Apparently, plastics products have become fundamental in modern lifestyles, regardless of regions and lands. However, how could plastics become so widely applied, while only 20 to 30 types of plastics are commonly applied? The answer is modification, the predominant approach for better polymer material. Today, taking PVC material as an example, we’ll learn about how modification improve the performance and functionality of common plastic material further to fulfill a wider range of modern life demands. If you intend to learn more about PVC plastics’ variations, this post won’t let you down. As an experienced plastic molding manufacturer and provider, we are always ready to share practical insights and provide premium service with our partners.
1. Introduction to PVC Modification
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC or vinyl) is a thermoplastic polymer which excels in economy and versatility. You can almost find PVC products everywhere, like building and construction sites, window and door profiles, pipes (both for potable water and wastewater), wire and cable insulation, medical devices, among others. It ranks among the world’s top three thermoplastics alongside polyethylene(PE) and polypropylene(PP). However, PVC performs badly in multiple processing and molding properties. For example, its high melt viscosity results in low fluidity which impedes processing procedures. Also, its instability under high temperature could easily leads to thermal decomposition. It also lacks resistance against aging, hardening, cracking and low temperature, meanwhile exhibiting an inferior toughness. Generally, modification is required to compensate for these shortcomings.
2. Various Modification for PVC
▶2.1 Chemical Modification
Chemical modification includes copolymerization, grafting reactions, and chlorination.
- Copolymerization Modification: Combining two monomers(original PVC and the added) to complete the copolymerization of vinyl chloride. Copolymerizing is essential for boosting PVC material’s properties, these improvments include processing performance optimization, lower molding temperature, new practical applications, or even developing innovative brand new materials. Meanwhile, common added monomers include vinyl acetate(EVA), vinylidene chloride, acrylonitrile, acrylates, maleic anhydride, and others.
- Grafting Reaction: Introducing additional monomer groups or another polymer onto the PVC side chain through grafting reactions. For example: In order to improve the materials overall performance, we have to control the quantity and polymerization degree of the vinyl chloride segments. To achieve that, we graft ethylene-vinyl acetate with vinyl chloride, resulting in an enhanced impact & aging resistance, and improved low-temperature brittleness for this modified material.
- Chlorination: This modification aims to elevate PVC’s heat resistance, allowing it to withstand temperatures 35–40°C higher than standard PVC, which is known as Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC). As for the modification process itself, it’s about chlorinating the material using the aqueous suspension method (or gas-phase method), increasing its chlorine content from the original 57% to approximately 65%. CPVC also boasts a higher density than PVC at 1.7 g/cm³ as well as superior flame resistance & tensile strength. The only drawback is its inferior impact strength. Multiple techniques are available for CPVC products manufacturing, including extrusion, injection molding, or calendering . Thanks to their unique versatility, this material is applied widely, including manufacturing pipes, sheets, profiles, foamed materials, adhesives, coatings, and modifiers.
▶2.2 Physical Modification
Physical modification enhances performance by incorporating additives, fillers, blends, or reinforcements.
1.Filling modification optimizes material properties by integrating inorganic/organic fillers, such as:
-Adding Acrylates Copolymer(ACR) boosts the molding and processing performance of PVC materials.
-Incorporating internal/external lubricants or polyethylene wax improves viscosity and flowability.
-Thermal stabilizers to boost heat resistance during processing while lowering decomposition temperatures.
-Antioxidants and UV inhibitors to extend product lifespan against aging.
Plasticizers to improve material plasticity and increase product flexibility.
2.Blending modification involves mixing two or more polymers to combine their advantages, such as:
-Adding wood flour reduces the specific gravity of PVC products, making them closer to natural wood.
-Metal powders like copper or aluminum boost electrical conductivity, while ferrite magnetic powder elevates magnetic performance.
-Calcium carbide increases hardness while cutting material costs, and red mud improves heat and light aging resistance—all while reducing expenses.
Some high-aspect-ratio fillers are also available for blending modification, including Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene(ABS), Methyl Methacrylate-Butadiene-Styrene (MBS), polyacrylates, Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE), EVA, nitrile rubber, EPDM rubber, CPVC, and dioctyl maleate.
3. Additionally, PVC properties can be enhanced through reinforced modification, cross-linking modification, foaming modification, radiation modification, and other advanced PVC modification techniques.
For instance, reinforcing with high-aspect-ratio mica powder;
-cross-linking with dicumyl peroxide (DCP) to boost strength;
-reducing PVC product density with azodicarbonamide foaming agents;
or irradiating with cobalt rays for superior strength.
3. Downstream Applications of Modified PVC Materials
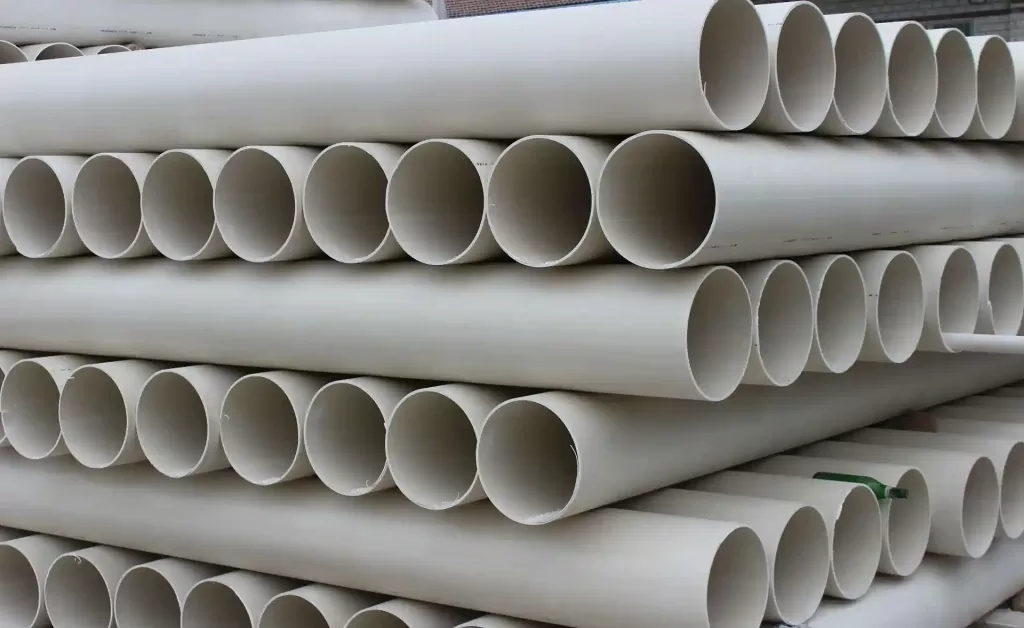
▶3.1 PVC Piping
The industry has seen an influx of small and medium enterprises in recent years, which has led to severe homogenization of mid-to-low-end products and therefore intensified market competition. This situation arises from the fact that technological and capital barriers in plastic pipe manufacturing are relatively low and accessible. PVC pipes, being the earliest adopted and most widely used plastic piping material in China, have seen a declining market share due to inconsistent production standards and uneven product quality among some manufacturers in recent years. PVC pipes exhibit excellent properties including easy installation, high resistance against pressure, flame, and weather, as well as superior ring stiffness and service lifespan. They are extensively applied in construction, municipal water supply/drainage, power, agriculture, and telecommunications sectors (primarily rigid products).
Looking ahead, several innovative PVC products will see tremendous growth potential in the plastic piping market, including large-diameter solid-wall PVC-U pipes, high-toughness PVC-M pipes, and small-to-medium diameter PVC-O pipelines .

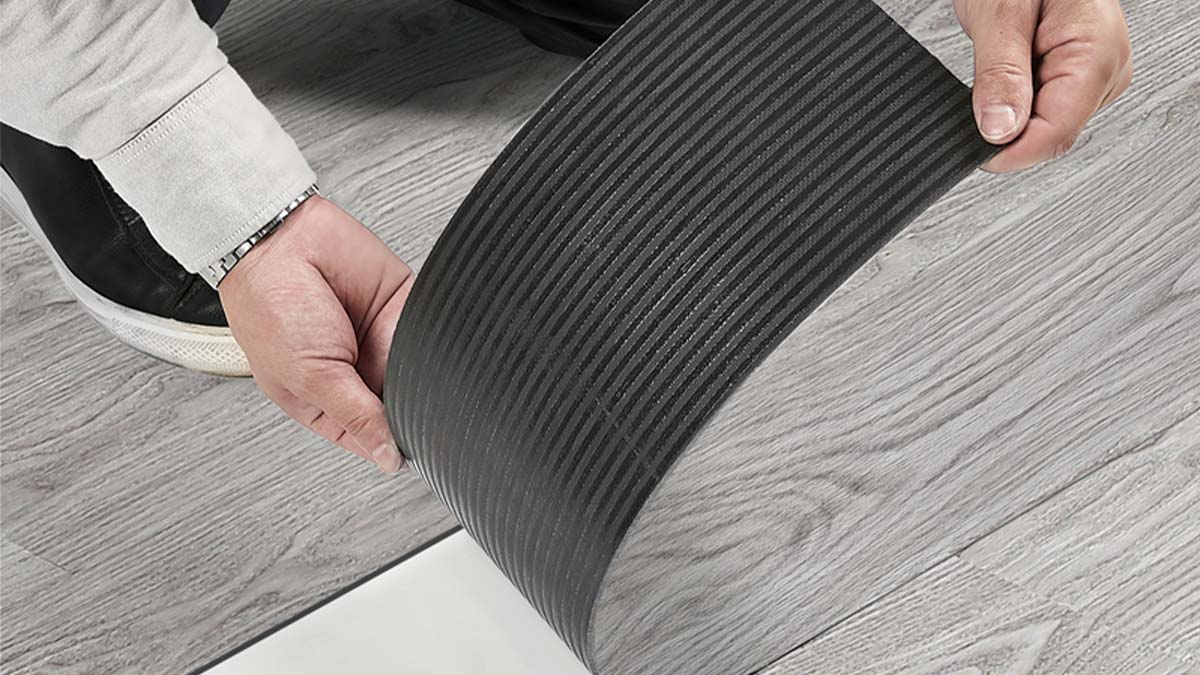
▶3.2 PVC Flooring
Currently, PVC flooring in China is predominantly utilized in public infrastructure, serving as pilot projects verifying its feasibility and utility, The choices include schools, hospitals, bus stations, and other populated public zones. During the pandemic, PVC flooring has played a pivotal role in the early containment efforts, aiding the rapid construction of temporary hospitals. Thus the public has become more aware of PVC flooring, paving the way for expansion in post-pandemic domestic market . The 2019 market demand shows promising prospects for PVC flooring, fueled by upgrades in public consumption and the thriving renovation trend. China’s growing eco-consciousness is unlocking fresh opportunities for innovative green building solutions.

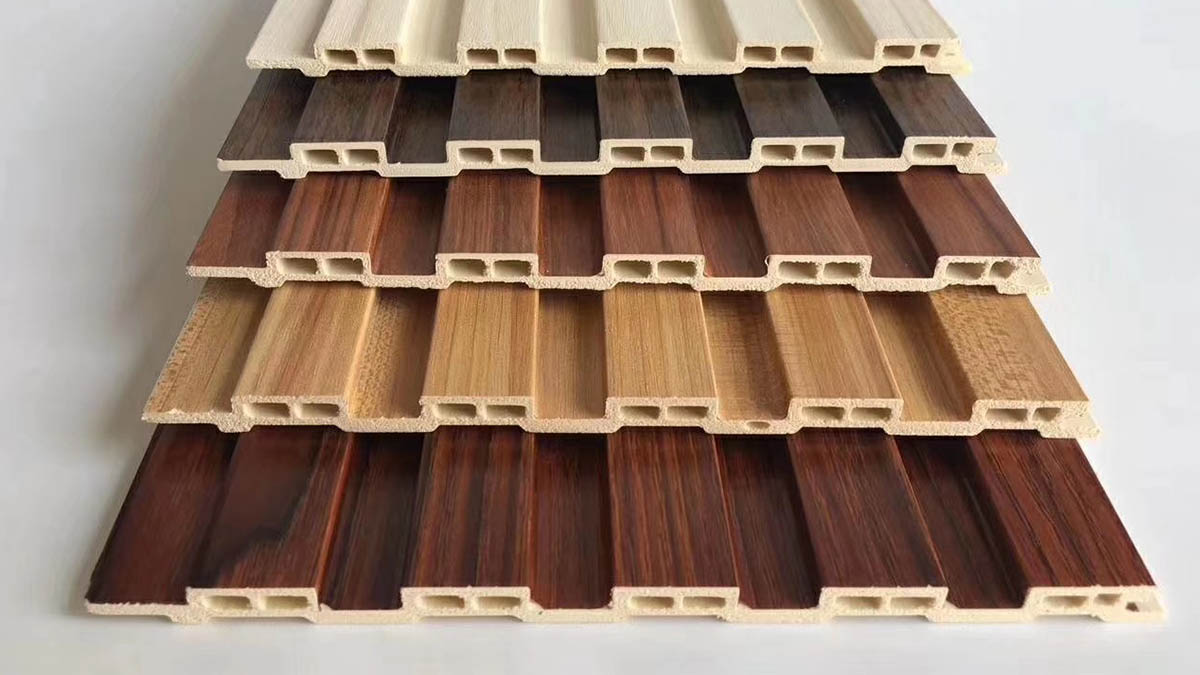
▶3.3 PVC Wood-Plastic Wall Panels
PVC Wood-Plastic Wall Panel is an innovative eco-friendly composite material. Crafted from bamboo powder, wood powder, calcium powder, and PVC, it undergoes high-temperature extrusion for seamless one-step molding. These panels showcase vibrant patterns rivaling wallpaper, paint, and stone finishes, while delivering a luxurious 3D visual effect and exquisite textured touch which is certain to become the ultimate upgrade to traditional wall coverings. The future of PVC wood-plastic integrated wall systems is evolving rapidly, with increasing market acceptance for whole-ceiling and whole-house concepts.

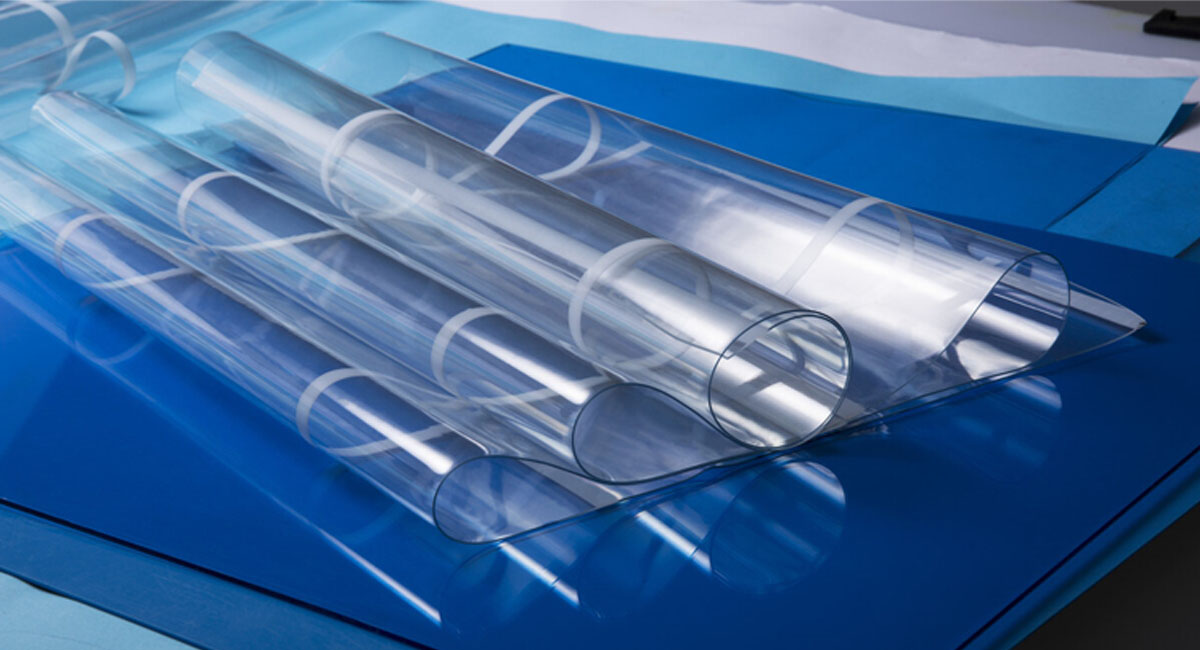
▶3.4 PVC Flexible Film
Soft PVC film products’ thickness ranges from 0.025~0.750mm and width up to 4m. And PVC Crystal Sheets available in thickness from 0.5~8.0mm and width up to 2m. Suspension-processed general-purpose PVC resins are typically used for producing flexible PVC calendered films, , with SG-5 and SG-3 being the most widely applied. Additionally, SG-7, SG-8, SG-1, SG-0, and matte PVC resins are also utilized based on specific product requirements. Today, PVC product manufacturers are demanding increasingly higher standards for resin performance in the advocation of high-quality development. By refining product models and offering a wider variety of PVC resins, the quality of soft PVC calendered films can be significantly enhanced, further solidifying their applications in the industry.

4. Conclusion
PVC is a widely used but limited thermoplastic. Modification is necessary to expand its functionality. Through chemical methods like copolymerization and chlorination, it gains heat resistance and durability. Physical modifications—additives, blending, and reinforcements—enhance flexibility and strength. These improvements expand PVC’s applications, from heat-resistant CPVC pipes to eco-friendly wood-plastic composites and flexible films. Modification ensures PVC remains versatile for construction, packaging, and industrial uses.
Want to get your PVC injection part manufactured? You are at the right place! As a reliable molding factory, KingStar excels in our dedicated expertise as well as advanced technique including various modification techniques. If you need detailed suggestions, or would like to develop further cooperation with us, please contact us at sales@kingstarmold.com.