In the injection molding industry now, everyone is leaning towards high-quality, personalized products, and environmentally friendly production. However, traditional decoration techniques such as spray painting and electroplating are really headache inducing – the steps are too many and cumbersome, the pollution is serious, and the cost keeps rising, which is not cost-effective at all. At this point, IMD (In Mold Decoration) technology comes in handy. This innovative automation process is slowly replacing old methods. Why is it so popular? The key is that the advantages are too prominent: high efficiency, environmentally friendly and pollution-free, and particularly flexible, able to adapt to various needs. So for companies that want to upgrade their products and enhance their competitiveness, IMD has long been the best choice.
KingStar, a top plastic injection molding company with years of experience in IMD, we have already mastered IMD technology and deeply integrated it into our product solutions. Next, we will provide a detailed analysis of IMD process:
1.1 Basic Analysis of IMD Process
IMD (In-Mold Decoration), whose core principle is to place the printed decorative films into an injection mold, inject resin into the back of the film, and integrate the two into one and cure them, achieving synchronous completion of injection molding and inlay decoration, making the product both decorative and functional.
1.2 Core Advantages of IMD
As a new type of automated production process, IMD has significant advantages compared to traditional processes: simplifying production steps, reducing disassembly components, shortening production cycles, and reducing costs; Improve product quality, support complex image presentation, and enhance product durability; No need for secondary work or additional manpower, especially suitable for scenarios where printing and painting processes such as backlight requirements, multi curved surfaces, metal imitation, and hair line processing are difficult to cope with. It is an efficient solution for product appearance decoration.

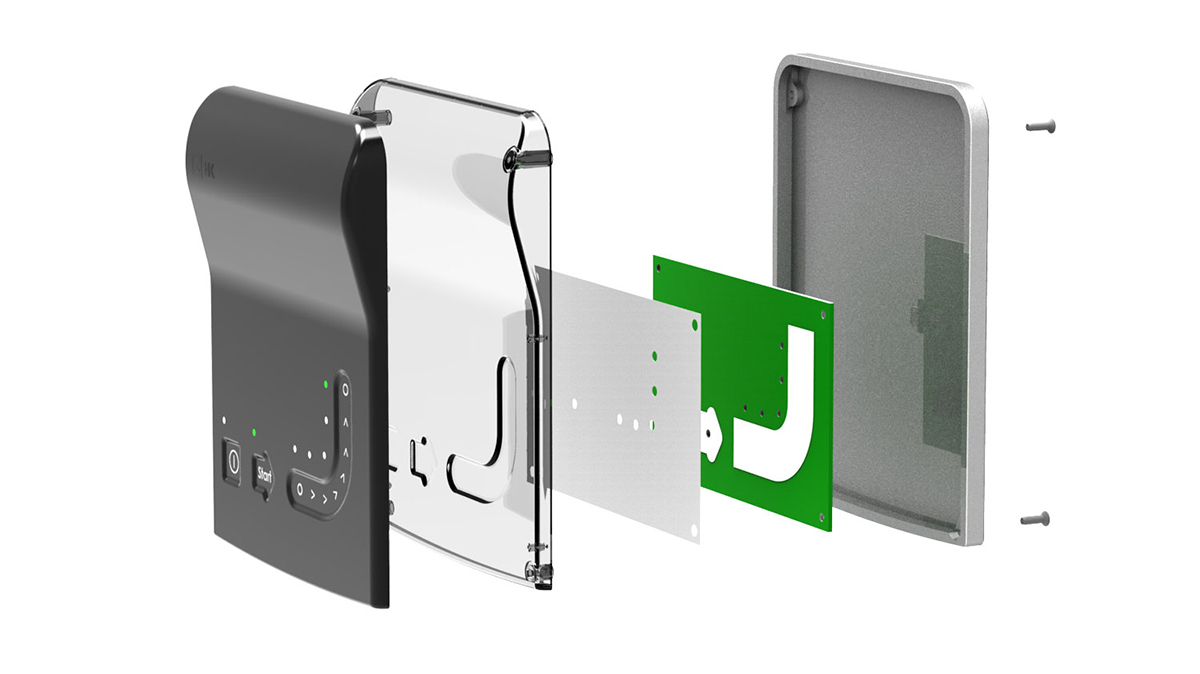
2. Classification and Core Differences of In-Mold Decoration
IMD is a general term, which is actually divided into three categories: IMR, IML, and IMF. IMR is often equated with IMD in the industry, while IML is classified separately. The core characteristics of the three types of processes are as follows:
| Process Type | English Full Name | Core Process | Applicable Scenarios | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMR | In-Mold Roller | Film placement in mold → Resin injection → Pattern transfer → Film release | 2D products, batch size 100k+ | Film acts only as a carrier, not integrated into final product; relies on release layer technology (Japanese monopoly); long lead time for custom sheets, high mold cost. |
| IML | In-Mold Label | Film printing → Die-cutting → Placement in mold → Resin bonding | 2D products, small curvature, no stretching | Ink layer located between film and resin; supports flexible batch production, easy to change patterns/colors. |
| IMF | In-Mold Film | Film printing → 3D forming (PC vacuum/high pressure) → Die-cutting → Injection molding | 3D products, high stretch requirements | Optimized from IML, focuses on complex 3D shapes; forming process is the core highlight. |
The Differences Between IMR and IML
- Product Characteristics: IML surface has a transparent PC/PET film of about 0.1mm, with wear-resistant patterns; IMR surface is only a few microns ink, and its wear resistance is poor.
- Process Details: IMR adopts gravure printing and automatic feeding of scrolls, suitable for large-scale production of single varieties; IML adopts screen printing and manual film positioning, suitable for small batch production of multiple varieties, with a development cycle of only one-third of IMR.
- Product Capability: IMR 3D molding height ≤ 1.5mm, unable to produce buttons; IML 3D molding can reach a height of 40mm and can process complex shapes such as flat, curved, and edge wrapping. It supports button production and has no restrictions on ink color.
3. Material and Equipment System
3.1 Core Materials
- IMD Foil: Mainly made of PET material, thin and suitable for offset printing, with excellent electroplating and transparency effects, capable of presenting delicate metallic texture. It consists of a thin film carrier, a separation layer, a surface hardening layer, a pattern layer, and an adhesive.
- Sheet Materials: Three commonly used materials are PC, PET, and PVC, with the following characteristics:
| Material | Primary Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Flat film panels, nameplates/labels | Chemical resistant, excellent insulation, UV resistant, low cost | Poor abrasion resistance, easily scratched, low transparency |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Embossed film panels, high-transparency window panels | High abrasion resistance, good toughness, high transparency, heat resistant | Moderate chemical resistance, weak UV resistance, high cost |
| Polyester (PET) | High-quality film panels, nameplates/labels (requires treatment) | Excellent insulation, chemical resistant, heat resistant and tough, can be embossed, wear/scratch resistant after treatment | Low transparency, weak UV resistance, high cost after treatment |
3.2 Key Equipment
- Core Processing Equipment: IMD-specific screen printing machine, punching positioning machine, outline die-cutting machine, high-pressure forming machine (such as LFORM200-D model, supporting high-pressure gas forming, infrared heating, and multi-cavity forming).
- Core Elements of Injection Molding: IMD foil, foil feeder, In- Mold Decoration mold, injection molding equipment and technology, working together to ensure the integrated effect of injection molding and decoration.

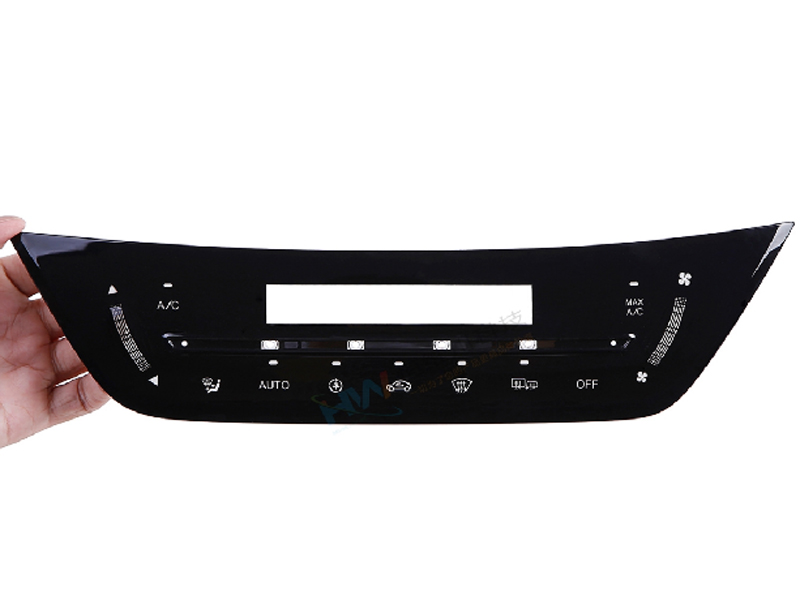
4. Core Process Flow
4.1 IMR (In-Mold Roller) Process Flow
Incoming foil → pre inspection → UV curing → injection molding (high-temperature and high-pressure transfer printing of film pattern) → removal of foil skin → removal of water outlet → inspection → packaging.
Key Steps: precise alignment of the film → vacuum fixation → mold closing injection molding → cooling and mold opening → removal of the molded part.
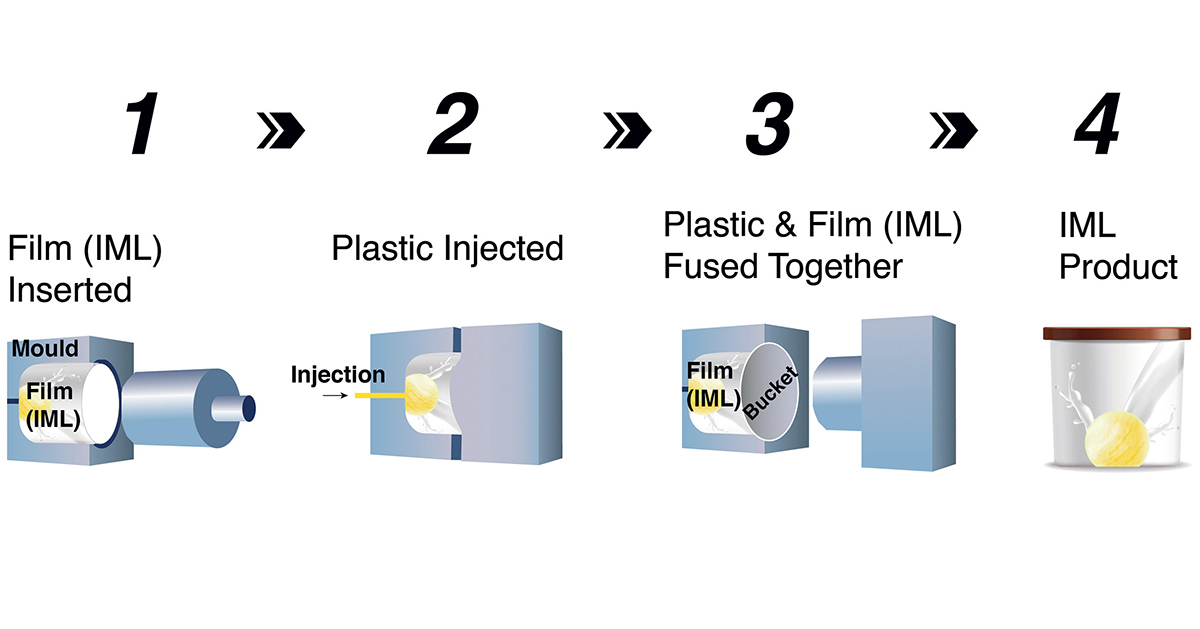
4.2 IML (In-Mold Label) Process Flow
Sheet cutting → pre baking (reducing shrinkage) → flat printing → ink drying and curing → applying protective film → punching positioning holes → thermoforming → cutting the periphery → injection molding → water outlet → packaging.
Key Steps: Printing patterns requires making a Philippine mesh; The design of hot forming molds directly affects product accuracy; Products with simple molding can prioritize cutting the outer edge to save film.
5. IMD Foil Printing Process
5.1 Main IMD Printing Methods
- Screen Printing: It consists of a screen printing plate, a scraper, ink, a printing table, and a substrate. By utilizing the ink permeability of the mesh, ink is transferred through pressure applied by a scraper, relying on rebound force to ensure printing accuracy. The ink layer is thick and suitable for small batch production (above 20Kpcs).
- Roller Printing: Composed of feeding unit, baking equipment, printing unit, etc. Using PET as the base film, ink is transferred through a printing drum, and the ink amount is controlled by a scraper. The printing speed is fast, the accuracy is high, and the ink layer is thin, suitable for large-scale production (MOQ>60Kpcs). Nissha Company in Japan holds over 90% of the market share.
5.2 IMD Printing Process Comparison
| Comparison Dimension | Screen Printing | Roller Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Equipment Investment | Low | High |
| Ink Layer Thickness | Thick | Thin |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | 20K pcs or above | 60K pcs or above |
| Unit Cost for 100K pcs | High | Low |
6. Application Fields and Industry Trends
6.1 Core Application Scenarios
- Communications: Mobile phone buttons (wear-resistant, multi-color texture), shell (integrated design, free texture), window lenses (high hardness, 3D decoration).
- Home Appliances: Control and decoration panels for rice cookers, washing machines, microwave ovens, etc., and intelligent operation area for refrigerators.
- Automotive: Interior and exterior components such as instrument panels, interior doors, lamp housings, wheels, bumpers, etc.
- Other Fields: computer keyboard and mouse cases, MP3/handheld computer decorative cases, cosmetics boxes, toys, sports and leisure equipment, etc.
6.2 Industry Development Trends
- Supply Chain Layout: The world’s top four ink manufacturers and top four film manufacturers have all increased their investment in the IMD industry, and Mitsubishi’s film production line has expanded from two to four.
- Corporate Activities: Foxconn has added an IMD production department, and printing industry giants are involved in the entire IMD process. Professional IMD ink and equipment exhibitions are frequently held in mainland China, and the industry’s popularity continues to rise.
7. Development Prospects
Next, KingStar, the best custom manufacturing company in China, will continue to focus on IMD technology research and development, further expanding its business to high-end application scenarios such as medical, smart homes, and new energy vehicles. We will rely on the dual drive of “technology+service” to provide global customers with more efficient, environmentally friendly, and innovative IMD solutions, and work together with partners in the industry chain to help the global manufacturing industry achieve high-quality upgrades.
If you would like to learn more information about analysis of IMD process, please feel free to contact KingStar at sales@kingstarmold.com at any time. We will reply to you within 24 hours and look forward to working with you!



