PVC Injection Molding?
PVC injection molding is a versatile process that can make all kinds of stuff, like:
- Pipe Fittings: PVC injection molding is commonly used to produce pipe fittings such as elbows, tees, couplings, and adapters for plumbing and piping systems.
- Electrical Components: PVC injection molding is used to manufacture electrical components like connectors, sockets, and switches for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
- Medical Devices: PVC injection molding is utilized in the healthcare industry to produce medical devices like syringes, test tubes, and medical tubing.
- Furniture: PVC injection molding is employed to create furniture components, including chair legs, table bases, and cabinet hardware for the furniture industry.
- Toys and Games: PVC injection molding is used to make toys and games such as action figures, dolls, and board game pieces for the toy industry.
- Agricultural Equipment: PVC injection molding is applied in the agricultural sector to create equipment like irrigation systems, farm machinery, and animal husbandry tools.