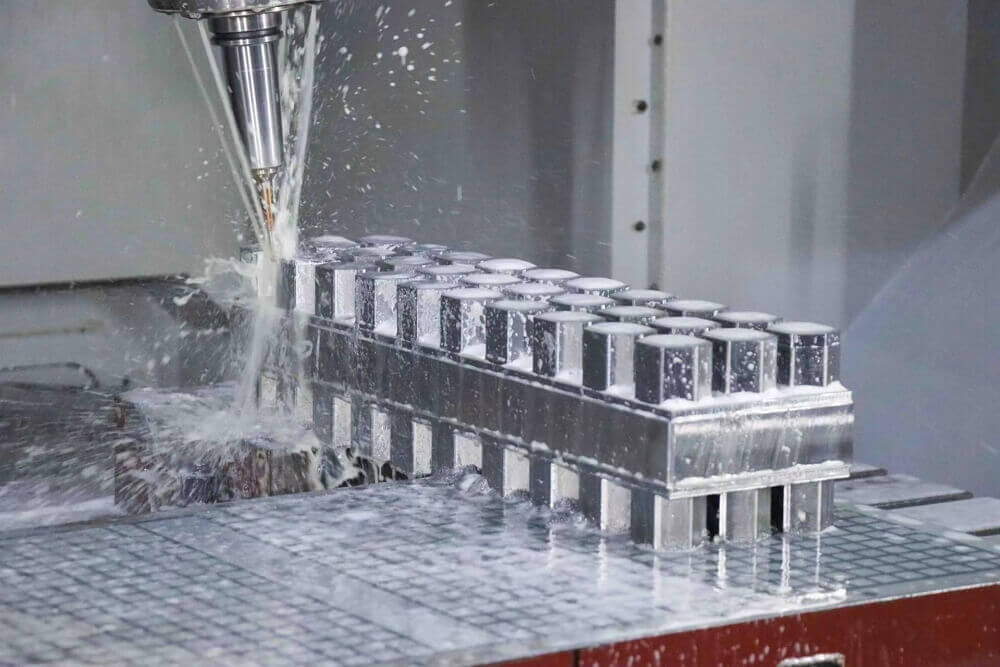
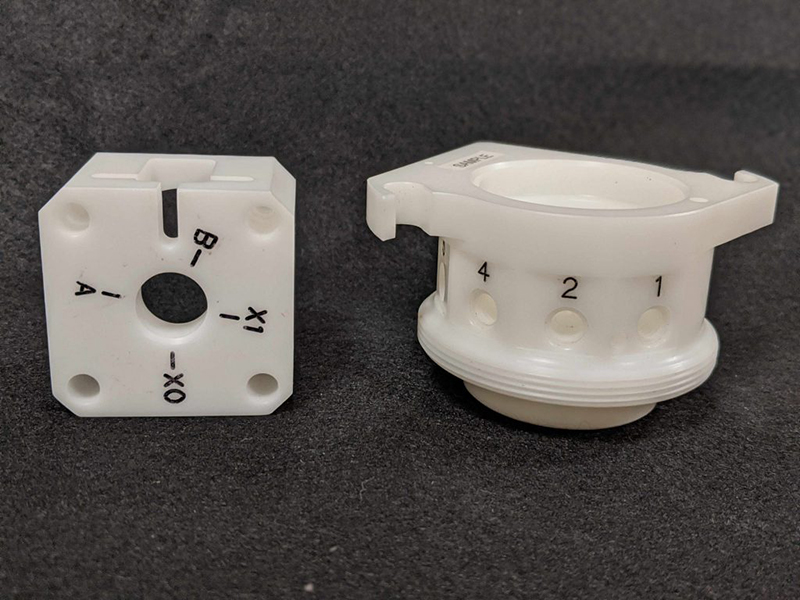
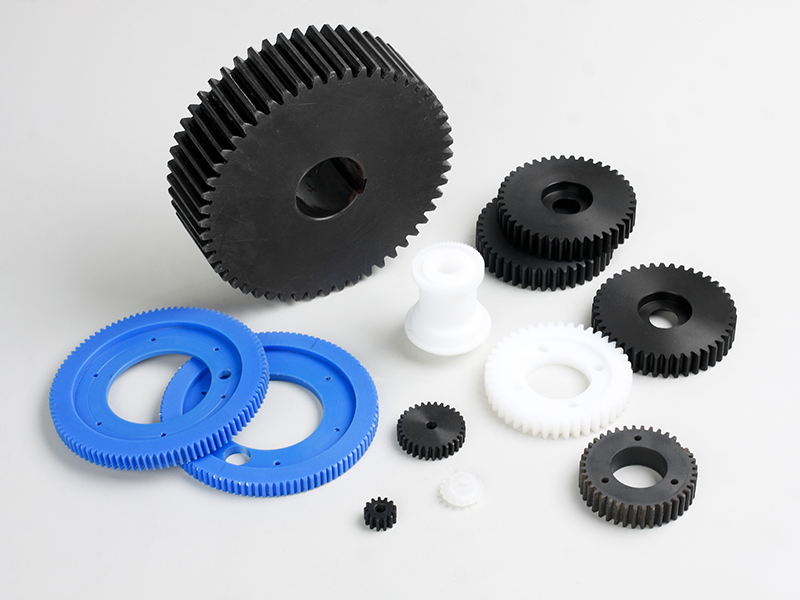
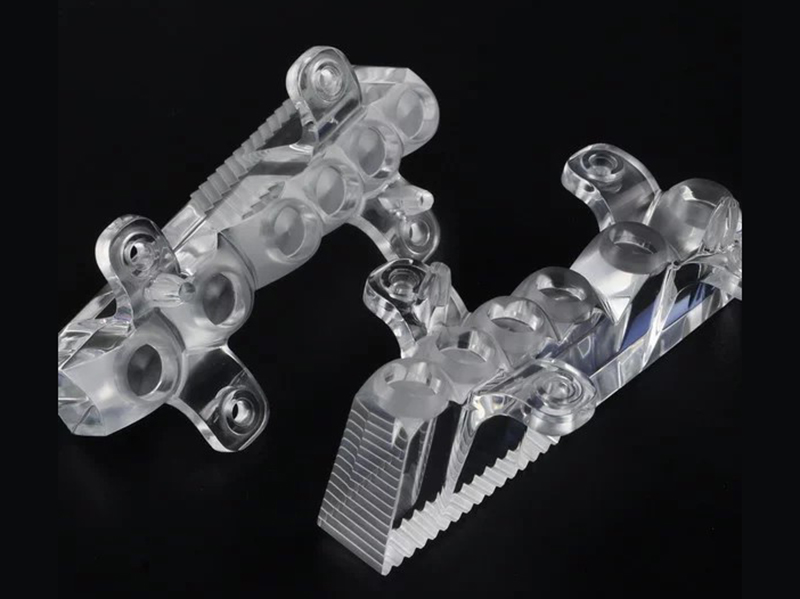
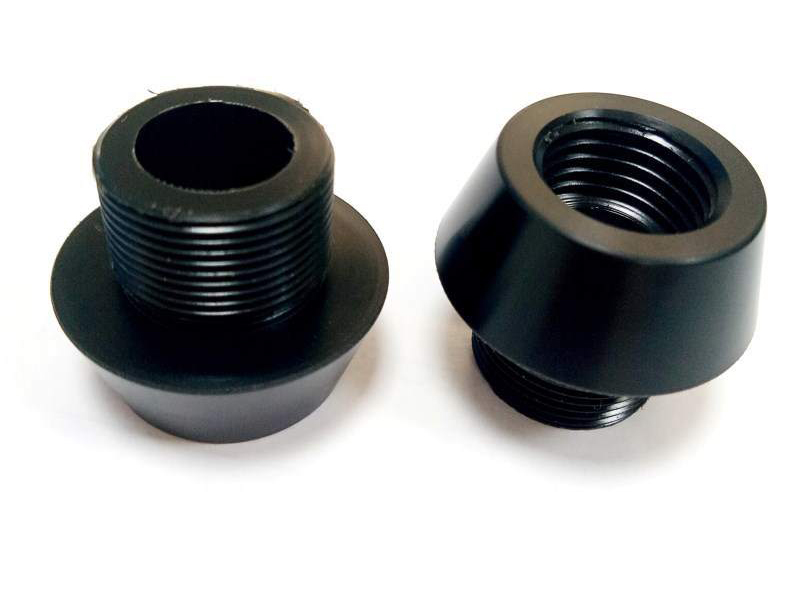
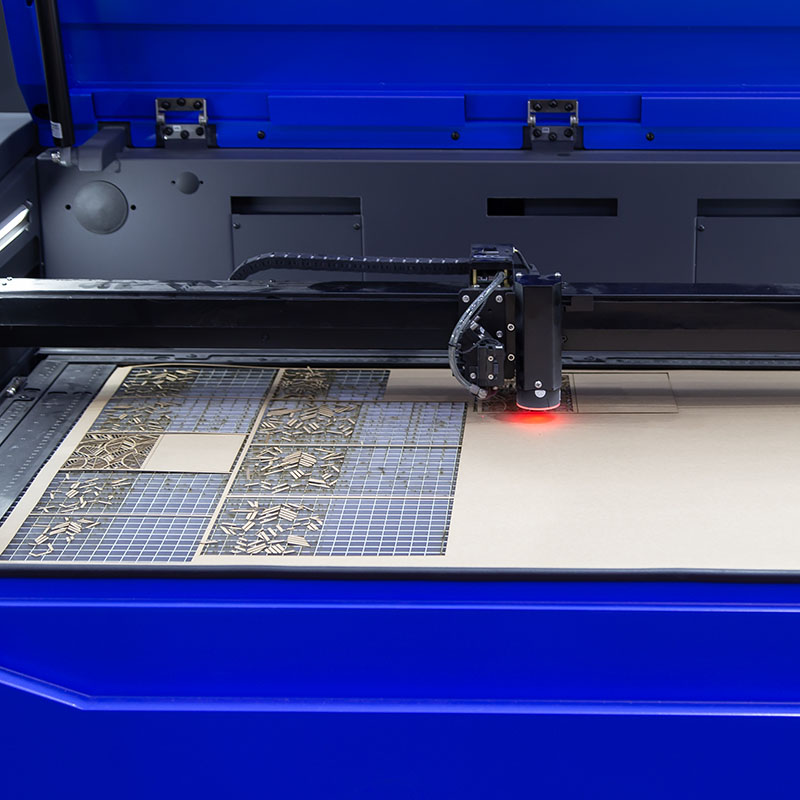
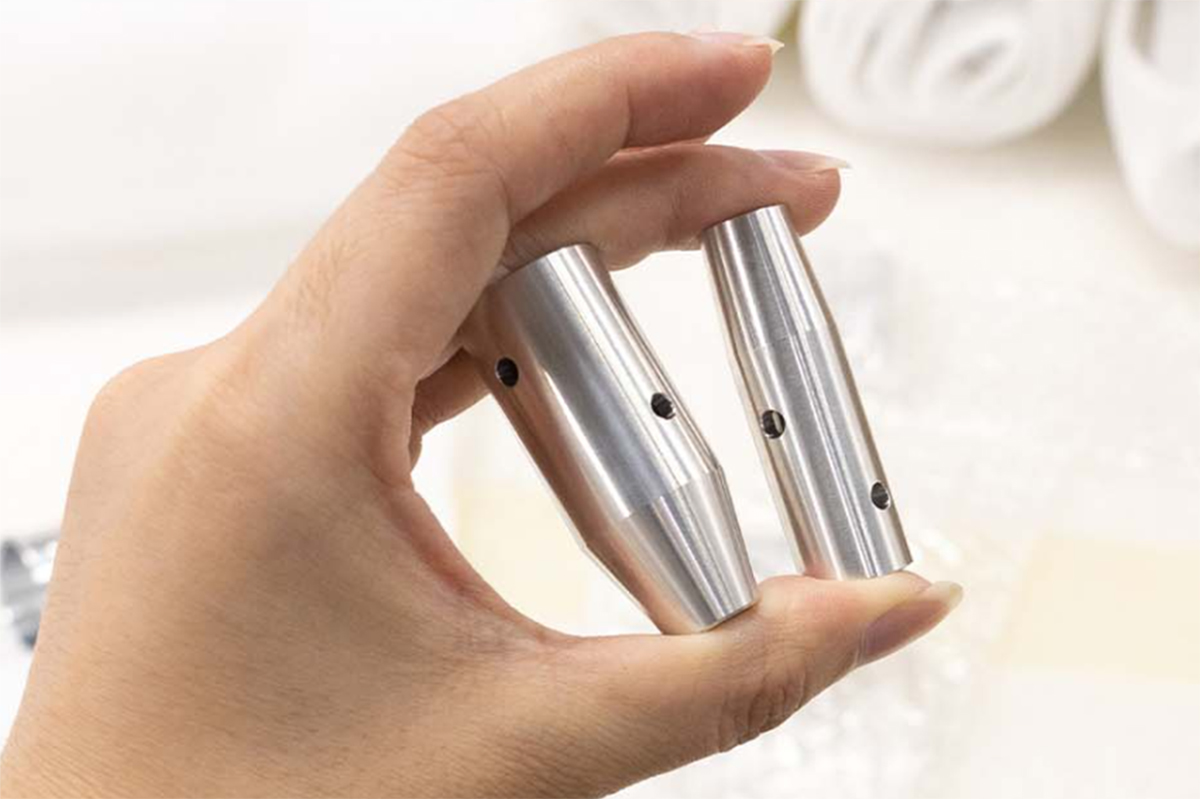
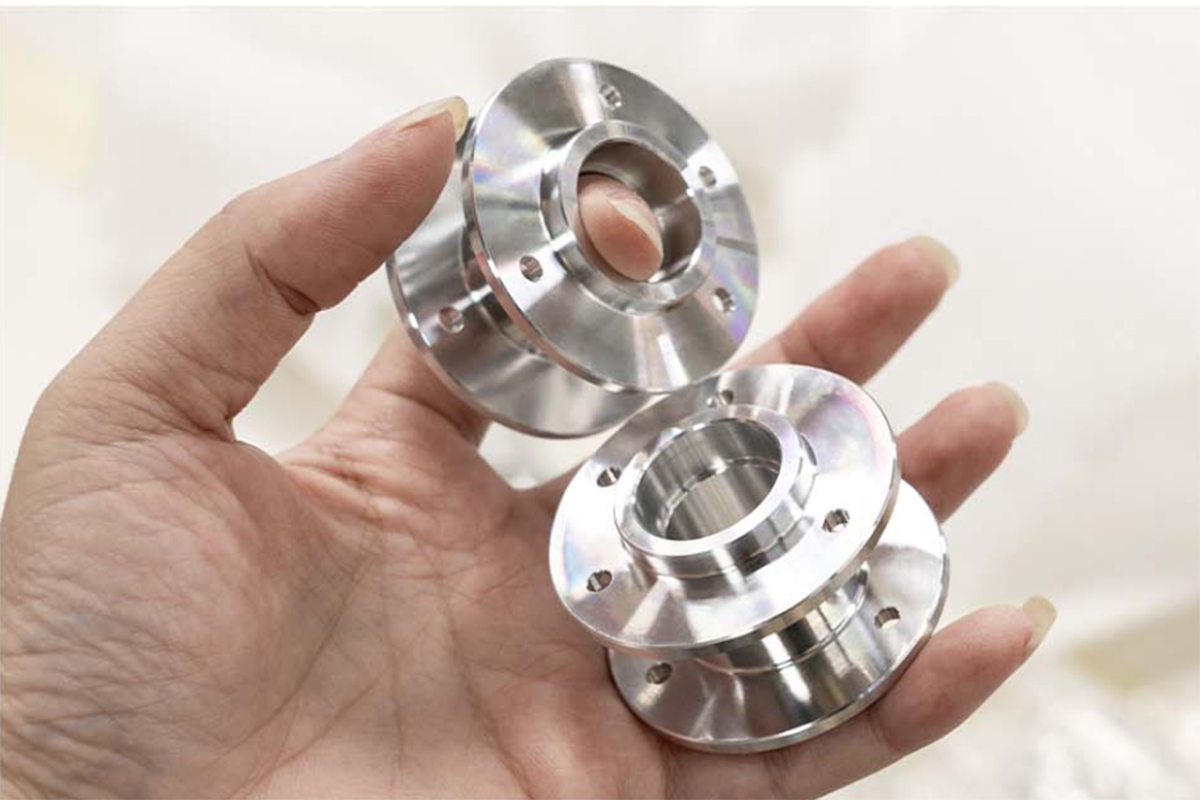
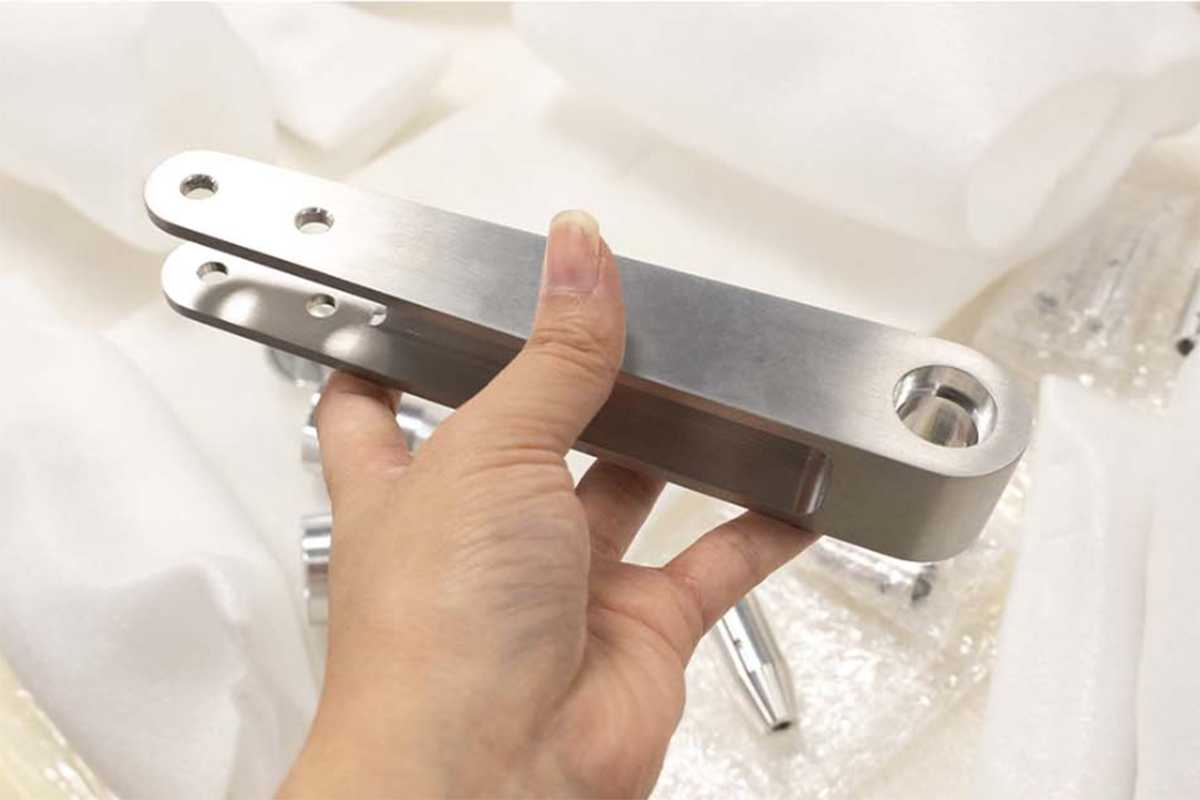
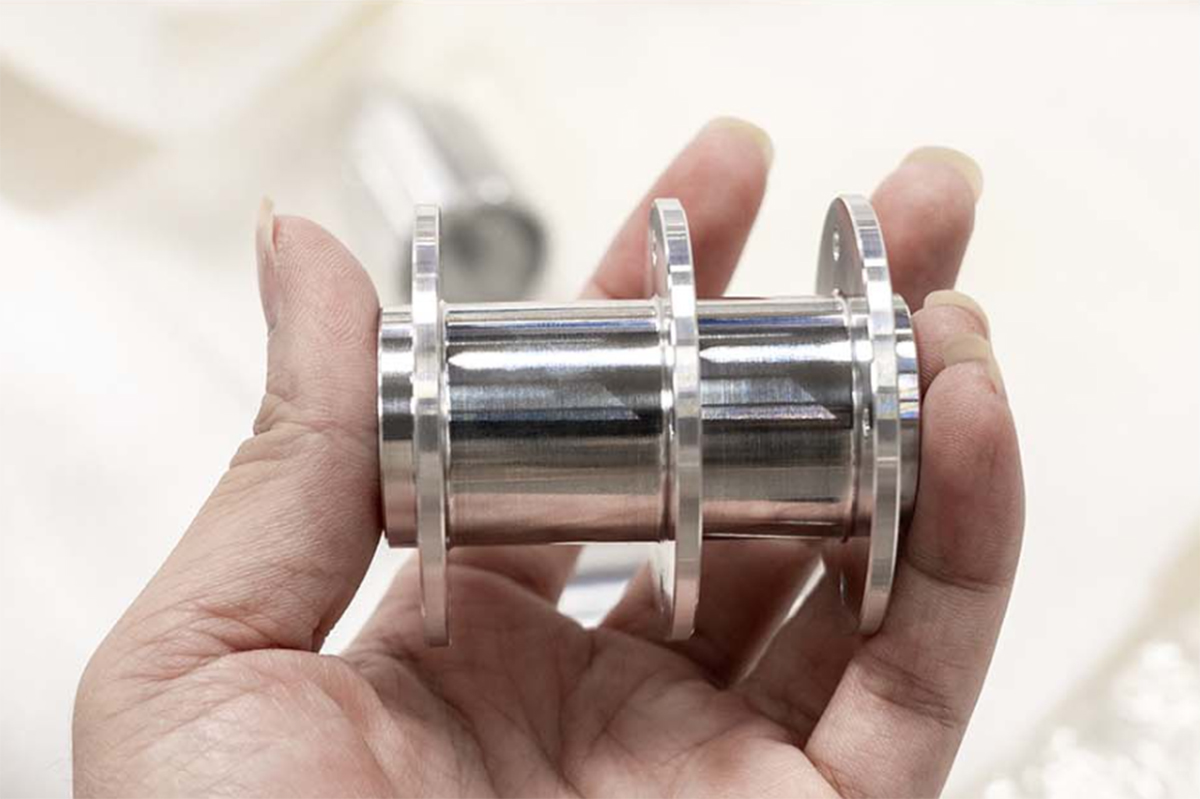
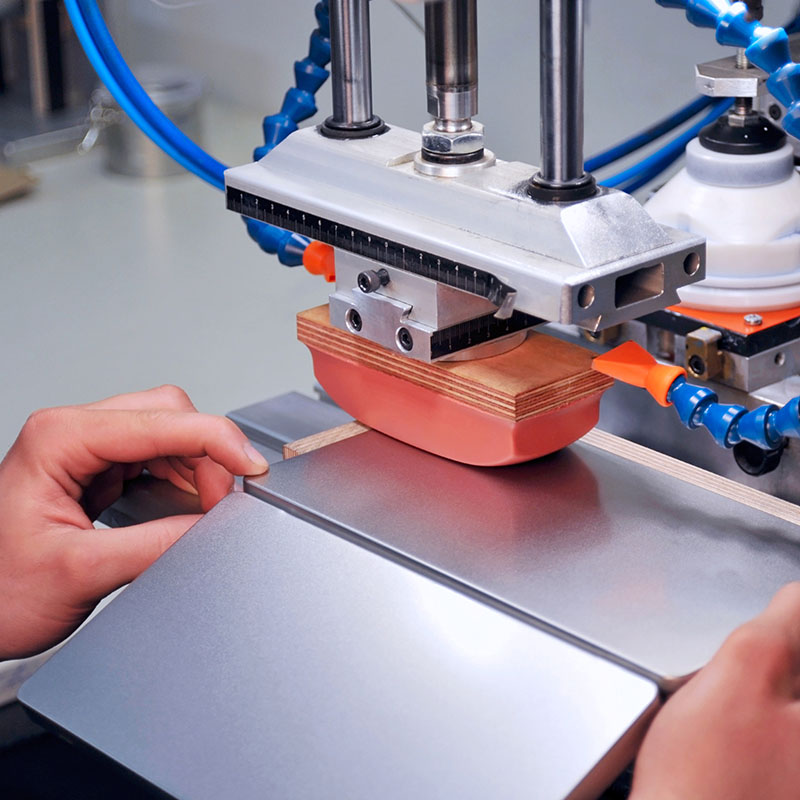
CNC Machining: An Overview
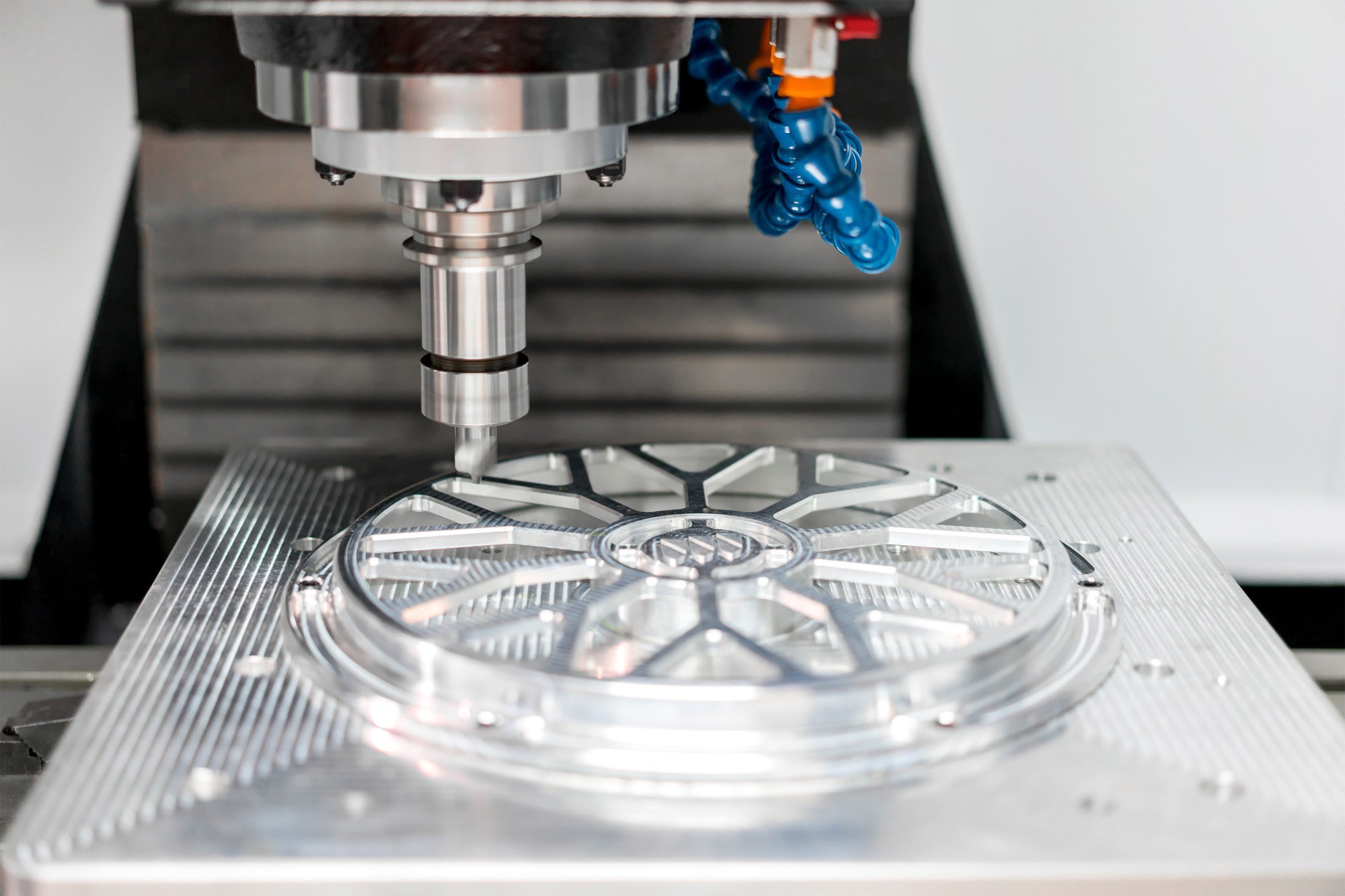
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, a manufacturing process that uses computerized controls and tools to precisely remove layers of material from an existing stock piece (the blank) to create a fully custom-designed component.
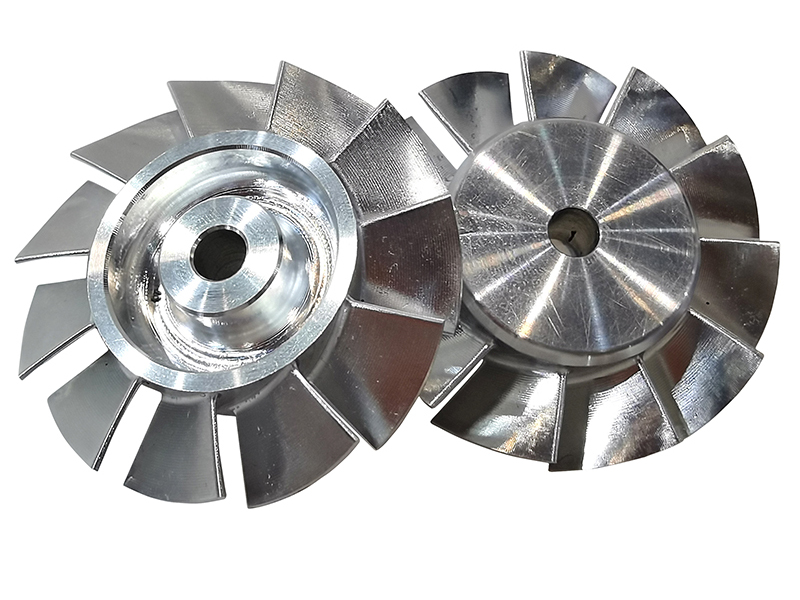
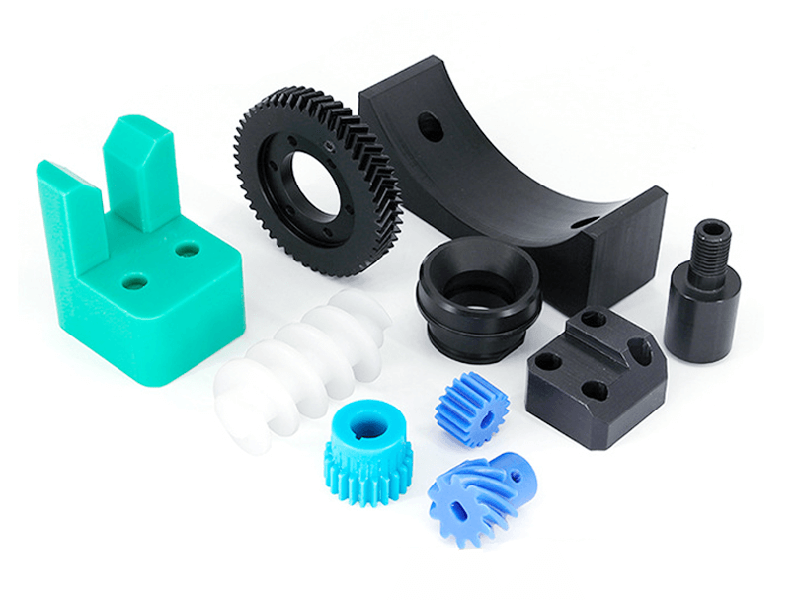
CNC machining is highly versatile and capable of working with various materials, including metals, plastics, woods, glass, foam, and composites. This flexibility makes it one of the most widely used manufacturing processes, including at KingStar Mold. Industries like telecommunications particularly benefit from CNC machining due to the high tolerances it provides compared to other methods.
Four Stages of CNC Machining
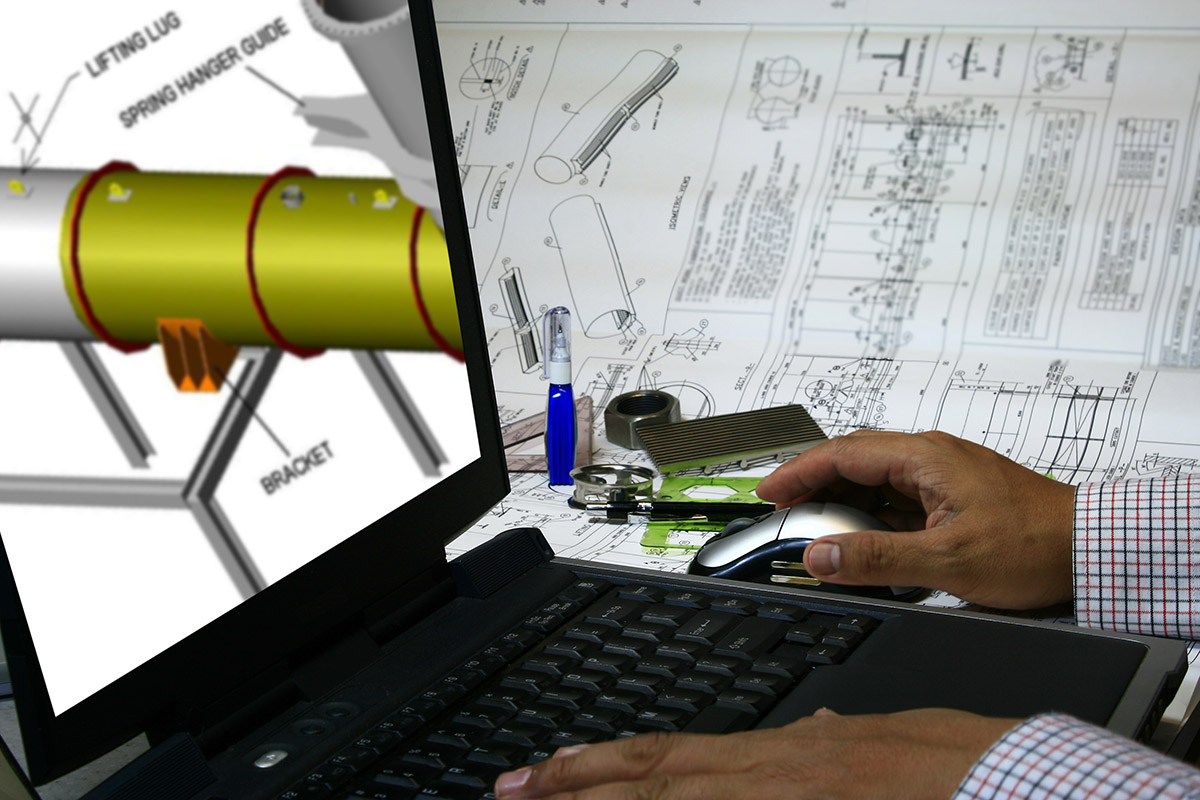
Model Design
This is the initial stock model upon which the product will be designed. Typically created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, this digital model provides the foundation for the manufacturing process. The design instructions are then fed into the manufacturing line.

Conversion
In this stage, the computer-aided design (CAD) is converted into machine-readable code, allowing the CNC machine to accurately produce the custom-designed part based on the provided specifications.

Machine Preparation
Before the CNC program can be executed, the machine must be properly prepared. This includes installing the necessary components, such as spindles, drill bits, and end mills, and ensuring all accessories are in place for optimal performance.

Execution
With everything set, the machine executes the program, using the tools to precisely manufacture the product in accordance with the design specifications fed into the system.
Reliable CNC Machining Company
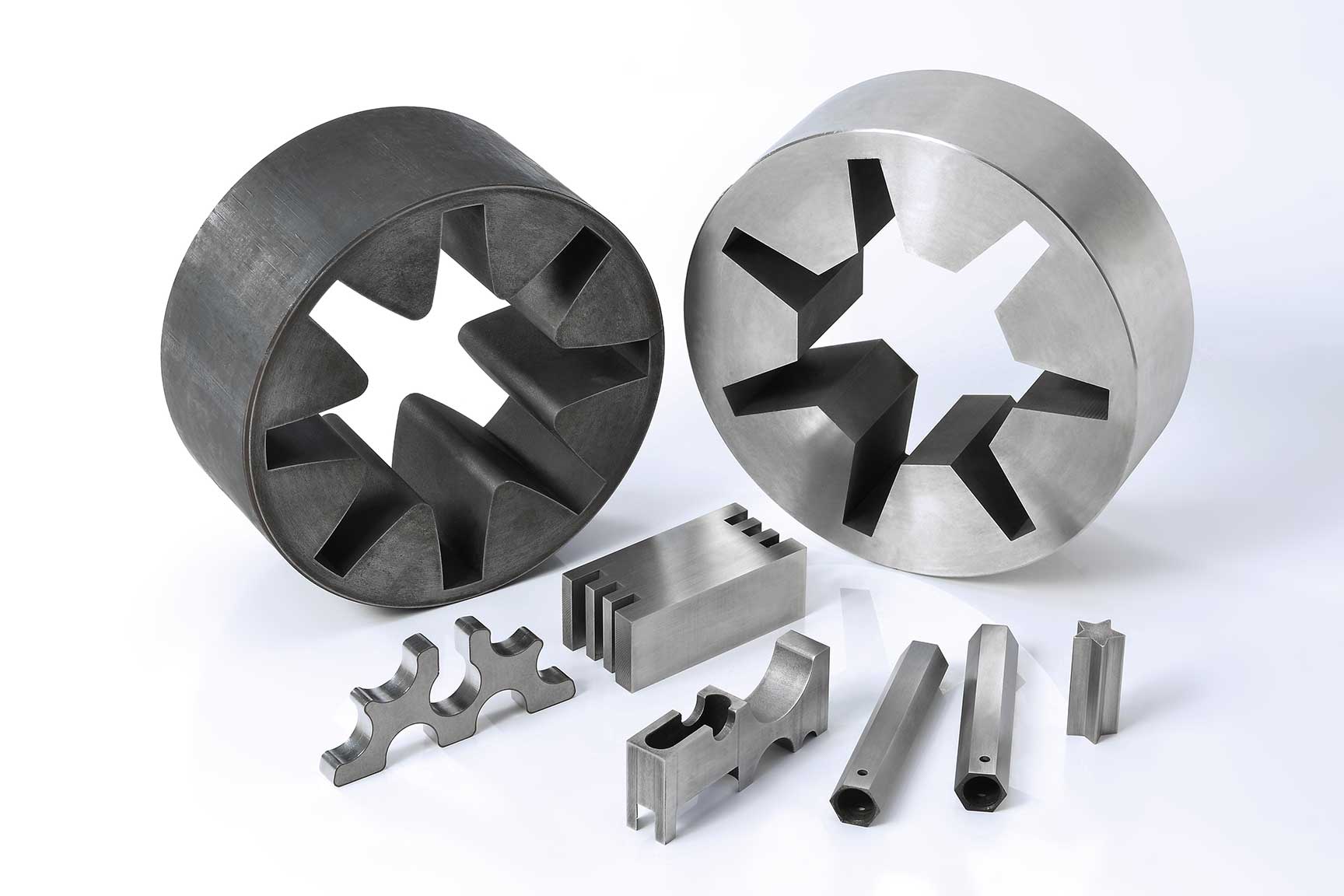
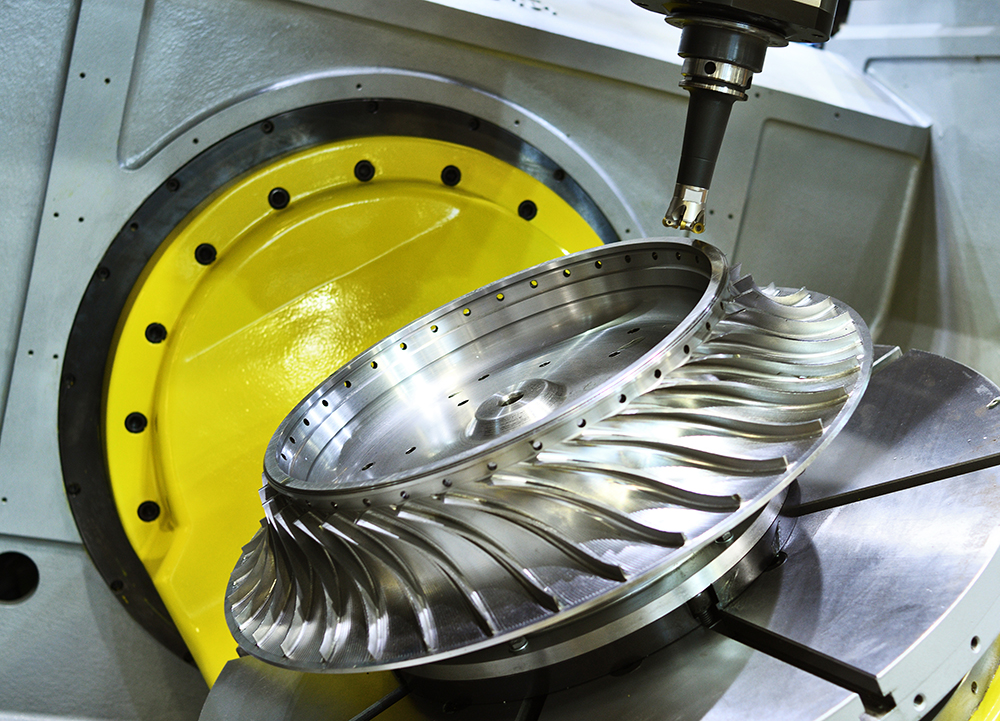


Precision CNC Machining for Plastic and Metal Components
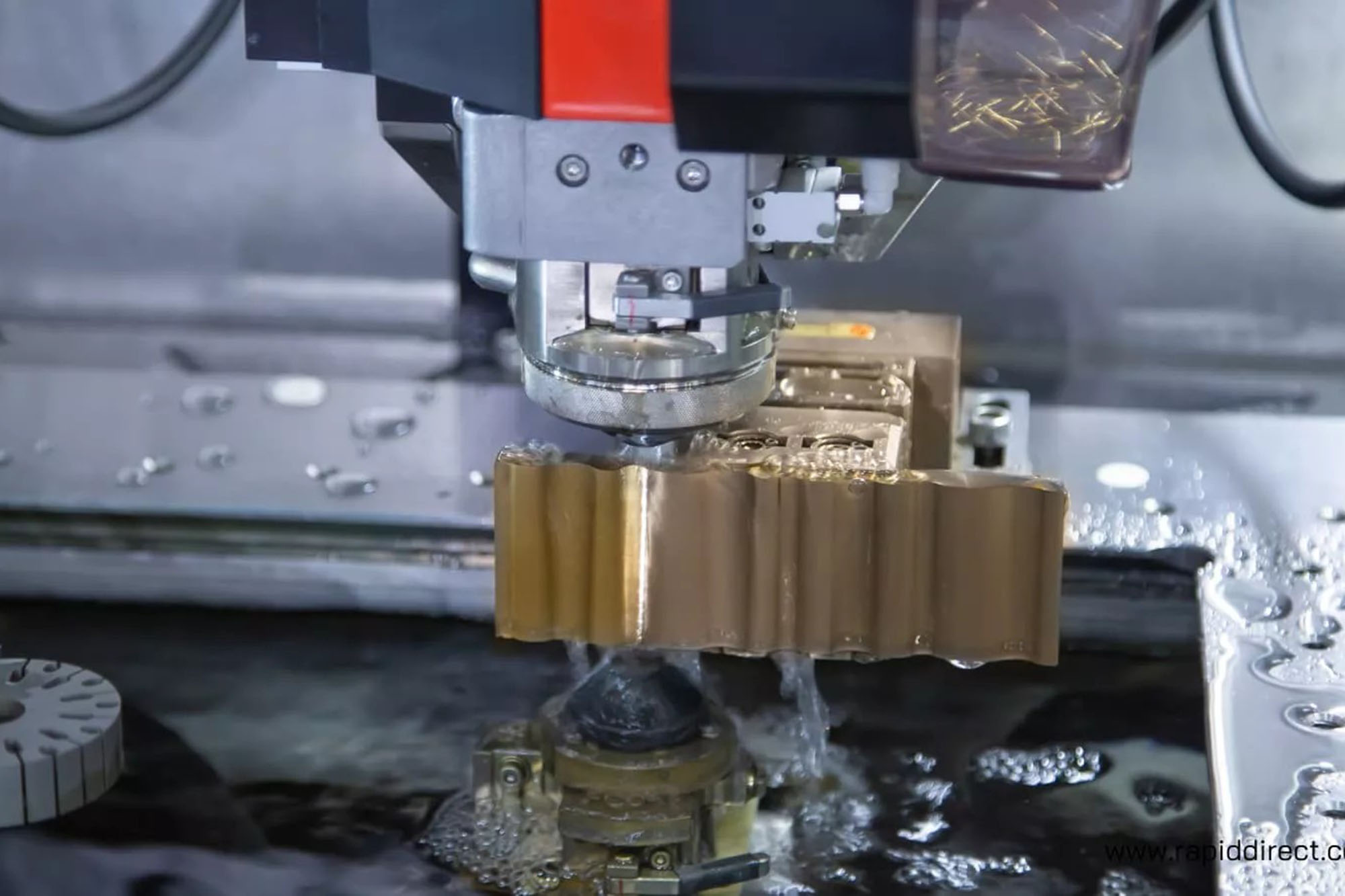
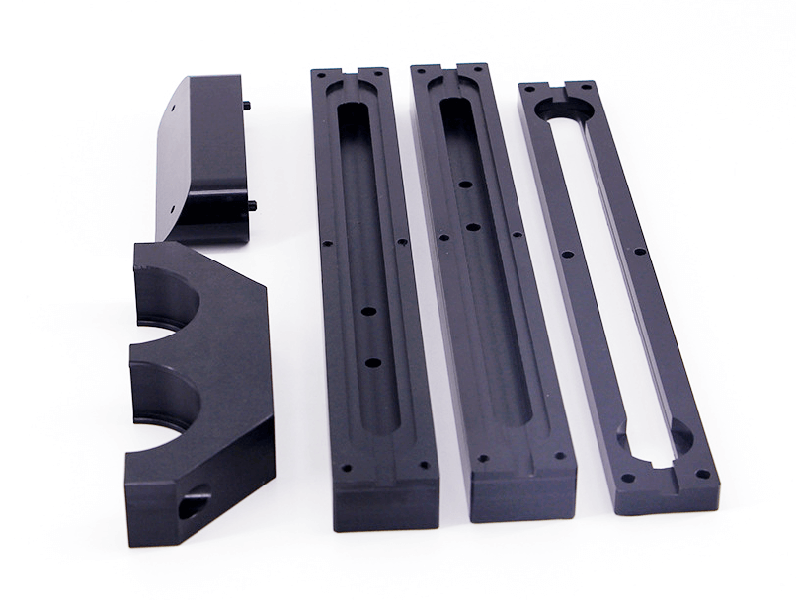
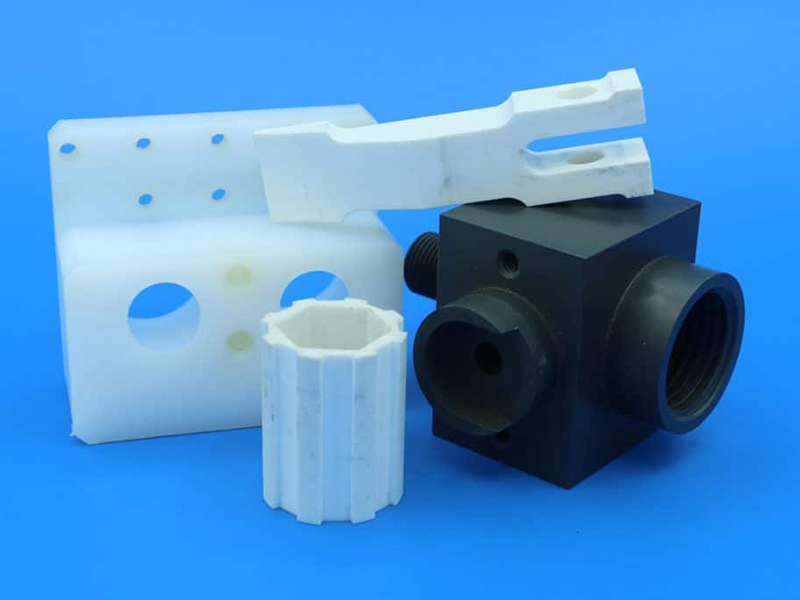
At KingStar Mold, we provide tailored CNC machining solutions designed to meet the unique needs of your project. Our expertise includes 3, 4, and 5-axis CNC machining, CNC turning, and high-precision machining, working with a wide variety of materials such as engineering-grade plastics, aluminum, stainless steel, bronze, and titanium. We can handle parts up to 80″ x 48″ x 24″ and deliver tight tolerances as small as 0.005″ for even the most intricate designs.
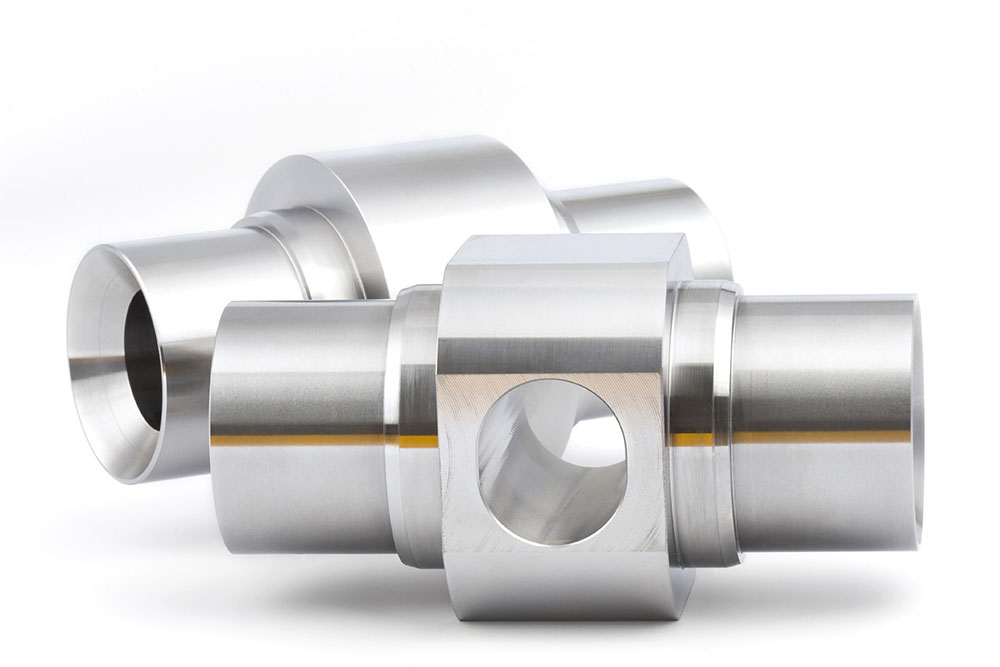

Metals

Plastics

Composites
| Our Capabilities | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximum Machine Size | 3000 × 1200 × 850 mm |
| In-House Equipment | Over 100 machines |
| Supported Materials | More than 200 options including metals, plastics, and carbon fiber |
| Typical Tolerances | ±0.05 mm for metals, ±0.2 mm for plastics |
| Production Lead Time | As fast as 4 days |
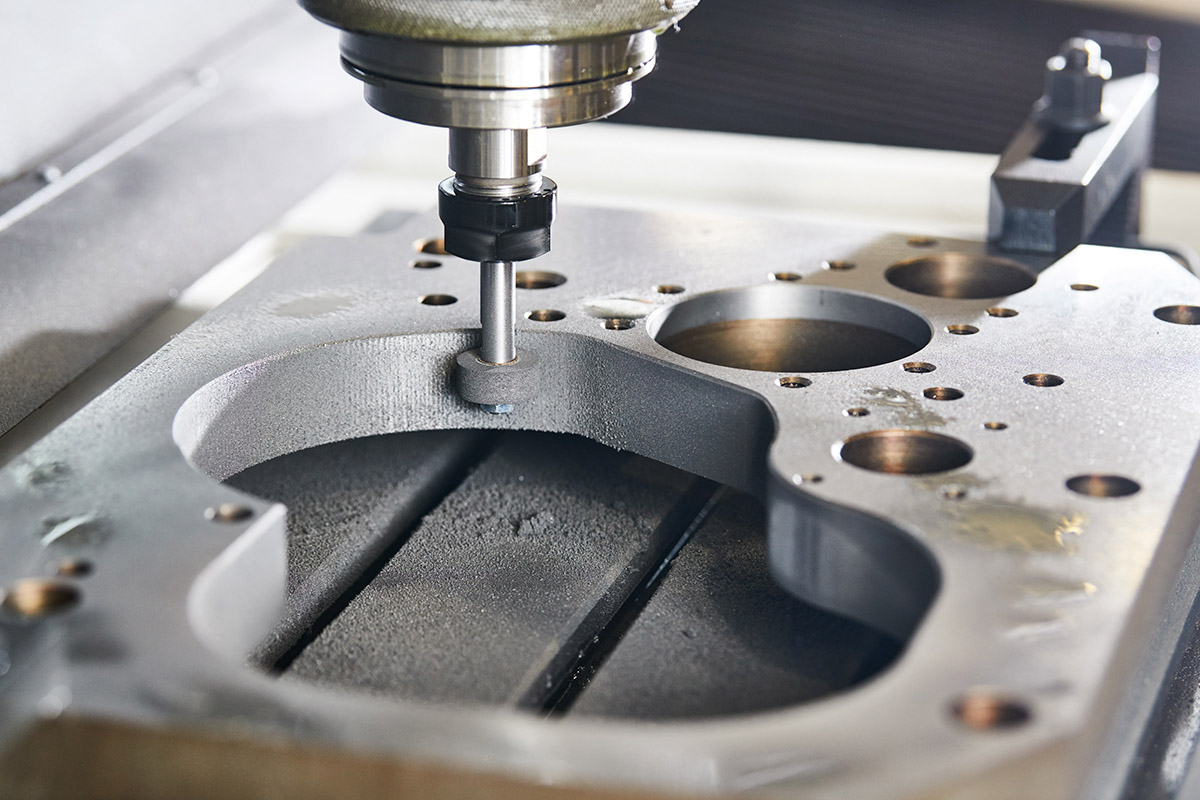
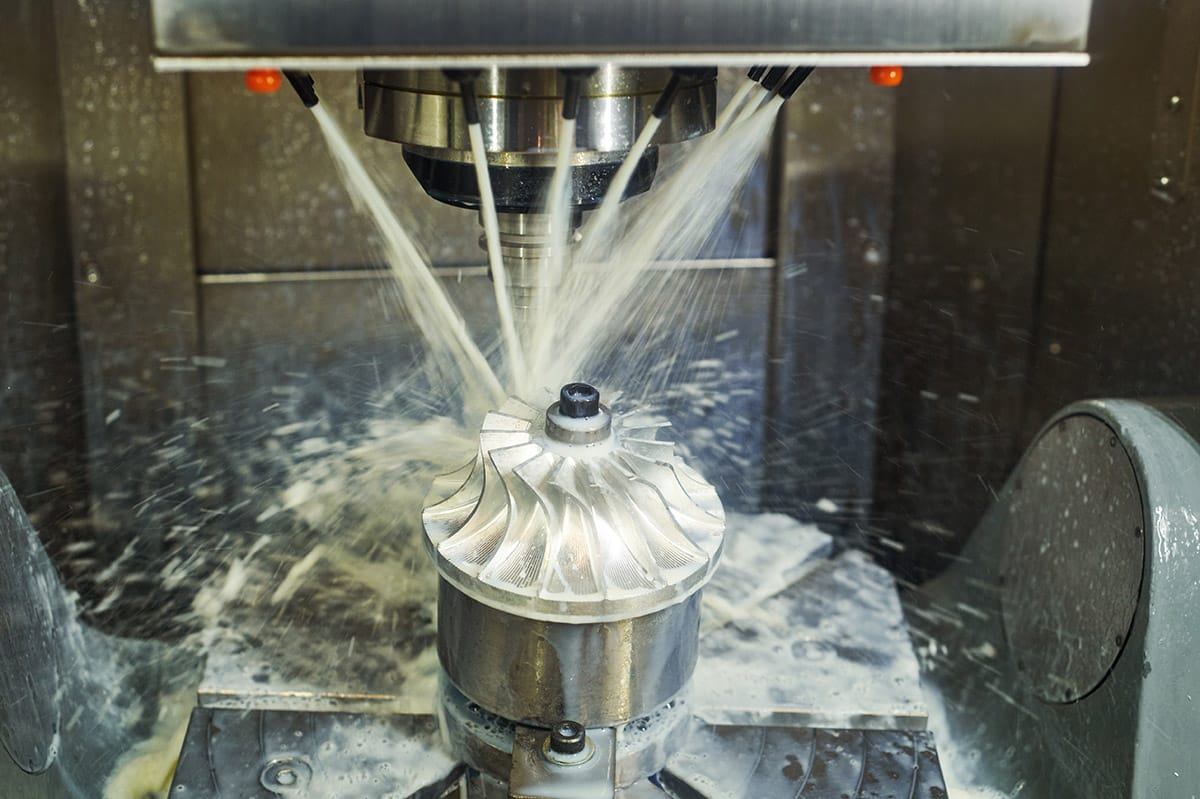
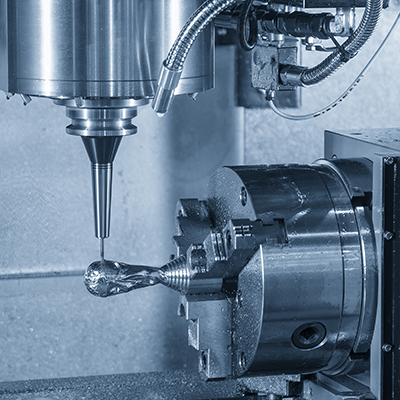
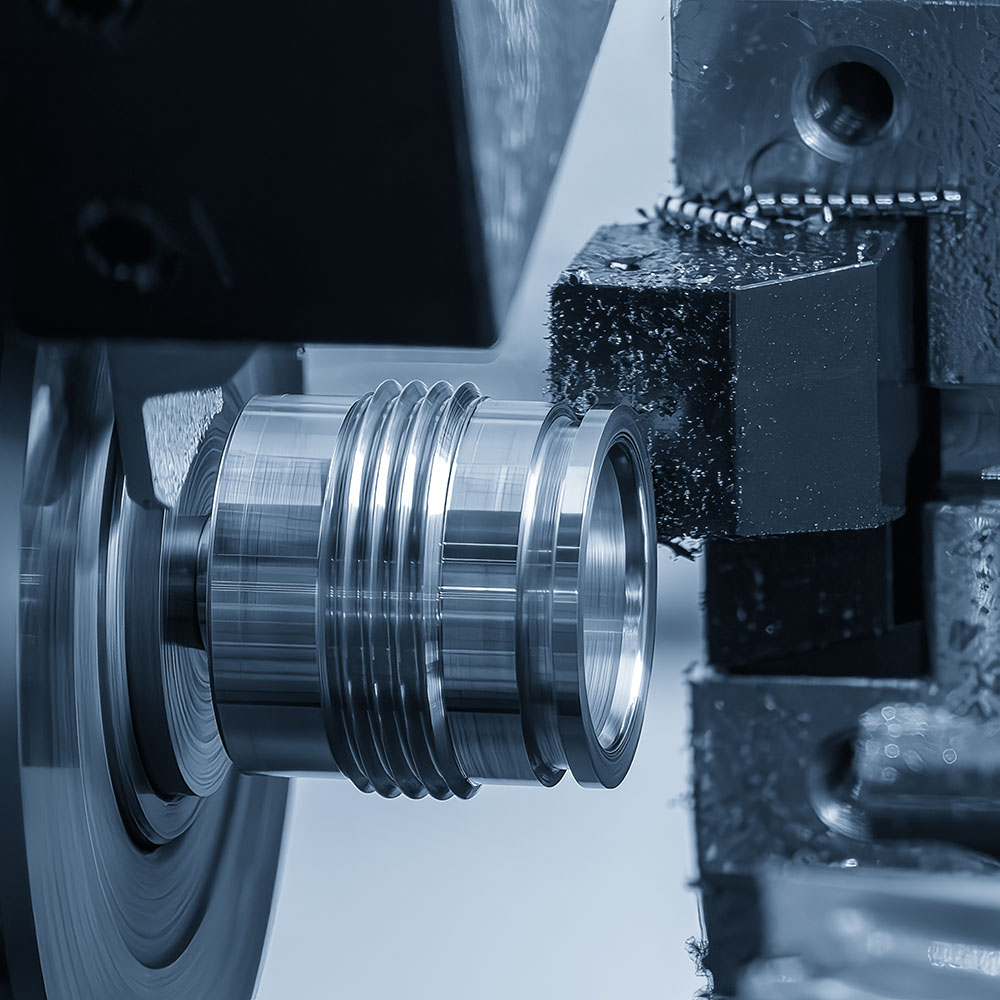



Advantages of KingStar Mold’s CNC Machining
Rapid Turnaround
We begin work on orders as soon as they arrive. Using the latest technologies and state-of-the-art machines, we can produce high-quality products and parts within the first 24 hours after receiving client approval.
Custom Finishes
We meticulously follow client specifications to produce parts with flawless precision. Whether crafting parts from solid metal or plastic, we ensure every detail is exactly as requested, with no room for error.
Scalability
Scalability is one of our core strengths. We can scale any part to the size you require without compromising on quality or functionality. Simply provide the instructions, and we’ll deliver on time.
Material Selection
We use only the finest raw materials, ensuring that every product that leaves our assembly line is durable, strong, and of the highest quality. Certified materials are at the heart of our manufacturing processes, ensuring reliability and longevity.
Precision Engineering
Our CNC machining services are built on precision engineering, ensuring every part is manufactured to exact specifications. With our advanced equipment, we achieve tight tolerances and deliver components with unmatched accuracy.
Cost Efficiency
We offer competitive pricing without sacrificing quality. By optimizing the machining process and minimizing waste, we provide cost-effective solutions that meet your budget while maintaining high standards of craftsmanship.
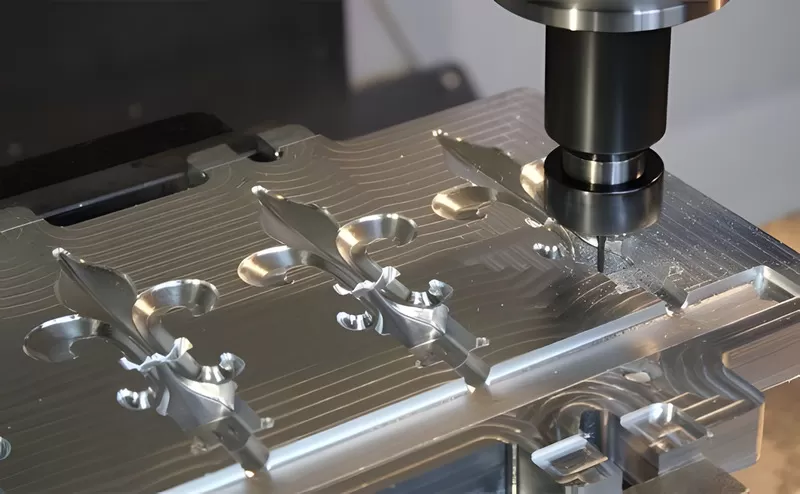

CNC Machining Tolerances and Capabilities
At KingStar Mold, we provide CNC milling and turning services with impressive tolerance levels of ±0.001″ for metals and ±0.002″ for plastics and composites. For projects that require even stricter tolerances, we are capable of meeting those specifications as well.
Our advanced CNC milling machines are capable of producing large parts up to 80″ x 48″ x 24″, while our precision lathes can handle parts up to 60″ in length and 32″ in diameter. We also specialize in machining standard thread sizes, tapped holes, and custom thread configurations. With our in-house post-processing and finishing capabilities, we ensure a seamless process that takes your part from concept to completion with precision and efficiency.
Our Satisfied Clients
Comparison Between Different CNC Machining Materials
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HB) | Machinability | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum 6061 | 2.70 | 275 | 95 | High | 310 | Aerospace, automotive, structural components |
| Stainless Steel 304 | 7.93 | 215 | 150 | Medium | 520 | Food processing, medical devices, marine equipment |
| Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | 4.43 | 880 | 330 | Low | 900 | Aerospace, medical implants, high-performance parts |
| Brass (C36000) | 8.49 | 150 | 65 | High | 345 | Plumbing, electrical connectors, decorative parts |
| Carbon Steel (1045) | 7.85 | 350 | 120 | Medium | 570 | Machinery parts, shafts, automotive components |
| POM (Acetal) | 1.41 | 55 | 70 | High | 65 | Precision gears, bearings, automotive parts |
| Nylon 6 | 1.15 | 50 | 80 | Medium | 75 | Mechanical parts, automotive, electrical insulation |
| Aluminum 2024 | 2.78 | 325 | 120 | High | 470 | Aircraft structures, military, aerospace components |
| Copper (C11000) | 8.92 | 70 | 40 | Medium | 210 | Electrical wiring, heat exchangers, electronics |
| Acrylic (PMMA) | 1.19 | 90 | 20 | High | 70 | Optical lenses, signage, automotive lighting |
| Magnesium AZ31 | 1.78 | 150 | 60 | Medium | 230 | Aerospace, automotive, military, electronics |
| Tool Steel (A2) | 7.85 | 450 | 450 | Low | 780 | Cutting tools, dies, molds |
CNC Machining Applications
CNC machining has a wide range of applications in both commercial and domestic settings. Some of the key applications include:
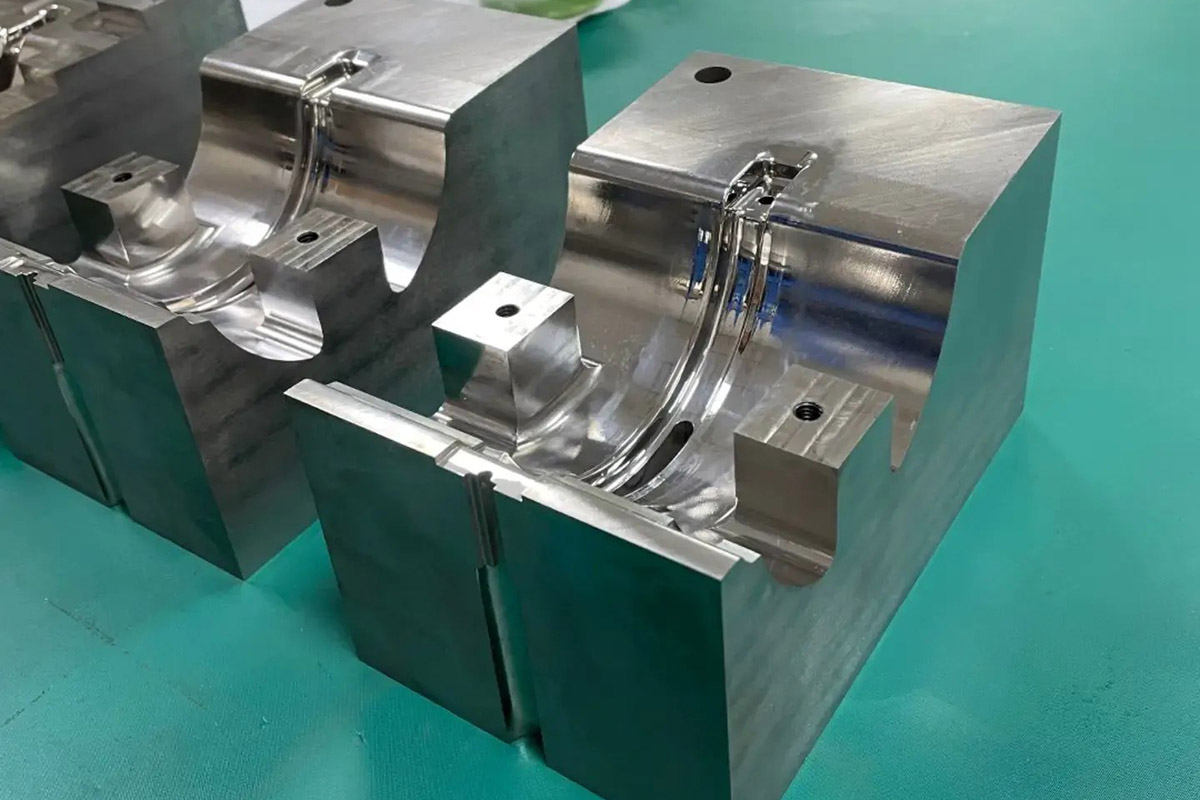

Injection Mold Building
This process involves using an insert to shape an object by injecting molten material into it while it’s still hot. Once the material solidifies, the final product is formed. Injection molding is commonly used for producing automotive parts, storage containers, furniture, and mechanical parts for machines, among many other products.
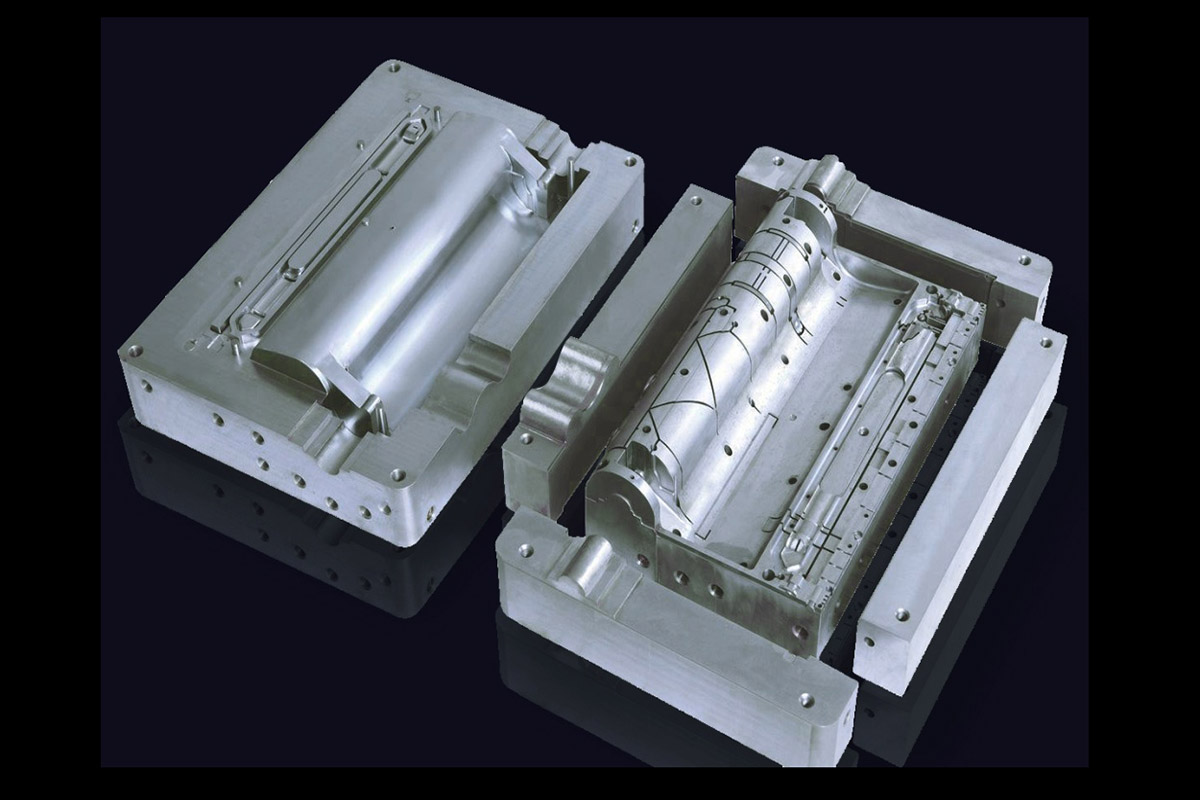

Rapid Prototyping
Prototyping is the creation of experimental models to solve specific problems. Traditionally time-consuming, rapid prototyping is now possible thanks to advanced technologies and machines. This process is widely applied in creating car parts and home appliance components in large quantities.

Surface Finishing
CNC machining is also used to enhance the appearance of a product by transforming a flat surface into a smooth, polished finish. This is particularly useful in industries such as automotive, home appliances, and other consumer products where aesthetics are important.
Precision Machining Tolerances
| Parameter | Metals With Drawing | Metals Without Drawing | Plastics With Drawing | Plastics Without Drawing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Dimension | ±0.01 mm | ISO 2768 Fine | ±0.05 mm | ISO 2768 Medium |
| Hole Diameters | ±0.008 mm | ISO 2768 Fine | ±0.05 mm | ISO 2768 Medium |
| Shaft Diameters | ±0.004 mm | ISO 2768 Fine | ±0.05 mm | ISO 2768 Medium |

Frequently Asked Questions
Simply upload your CAD files and project details through our website (click here to go to contact page or click the “request a quote” button at the top right corner of the page, and fill in the form that appears) or contact our team() directly. We’ll respond quickly with a detailed quote, lead time, and suggestions to optimize your design for cost and manufacturability.
We accept common 3D and 2D file formats including STEP, IGES, STL, and DWG. To ensure the best results, it’s helpful to include both 3D models and detailed 2D drawings with tolerances and surface finish requirements. There are 2 ways to send them to us: click here to the contact page to directly upload the files or send them via email: sales@kingstarmold.com